Science and Technology
In News: A new research clarifies how sepsis can lead to cell death.
Sepsis:
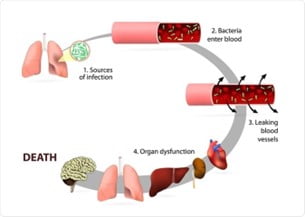
- Sepsis is a life-threatening condition arising from the body’s overreactive response against an infection, leading it to injure its own tissues and organs.
- The first known reference to “sepsis” dates back more than 2,700 years, when the Greek poet Homer used it as a derivative of the word “sepo,” meaning “I rot.
- Affects 750,000 people in the US and nearly 50 million people globally each year.
- Sepsis accounted for 11 million deaths worldwide in 2017, and is the most expensive medical condition in the US, costing over tens of billions of dollars annually.
How autoimmunity works
- The body’s response to infection starts when immune cells recognise components of the invading pathogen.
- These cells then release molecules like cytokines that help eliminate the infection.
- Cytokines are a broad group of small proteins that recruit other immune cells to the site of infection or injury.
- Excessive and uncontrolled cytokine production can lead to a dangerous cytokine storm that can cause sepsis.
- Cytokine storms occur in graft versus host disease, transplant complications, viral infections, including COVID-19.
- This uncontrolled immune response can lead to multi-organ failure and death.
Tumour necrosis factor(TNF):
- It is the most potent cytokines
- It induces tumour cells to die when the immune system is stimulated by a bacterial extract called Coley’s toxin (a lipopolysaccharide, or LPS – component of outer membrane of certain types of bacteria).
- LPS is the strongest known trigger of TNF, which, once on alert, aids in the recruitment of immune cells to the infection site to eliminate invading bacteria.
- In normal conditions, TNF promotes beneficial processes such as cell survival and tissue regeneration.
- Uncontrolled TNF production can lead to the development of rheumatoid arthritis and similar inflammatory conditions.
- Uncontrolled TNF during infections can lead to sepsis.
- Hence, TNF production must be tightly regulated to avoid sustained inflammation and continuous proliferation of immune cells and to prevent excessive tissue and organ damage from inflammation and an overactive immune response.
Treatment:
- Blocking TNF activity can effectively treat numerous autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.
- Neutralizing TNF can prevent the death of the animal from bacterial LPS
- Blood cells made in the bone marrow, or myeloid cells, are known to be the major producers of TNF.
- TRIF and CD14 as potential treatment targets for sepsis, with the ability to both reduce cell death and inflammation.
- TNF blockers have been unsuccessful in preventing the cytokine storm that can arise from COVID-19 infections and sepsis.
Source: The hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Which one of the following statements best describes the role of B cells and T cells in the human body ? (2022
- They protect the body from environmental allergens.
- They alleviate the body’s pain and inflammation.
- They act as immunosuppressants in the body.
- They protect the body from the diseases caused by pathogens.














