History and Art and Culture
Context: Salman Rushdie’s latest work, “Victory City” is a fictionalized telling of the story of Vijayanagara, one of the richest and most powerful kingdoms in medieval India.
About Vijayanagara Empire:
- The Vijayanagara Empire, also called Karnata Kingdom, was based in the Deccan Plateau region in South India.
- It was established in 1336 by the brothers Harihara I and Bukka Raya I of the Sangama dynasty, members of a pastoralist cowherd community that claimed Yadava lineage.
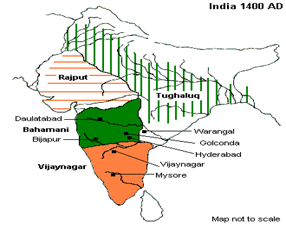

- At its peak, it subjugated almost all of South India’s ruling families and pushed the sultans of the Deccan beyond the Tungabhadra-Krishna River doab region, in addition to annexing modern day Odisha (ancient Kalinga) from the Gajapati Kingdom thus becoming a notable power.
- It lasted until 1646, although its power declined after a major military defeat in the Battle of Talikota in 1565 by the combined armies of the Deccan sultanates.
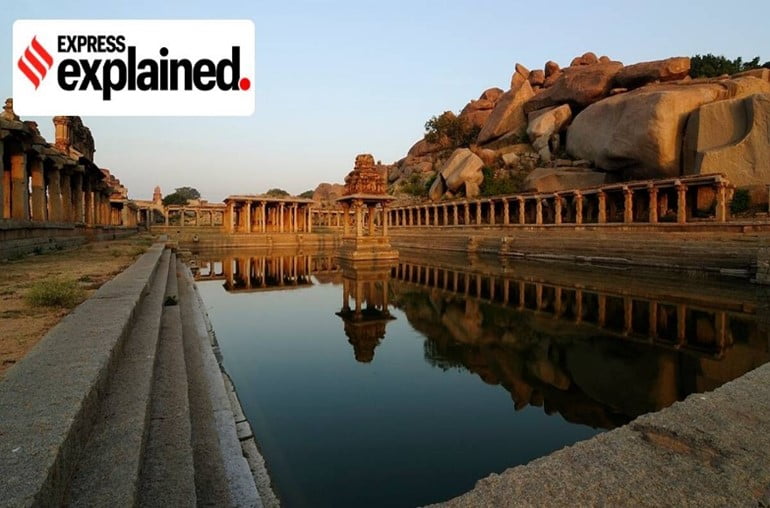
- The empire is named after its capital city of Vijayanagara, whose ruins surround present day Hampi, now a World Heritage Site in Karnataka, India.
Economy conditions during Vijayanagara kingdom:
- The economy of the kingdom was largely dependent on agriculture, and trade thrived in its many ports on either coast.
- The empire’s principal exports were pepper, ginger, cinnamon, cardamom, myrobalan, tamarind timber, ana fistula, precious and semi-precious stones, pearls, musk, ambergris, rhubarb, aloe, cotton cloth, and porcelain.
- Abd al-Razzaq Samarqand chronicled the high degree of monetization in the Vijayanagara kingdom.
- In his classic History of South India, K A Nilakanta Sastri wrote that coins were minted by the state as well as by merchant guilds using gold, silver, copper, and brass, and their value depended on material weight.
Governance:
- The rulers of the Vijayanagara Empire maintained the administrative methods developed by their predecessors, the Hoysala, Kakatiya and Pandya kingdoms.
- The King, ministry, territory, fort, treasury, military, and ally formed the seven critical elements that influenced every aspect of governance.
- The King was the ultimate authority, assisted by a cabinet of ministers (Pradhana) headed by the prime minister (Mahapradhana).
- Other important titles recorded were the chief secretary (Karyakartha or Rayaswami) and the imperial officers (Adhikari).
- All high-ranking ministers and officers were required to have military training.
- A secretariat near the king’s palace employed scribes and officers to maintain records made official by using a wax seal imprinted with the ring of the king.
Religious belief system:
- The Vijayanagara kings were tolerant of all religions and sects, as writings by foreign visitors show.
- The kings used titles such as Gobrahamana Pratipalanacharya (literally, “protector of cows and Brahmins”) that testified to their intention of protecting Hinduism.
- Yet at the same time adopted Islamicate court ceremonies, dress, and political language, as reflected in the title Hindu-rāya-suratrāṇa.
- The empire’s founders, the Sangama brothers (Harihara I and Bukka Raya I) came from a pastoral cowherd background (the Kuruba people) that claimed Yadava lineage.
- The founders of the empire were devout Shaivas (worshippers of the god Shiva) but made grants to Vishnu temples.
- Their patron saint Vidyaranya was from the Advaita order at Sringeri.
- The Varaha (the boar, an Avatar of Vishnu) was the emblem of the empire.
- Over one-fourth of the archaeological dig found an “Islamic Quarter” not far from the “Royal Quarter”.
- A Sanskrit work, Jambavati Kalyanam by King Krishnadevaraya, refers to Lord Virupaksha as Karnata Rajya Raksha Mani or “protective jewel of Karnata Empire”.
Contribution to Literature:
- During the rule of the Vijayanagara Empire, poets, scholars and philosophers wrote primarily in Kannada, Telugu and Sanskrit.
- The administrative and court languages of the Empire were Kannada and Telugu, the latter gained even more cultural and literary prominence during the reign of the last Vijayanagara kings, especially Krishnadevaraya.
- Most Sanskrit works were commentaries either on the Vedas or on the Ramayana and Mahabharata epics, written by well-known figures such as Sayanacharya and Vidyaranya that extolled the superiority of the Advaita philosophy over other rival Hindu philosophies.
- Other writers were famous Dvaita saints of the Udupi order such as Jayatirtha (earning the title Tikacharya for his polemicial writings), Vyasatirtha who wrote rebuttals to the Advaita philosophy and of the conclusions of earlier logicians, and Vadirajatirtha and Sripadaraya both of whom criticized the beliefs of Adi Sankara.
Contributions to culture and architecture:
- Vijayanagara has been remembered as an era of “cultural conservatism”, when classical forms of Hinduism were preserved amidst the growing Islamization of the rest of the subcontinent, especially the North.
- Literature in Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, as well as Sanskrit, was produced in the kingdom, with new writing styles and methods emerging.
- According to art historian Percy Brown, Vijayanagara architecture is “a vibrant combination and blossoming of the Chalukya, Hoysala, Pandya, and Chola styles, idioms that prospered in previous centuries.”
- The Prasanna Virupaksha temple of Bukka I and many of the great monuments of the empire date from Krishna Deva Raya’s time.
- Among these are the Hazara Rama temple, the Krishna temple, and the Ugra Narasimha idol, all at Vijayanagara.
- They are striking examples of Vijayanagar’s characteristic style and intricate artistry.
- Vijayanagara’s capital Hampi is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, known for its sophisticated fortifications as well as innumerable temples and other architectural marvels.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) With reference to Indian history, who of the following were known as “Kulah-Daran” ? (2022)
- Arab merchants
- Qalandars
- Persian calligraphists
- Sayyids
Q.2) According to Portuguese writer Nuniz, the women in the Vijayanagara empire were expert in which of the following areas? (2021)
- Wrestling
- Astrology
- Accounting
- Soothsaying
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4













