Governance
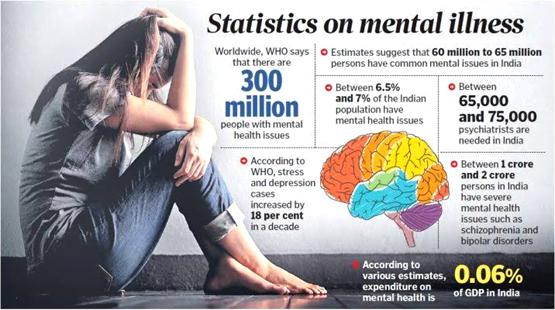
Context: The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) in a report flagged the “inhuman and deplorable” condition of all 46 government-run mental healthcare institutions across the country.
About Mental Healthcare Act, 2017:
- The act provides for the rights of persons with mental illness, including the right to access mental health care and treatment, the right to make decisions about their treatment, the right to confidentiality, and the right to legal aid.
- It establishes mental health services at the district level to provide access to mental healthcare and Mental Health Review Boards (MHRBs) to oversee the treatment of persons with mental illness and to protect their rights.
- It decriminalizes attempted suicide, recognizing that suicide is often a symptom of mental illness, and provides care and treatment for persons who attempt suicide.
- It establishes a Central Mental Health Authority and State Mental Health Authorities to regulate mental healthcare and services and to promote mental health.
- The act prohibits the use of Electro-Convulsive Therapy (ECT) without anaesthesia and the use of seclusion and restraint in mental health establishments, except in exceptional circumstances.
- The act provides for advance directives, which allow individuals to express their preferences for treatment and care in the event that they are unable to make decisions for themselves.
- The Act discourages using physical restraints (such as chaining), unmodified electro-convulsive therapy (ECT).
- This Act makes provision for the appointment of nominated representative by the mentally ill person.
- In case of absence of any recommendation by the mentally ill person, any relative, care giver, suitable persons may be appointed to act as the nominated representative.
- It provides for the setting up of Central Mental Authority Fund and State Mental Health Authority Fund to keep an account of all the grants, loans, fees, charges, sums etc., made by the authorities under this Act.
- Provision for Mental Health Review Boards – are quasi-judicial bodies shall be mainly responsible for:
- Registering, reviewing, altering, modifying or cancelling an advance directive appointing a nominated representative.
Source TH
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Maternity Benefit Amendment Act, 2017? (2019)
- Pregnant women are entitled for three months pre-delivery and three months post-delivery paid leave.
- Enterprises with creches must allow the mother minimum six creche visits daily.
- Women with two children get reduced entitlements.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3











