Environment & Ecology
Context: According to study conducted by Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air (CREA), Seven years after the December 2015 emission standard notification for coal-based power stations, not one single power station in West Bengal has installed Flue Gas Desulphurisation (FGD) technology to reduce SO2 emissions.
- The emission standards were notified for the first time in December 2015 in India for coal-based power stations to limit emissions of sulphur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and mercury (Hg), along with tightening particulate matter emissions standards and setting water consumption limits.
Key findings of the report:
- None of the coal-based power stations in West Bengal installed SO2 control technology over the past seven years since the emission standard notification for coal-based power stations was published in December 2015.
- Private sector power generation units are the worst when it comes to retrofits to control SO2 emissions; not one of them has awarded the bids after seven years of emission norms being in force.
- The coal consumption for grid-connected power generation in West Bengal has increased from 44 MT in 2015 to 54 MT in 2021.
About Flue Gas Desulphurisation (FGD):
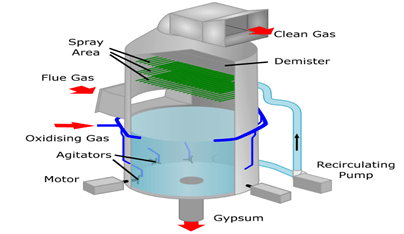
- Flue-gas desulfurization(FGD) is a set of technologies used to remove Sulphur dioxide (SO2) from exhaust flue gases of fossil-fuel power plants and from the emissions of other Sulphur dioxide-emitting processes such as waste incineration.
- FGD systems may involve wet scrubbing or dry scrubbing.
- In wet FGD systems, flue gases are brought in contact with an absorbent, which can be either a liquid or a slurry of solid material. The Sulphur dioxide dissolves in or reacts with the absorbent and becomes trapped in it.
- In dry FGD systems, the absorbent is dry pulverized lime or limestone; once absorption occurs, the solid particles are removed by means of baghouse filters.
About Sulphur dioxide:
- It is an inorganic compound, heavy, colourless, and poisonous gas. It is produced in large quantities in intermediate steps of sulphuric acid manufacture.
- It has a pungent, irritating odour, similar to the smell of a just-struck match.
- In nature, it occurs in volcanic gases and in a solution of some water warm springs.
- Usually, it is prepared industrially by the burning in air or oxygen of sulphur or such compounds of sulphur as iron pyrite or copper pyrite.
- In large quantities, sulphur dioxide is formed in the combustion of sulphur-containing fuels.
- It can combine in the atmosphere with water vapour to form sulphuric acid which is a major component of acid rain.
- Under moderate pressures at room temperatures, sulphur dioxide can be liquified and the liquid freezes at -73 degree Celsius and boils at -10 degree Celsius under atmospheric pressure.
Sulphur Dioxide uses are:
- It is used in the preparation of sulphuric acid, sulphur trioxide, and sulphites.
- It is also used as a disinfectant.
- It is used in a refrigerant, a reducing agent, a bleach, and food preservation mainly in dried fruits.
Sulphur Dioxide (SO2) and Air Pollution:
- SO2 emissions are a significant contributor to air pollution. High concentrations of SO2 in the air generally lead to the formation of other Sulfur Oxides (SOx).
- SOx can react with other compounds in the atmosphere to form small particles. These particles contribute to Particulate Matter (PM) pollution.
- Small particles may penetrate deeply into the lungs and in sufficient quantity can contribute to health problems.
- Air Pollution is a huge public health concern, with 91% of the world’s population living in areas where outdoor air pollution exceeds guideline limits by the World Health Organization (WHO) and as a result, 4.2 million people die prematurely every year.
- The greatest source of SO2 in the atmosphere is the burning of fossil fuels in power plants and other industrial facilities.
- Other sources include industrial processes such as extracting metal from ore, natural sources such as volcanoes, and locomotives, ships and other vehicles and heavy equipment that burn fuel with high sulphur content.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following statements:
- The Climate Group is an international non-profit organisation that drives climate action by building large networks and runs them.
- The International Energy Agency in partnership with the Climate Group launched a global initiative “EP100”.
- EP100 brings together leading companies committed to driving innovation in energy efficiency and increasing competitiveness while delivering on emission reduction goals.
- Some Indian companies are members of EP100.
- The International Energy Agency is the Secretariat to the “Under2 Coalition”.
Which of the statements given above are correct? (2022)
- 1,2, 4 and 5
- 1,3 and 4 only
- 2,3 and 5 only
- 1,2, 3, 4 and 5
Q.2) Consider the following:
- Carbon monoxide
- Nitrogen oxide
- Ozone
- Sulphur dioxide
Excess of which of the above in the environment is/are cause(s) of acid rain? (2022)
- 1, 2 and 3
- 2 and 4 only
- 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4












