Economics, Environment & Ecology
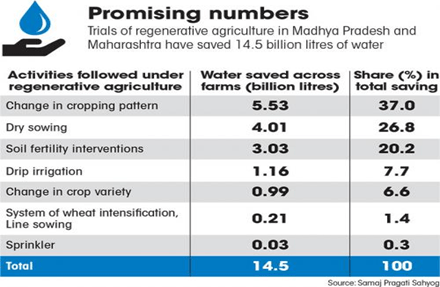
Context: Recently, the experience of farmers in Madhya Pradesh who follow regenerative farming methods finds the reduced need for frequent irrigation which conserves water and energy.
About Regenerative Farming:
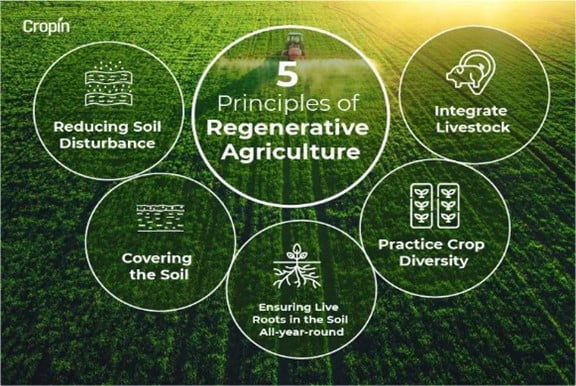
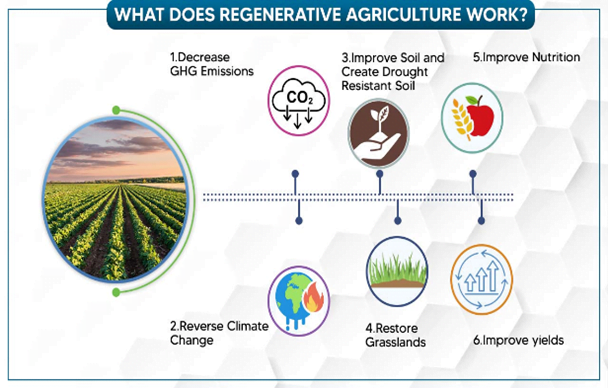
- It is a farming and grazing practices that benefits by reversing climate change, by rebuilding soil organic matter and restoring degraded soil biodiversity.
- It aims to improve soil and water for better agriculture in future by increasing soil organic matter.
- It uses methods of chemical-less farming by using natural inputs, manures, mulching and cultivation practices such as crop rotation, diversification, multi-cropping, sowing of diverse and native varieties.
- Natural inputs help improve soil structure and its organic carbon content.
- Planting water-guzzling and water-efficient crops together or in alternating cycles reduces the frequency and intensity of irrigation.
Need of Regenerative agriculture in India:
- Soil degradation: Agriculture today, including the use of heavy machinery, fertilizers and pesticides to maximize food production, is contributing to soil degradation and loss.
- Within 50 years, there may not be enough soil left to feed the world, according to the regenerative farming organization Regeneration International.
- Climate Change: Intensive farming also churns up CO2 naturally stored in soil and releases it into the atmosphere. This contributes to the global warming that is driving climate change.
- Agriculture accounts for over a third of greenhouse gas emissions globally, according to the United Nations (UN).
- Extreme events: Damaged soil and eroded land can make environments more vulnerable to extreme weather events like flooding, which are increasing in frequency and intensity as the Earth warms.
Potential Benefits of Regenerative Agriculture
- Multiple benefits: Regenerative farming can improve:
- Crop yields
- Volume of crops produced
- Health of soil
- Soil’s ability to retain water
- Reducing soil erosion.
- Feeding people: Improved yields will help feed the world as the global population grows.
- Environmental benefits: Regenerative farming can also reduce emissions from agriculture and turn the croplands and pastures, which cover up to 40% of Earth’s ice-free land area, into carbon sinks.
- These are environments that naturally absorb CO2 from the atmosphere.
Major Challenges associated with Agriculture
- According to the UN’s World Water Development Report, 2022, the country extracts 251 cubic km or more than a quarter of the world’s groundwater withdrawal each year.
- 90 per cent of this water is used for agriculture.
- No gain in production: A study by the Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi, shows that over 39 million hectares (ha) of area in the country under wheat, rice and maize have not shown improvement in the past decade.
- Groundwater: The Green Revolution of the 1960s pulled India from the brink of starvation, transformed the country’s ability to feed itself and turned it into a big food exporter.
- But the revolution also made India the world’s biggest extractor of groundwater.
- Degrading soil health: A 2022 report by Delhi-based think tank Centre for Science and Environment (CSE), State of Bio Fertilizers and Organic Fertilizers in India, shows the severe and widespread deficiency of organic carbon and micronutrients in Indian soils.
- Lack of scientific study: Civil society organizations and farmers do not have the capacity to conduct long-term studies.
Way Forward:
In India, the Union government is promoting regenerative agriculture with an aim to reduce application of chemical fertilisers and pesticides and to lower input costs. States like Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Sikkim and Gujarat too have introduced schemes to promote it.
According to the UN Food and Agriculture Organization, healthy soil helps in better water storage, transmission, filtering and reduces agricultural run-off. Studies have established that one per cent increase in soil organic matter (an indicator of soil health) per 0.4 ha increases water storage potential by more than 75,000 litres.
Thus, the concerted research is required to understand the role of regenerative agriculture in saving water. The scientific findings will further help inform policy measures and future initiatives.
Source: DownToEarth
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Consider the following statements:
- The Climate Group is an international non-profit organisation that drives climate action by building large networks and runs them.
- The International Energy Agency in partnership with the Climate Group launched a global initiative “EP100”.
- EP100 brings together leading companies committed to driving innovation in energy efficiency and increasing competitiveness while delivering on emission reduction goals.
- Some Indian companies are members of EP100.
- The International Energy Agency is the Secretariat to the “Under2 Coalition”.
Which of the statements given above are correct? (2022)
- 1,2, 4 and 5
- 1,3 and 4 only
- 2,3 and 5 only
- 1,2, 3, 4 and 5
Q.2) Which one of the following best describes the term “greenwashing”? (2022)
- Conveying a false impression that a company’s products are eco-friendly and environmentally sound
- Non-inclusion of ecological/ environmental costs in the Annual Financial Statements of a country
- Ignoring the consequences disastrous ecological while infrastructure development undertaking
- Making mandatory provisions for environmental costs in a government project/programme











