Economics
Context: The World Economic Forum (WEF) has chosen Hyderabad for establishing its Centre for the Fourth Industrial Revolution focused on healthcare and life sciences. C4IR Telangana will be the 18th centre to join WEF’s Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR) network that spans four continents.
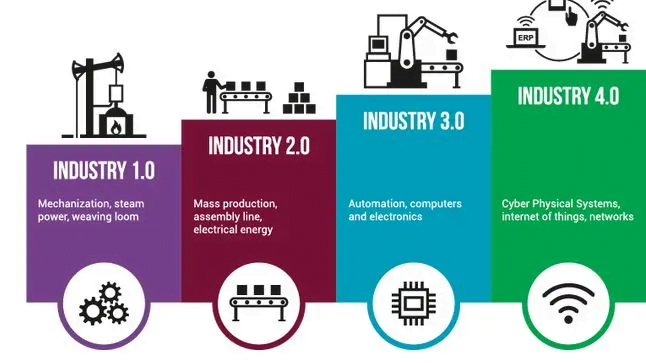
- The first industrial revolution used water and steam power to mechanise production (the 1800s).
- The second used electric power to create mass production (the early 1900s).
- The third used electronics and information technology to automate production (the late 1900s).
About Industrial Revolution 4.0:
- The term ‘Industry 4.0’ was coined by the German government in 2011.
- Industry 4.0 refers to a new phase in the Industrial Revolution that focuses heavily on interconnectivity, automation, machine learning, and real-time data.
- Industry 4.0, which encompasses IoTs and smart manufacturing, marries physical production and operations with smart digital technology, machine learning, and big data .
- Industry 4.0 comes into play when every company and organization operating today is different, they all face a common challenge—the need for connectedness and access to real-time insights across processes, partners, products, and people.
Industry 4.0 Technologies:

Significance of Industrial Revolution 4.0:
- It has the potential to raise global income levels and improve the quality of life for populations around the world.
- It will also lead to a supply-side miracle, with long-term gains in efficiency and productivity.
- Transportation and communication costs will drop, logistics and global supply chains will become more effective, and the cost of trade will diminish, all of which will open new markets and drive economic growth.
- Governments will gain new technological powers to increase their control over populations, based on pervasive surveillance systems and the ability to control digital infrastructure. .
- Advances in technology will create the potential to reduce the scale or impact of violence, through the development of new modes of protection, for example, or greater precision in targeting.
Challenges of IR 4.0:
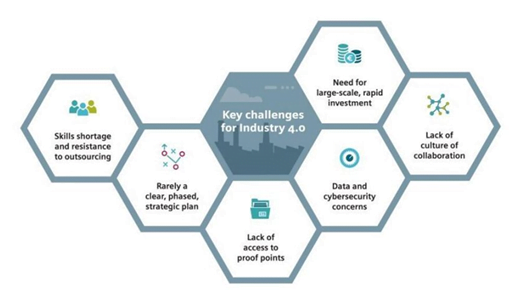
- The immediate fear is that of job loss, particularly in the informal sector.
- It could yield greater inequality, particularly in its potential to disrupt labor markets.
- Besides all these, there are several other critical concerns surrounding safety, ethics, and the short- and long-term socio-economic impact that remain unanswered.
- There is a growing concern that the existing fallacies in humans might only get more accentuated after 4IR.
- There are several studies that show how facial recognition technologies have a higher chance of misidentifying African and Asian people compared to their Western counterparts. It is also going to be skewed as developing and least developed countries lack the data framework and infrastructure.
- It will also profoundly impact the nature of national and international security, affecting both the probability and the nature of the conflict. This will lead to new fears.
- One of the greatest individual challenges posed by new information technologies is privacy.
Need for India to adopt IR 4.0:
- Advanced data analysis will help its manufacturing capacity and increase the quality of the product.
- Business Analytics will work on the prediction and prevention of production defects.
- Digitization of numerous manufacturing processes will lead to cost reduction with an improved experience for consumers.
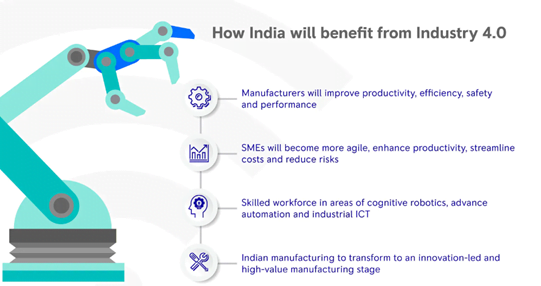
- The implementation of automation will reduce manufacturing cycles, decrease cycle time, and will reduce wasteful use of capital.
- IoT and man-machine connectivity will help supply chains to decrease lead times.
Status in India:
- India is moving towards becoming a hub of global manufacturing, 3D printing, machine learning, data analytics, and IoT are key to promoting industrial growth,
- In November 2020, the Modern Coach Factory (MCF) at Raebareli, Uttar Pradesh, rolled out smart railway coaches that are fitted with a battery of sensors to provide a comfortable experience to passengers.
- In May 2020, the Union Ministry of Heavy Industries launched the Smart Advanced Manufacturing and Rapid Transformation Hub (SAMARTH) scheme, which brings together manufacturers, vendors, and customers to make them aware of 4IR technologies.
- In 2022’s budget speech, the Union finance minister announced a slew of new 4IR-driven projects, including Drone Shakti, to encourage start-ups that will facilitate the use of drone services.
- India even has a 4IR centre in Mumbai run by WEF, which is closely working with several state governments.
- The Centre has recently come up with the Fourth Industrial Revolution for Sustainable Transformation (FIRST) Cancer Care model in which 4IR technologies would be used to provide better healthcare for cancer patients
- In February 2022, Government launched the pan-India 3D maps programme by Genesys International for the 100 smart cities.
- The company plans to map an entire city in intricate detail so that many 4IR revolution technology-based projects, such as driverless cars, will become easier to implement.
Way Forward:
- Industry 4.0 has started to make an influence in manufacturing and other various sectors in India.
- Data-driven decision-making is getting implemented in numerous fields.
- Though certain steps have already been taken, a lot of work needs to be done.
- Instead of just spending more capital, the emphasis must be on increasing the current asset base.
- The implementation of smart manufacturing, data analytics, and the Internet of Things will give a positive direction to Indian industries.
- To secure India’s active involvement in the fourth industrial revolution, it will be necessary to restructure some vital domestic industries and strengthen institutional capability.
Source: DownToEarth














