IASbaba Prelims 60 Days Plan, Rapid Revision Series (RaRe)
Archives
Hello Friends
The 60 Days Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series is IASbaba’s Flagship Initiative recommended by Toppers and loved by the aspirants’ community every year.
It is the most comprehensive program which will help you complete the syllabus, revise and practice tests on a daily basis. The Programme on a daily basis includes
Daily Prelims MCQs from Static (Monday – Saturday)
- Daily Static Quiz will cover all the topics of static subjects – Polity, History, Geography, Economics, Environment and Science and technology.
- 20 questions will be posted daily and these questions are framed from the topics mentioned in the schedule.
- It will ensure timely and streamlined revision of your static subjects.
Daily Current Affairs MCQs (Monday – Saturday)
- Daily 5 Current Affairs questions, based on sources like ‘The Hindu’, ‘Indian Express’ and ‘PIB’, would be published from Monday to Saturday according to the schedule.
Daily CSAT Quiz (Monday – Friday)
- CSAT has been an Achilles heel for many aspirants.
- Daily 5 CSAT Questions will be published.
Note – Daily Test of 20 static questions, 5 current affairs, and 5 CSAT questions. (30 Prelims Questions) in QUIZ FORMAT will be updated on a daily basis.
To Know More about 60 Days Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series – CLICK HERE
60 Day Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series Schedule – CLICK HERE
60 Day Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series Questions & Solutions DAY 44– CLICK HERE
Important Note
- Comment your Scores in the Comment Section. This will keep you accountable, responsible and sincere in days to come.
- It will help us come out with the Cut-Off on a Daily Basis.
- Let us know if you enjoyed today’s test 🙂
- You can post your comments in the given format
- (1) Your Score
- (2) Matrix Meter
- (3) New Learning from the Test
Test-summary
0 of 30 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
Information
The following Test is based on the syllabus of 60 Days Plan-2023 for UPSC IAS Prelims 2022.
To view Solutions, follow these instructions:
- Click on – ‘Start Test’ button
- Solve Questions
- Click on ‘Test Summary’ button
- Click on ‘Finish Test’ button
- Now click on ‘View Questions’ button – here you will see solutions and links.
You have already completed the test before. Hence you can not start it again.
Test is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the test.
You have to finish following test, to start this test:
Results
0 of 30 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have scored 0 points out of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 30
1. Question
Which of the following most accurately describes the meaning of the term ‘Environmental Determinism?
Correct
Solution: (a)
Explanation:
Environmental Determinism
- Environmental determinism is the belief that the environment, most notably its physical factors such as landforms and climate, determines the patterns of human culture and societal development. Environmental determinists believe that ecological, climatic, and geographical factors alone are responsible for human cultures and individual decisions. Also, social conditions have virtually no impact on cultural development.
- The main argument of environmental determinism states that an area’s physical characteristics like climate have a substantial impact on the psychological outlook of its inhabitants. These different outlooks then spread throughout a population and help define the overall behavior and culture of a society. For instance, it was said that areas in the tropics were less developed than higher latitudes because the continuously warm weather there made it easier to survive and thus, people living there did not work as hard to ensure their survival.
- Another example of environmental determinism would be the theory that island nations have unique cultural traits solely because of their isolation from continental societies.
- Option b is definition of doctrine of Possibilism, option c is the definition of doctrine of neo determinism and option d is the explanation of the term Climate justice.
Solution: (a)
Explanation:
Environmental Determinism
- Environmental determinism is the belief that the environment, most notably its physical factors such as landforms and climate, determines the patterns of human culture and societal development. Environmental determinists believe that ecological, climatic, and geographical factors alone are responsible for human cultures and individual decisions. Also, social conditions have virtually no impact on cultural development.
- The main argument of environmental determinism states that an area’s physical characteristics like climate have a substantial impact on the psychological outlook of its inhabitants. These different outlooks then spread throughout a population and help define the overall behavior and culture of a society. For instance, it was said that areas in the tropics were less developed than higher latitudes because the continuously warm weather there made it easier to survive and thus, people living there did not work as hard to ensure their survival.
- Another example of environmental determinism would be the theory that island nations have unique cultural traits solely because of their isolation from continental societies.
- Option b is definition of doctrine of Possibilism, option c is the definition of doctrine of neo determinism and option d is the explanation of the term Climate justice.
Incorrect
Solution: (a)
Explanation:
Environmental Determinism
- Environmental determinism is the belief that the environment, most notably its physical factors such as landforms and climate, determines the patterns of human culture and societal development. Environmental determinists believe that ecological, climatic, and geographical factors alone are responsible for human cultures and individual decisions. Also, social conditions have virtually no impact on cultural development.
- The main argument of environmental determinism states that an area’s physical characteristics like climate have a substantial impact on the psychological outlook of its inhabitants. These different outlooks then spread throughout a population and help define the overall behavior and culture of a society. For instance, it was said that areas in the tropics were less developed than higher latitudes because the continuously warm weather there made it easier to survive and thus, people living there did not work as hard to ensure their survival.
- Another example of environmental determinism would be the theory that island nations have unique cultural traits solely because of their isolation from continental societies.
- Option b is definition of doctrine of Possibilism, option c is the definition of doctrine of neo determinism and option d is the explanation of the term Climate justice.
Solution: (a)
Explanation:
Environmental Determinism
- Environmental determinism is the belief that the environment, most notably its physical factors such as landforms and climate, determines the patterns of human culture and societal development. Environmental determinists believe that ecological, climatic, and geographical factors alone are responsible for human cultures and individual decisions. Also, social conditions have virtually no impact on cultural development.
- The main argument of environmental determinism states that an area’s physical characteristics like climate have a substantial impact on the psychological outlook of its inhabitants. These different outlooks then spread throughout a population and help define the overall behavior and culture of a society. For instance, it was said that areas in the tropics were less developed than higher latitudes because the continuously warm weather there made it easier to survive and thus, people living there did not work as hard to ensure their survival.
- Another example of environmental determinism would be the theory that island nations have unique cultural traits solely because of their isolation from continental societies.
- Option b is definition of doctrine of Possibilism, option c is the definition of doctrine of neo determinism and option d is the explanation of the term Climate justice.
-
Question 2 of 30
2. Question
Consider the following statements with respect to Demographic Transition Theory
- It can be used to describe and predict the future population of any area.
- It shows how population growth changes as society progresses from rural agrarian and illiterate to urban industrial and literate society.
- These changes occur in stages which are collectively known as the democratic cycle.
Choose the correct code:
Correct
Solution: (b)
Explanation:
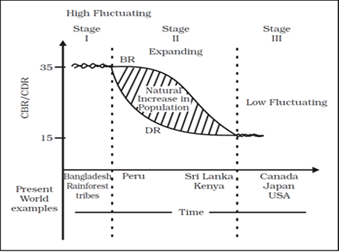
DEMOGRAPHIC TRANSITION
- Demographic transition theory can be used to describe and predict the future population of any area.
- The theory tells us that population of any region changes from high births and high deaths to low births and low deaths as society progresses from rural agrarian and illiterate to urban industrial and literate society.
- These changes occur in stages which are collectively known as the demographic cycle.
 Incorrect
Incorrect
Solution: (b)
Explanation:
DEMOGRAPHIC TRANSITION
- Demographic transition theory can be used to describe and predict the future population of any area.
- The theory tells us that population of any region changes from high births and high deaths to low births and low deaths as society progresses from rural agrarian and illiterate to urban industrial and literate society.
- These changes occur in stages which are collectively known as the demographic cycle.

-
Question 3 of 30
3. Question
Which one of the following continents has the highest growth of population?
Correct
Solution: (a)
Explanation:
The annual population growth rates of all the continents of the world according to the United Nations’ World Population Prospects 2021 report:
- Africa: 2.53%
- Asia: 0.91%
- Europe: 0.05%
- Latin America and the Caribbean: 0.72%
- Northern America: 0.50%
- Oceania: 1.24%
Incorrect
Solution: (a)
Explanation:
The annual population growth rates of all the continents of the world according to the United Nations’ World Population Prospects 2021 report:
- Africa: 2.53%
- Asia: 0.91%
- Europe: 0.05%
- Latin America and the Caribbean: 0.72%
- Northern America: 0.50%
- Oceania: 1.24%
-
Question 4 of 30
4. Question
Which of the following are examples of push factors that might cause individuals to migrate from one place to another?
- Unemployment
- Poor living conditions,
- Political turmoil
- Unpleasant climate
- Job opportunities
- Religious Freedom
- Better infrastructure
Choose the correct code:
Correct
Solution: (b)
Explanation:
- Push factors are circumstances or conditions that drive people to leave their homes and seek opportunities elsewhere.
- Factors such as unemployment, poor living conditions, political turmoil, and unpleasant climate are often cited as reasons why people might leave their homes and migrate to other places.
- In contrast, job opportunities, religious freedom, and better infrastructure are more likely to be considered as pull factors that attract individuals to a particular place
Incorrect
Solution: (b)
Explanation:
- Push factors are circumstances or conditions that drive people to leave their homes and seek opportunities elsewhere.
- Factors such as unemployment, poor living conditions, political turmoil, and unpleasant climate are often cited as reasons why people might leave their homes and migrate to other places.
- In contrast, job opportunities, religious freedom, and better infrastructure are more likely to be considered as pull factors that attract individuals to a particular place
-
Question 5 of 30
5. Question
Consider the following statements
- More women in the population of a region mean that women have a better status in that region.
- Females have a biological advantage over men as they tend to be more resilient than males.
Choose the correct code:
Correct
Solution: (b)
Explanation:
The number of women in a population does not necessarily indicate that they have a better status in that region. Women may still face gender-based discrimination and inequalities in various areas, such as education, employment, and political representation, despite their numerical advantage in the population. Therefore, it is essential to consider other factors that affect the status of women in a region, such as cultural and social norms, legal frameworks, and access to resources and opportunities.Hence statement 1 is incorrect
Women are biologically more stronger than men and hence tend to outlive their male counterparts, finds a study challenging the per-conceived notion that the female sex is weaker. The findings showed that women do not just outlive men in normal times, but they are also more likely to survive even in the worst of circumstances such as famines and epidemics. Women’s increased life expectancy is because they tend to have a survival advantage in infancy rather than adulthood. In times of adversity, newborn girls are more likely to survive than newborn boys.Hence statement 2 is correct
Incorrect
Solution: (b)
Explanation:
The number of women in a population does not necessarily indicate that they have a better status in that region. Women may still face gender-based discrimination and inequalities in various areas, such as education, employment, and political representation, despite their numerical advantage in the population. Therefore, it is essential to consider other factors that affect the status of women in a region, such as cultural and social norms, legal frameworks, and access to resources and opportunities.Hence statement 1 is incorrect
Women are biologically more stronger than men and hence tend to outlive their male counterparts, finds a study challenging the per-conceived notion that the female sex is weaker. The findings showed that women do not just outlive men in normal times, but they are also more likely to survive even in the worst of circumstances such as famines and epidemics. Women’s increased life expectancy is because they tend to have a survival advantage in infancy rather than adulthood. In times of adversity, newborn girls are more likely to survive than newborn boys.Hence statement 2 is correct
-
Question 6 of 30
6. Question
Consider the following statements with respect to the Age-Sex Pyramid
- It represents the number of males and females in the different age groups.
- The left side shows the percentage of females while the right side shows percentage of males.
- Australia’s age sex pyramid is bell shaped and tapered towards the top.
Choose the correct code:
Correct
Solution: (d)
Explanation:
- The Age-Sex Pyramid is a graphical representation of the distribution of a population by age and sex. It shows the number or percentage of males and females in different age groups.Hence statement 1 is correct
- The Age-Sex Pyramid typically shows the percentage or number of males on the left-hand side and the percentage or number of females on the right-hand side.Hence Statement 2 is Incorrect
- Australia’s age-sex pyramid is typically bell-shaped, with a wider base representing a larger proportion of younger people, and a narrower top representing a smaller proportion of older people.Hence statement 3 is correct
Incorrect
Solution: (d)
Explanation:
- The Age-Sex Pyramid is a graphical representation of the distribution of a population by age and sex. It shows the number or percentage of males and females in different age groups.Hence statement 1 is correct
- The Age-Sex Pyramid typically shows the percentage or number of males on the left-hand side and the percentage or number of females on the right-hand side.Hence Statement 2 is Incorrect
- Australia’s age-sex pyramid is typically bell-shaped, with a wider base representing a larger proportion of younger people, and a narrower top representing a smaller proportion of older people.Hence statement 3 is correct
-
Question 7 of 30
7. Question
Consider the following statements about Rural Urban composition of the population
- In general terms, rural areas are those where people are engaged in primary activities and urban areas are those where the majority of the working population is engaged in non-primary activities.
- In Western countries, females outnumber males in rural areas and males outnumber females in urban areas.
- In countries like India, Pakistan and Nepal, males outnumber females in rural areas and females outnumber males in urban areas.
Choose the correct code:
Correct
Solution: (b)
Explanation:
RURAL URBAN COMPOSITION
- The division of population into rural and urban is based on the residence. This division is necessary because rural and urban life styles differ from each other in terms of their Livelihood and social conditions. The age-sex-occupational structure, density of population and level of development vary between rural and urban areas.
- The criteria for differentiating rural and urban population varies from country to country. In general terms rural areas are those where people are engaged in primary activities and urban areas are those when majority of the working population is engaged-in non-primary activities.
- The rural and urban differences in sex ratio in Canada and West European countries like Finland are just the opposite of those in African and Asian countries like Zimbabwe and Nepal respectively.
- In Western countries, males outnumber females in rural areas and females outnumber the males in urban areas. In countrieslike Nepal, Pakistan and India the case is reverse.
- The excess of females in urban areas of U.S.A., Canada and Europe is the result of influx of females from rural areas to avail of the vast job opportunities. Farming in these developed countries is also highly mechanised and remains largely a male occupation. By contrast the sex ratio in Asian urban areas remains male dominated due to the predominance of male migration. It is also worth noting that in countries like India, female participation in farming activity in rural area is fairly high. Shortage of housing, high cost of living, paucity of job opportunities and lack of security in cities, discourage women to migrate from rural to urban areas.
Incorrect
Solution: (b)
Explanation:
RURAL URBAN COMPOSITION
- The division of population into rural and urban is based on the residence. This division is necessary because rural and urban life styles differ from each other in terms of their Livelihood and social conditions. The age-sex-occupational structure, density of population and level of development vary between rural and urban areas.
- The criteria for differentiating rural and urban population varies from country to country. In general terms rural areas are those where people are engaged in primary activities and urban areas are those when majority of the working population is engaged-in non-primary activities.
- The rural and urban differences in sex ratio in Canada and West European countries like Finland are just the opposite of those in African and Asian countries like Zimbabwe and Nepal respectively.
- In Western countries, males outnumber females in rural areas and females outnumber the males in urban areas. In countrieslike Nepal, Pakistan and India the case is reverse.
- The excess of females in urban areas of U.S.A., Canada and Europe is the result of influx of females from rural areas to avail of the vast job opportunities. Farming in these developed countries is also highly mechanised and remains largely a male occupation. By contrast the sex ratio in Asian urban areas remains male dominated due to the predominance of male migration. It is also worth noting that in countries like India, female participation in farming activity in rural area is fairly high. Shortage of housing, high cost of living, paucity of job opportunities and lack of security in cities, discourage women to migrate from rural to urban areas.
-
Question 8 of 30
8. Question
Consider the following statements regarding Growth and Development
- Both growth and development refer to changes over a period of time.
- Growth is quantitative and value-neutral, it may have a positive or a negative sign.
- Development means a qualitative change which is always value positive.
- Development cannot take place until there is an addition to the existing conditions.
Choose the correct code:
Correct
Solution: (d)
Explanation:
Growth and Development
- Both growth and development refer to changes over a period of time.
- The difference is that growth is quantitative and value neutral. It may have a positive or a negative sign. This means that the change may be either positive (showing an increase) or negative (indicating a decrease).
- Development means a qualitative change which is always value positive. This means that development cannot take place unless there is an increment or addition to the existing conditions. Development occurs when positive growth takes place. Yet, positive growth does not always lead to development. Development occurs when there is a positive change in quality.
- For example, if the population of a city grows from one lakh to two lakhs over a period of time, we say the city has grown. However, if a facilities like housing, provision of basic services and other characteristics remain the same, then this growth has not been accompanied by development.
Incorrect
Solution: (d)
Explanation:
Growth and Development
- Both growth and development refer to changes over a period of time.
- The difference is that growth is quantitative and value neutral. It may have a positive or a negative sign. This means that the change may be either positive (showing an increase) or negative (indicating a decrease).
- Development means a qualitative change which is always value positive. This means that development cannot take place unless there is an increment or addition to the existing conditions. Development occurs when positive growth takes place. Yet, positive growth does not always lead to development. Development occurs when there is a positive change in quality.
- For example, if the population of a city grows from one lakh to two lakhs over a period of time, we say the city has grown. However, if a facilities like housing, provision of basic services and other characteristics remain the same, then this growth has not been accompanied by development.
-
Question 9 of 30
9. Question
Who one of the following scholars introduced the concept of Human Development which led to the development of the Human Development Index in the year 1990?
Correct
Solution: (a)
Explanation:
The origins of the HDI are found in the annual Human Development Reports produced by the Human Development Report Office of the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). These were devised and launched by Pakistani economist Mahbub ul Haq in 1990, and had the explicit purpose “to shift the focus of development economics from national income accounting to people-centered policies”. Haq believed that a simple composite measure of human development was needed to convince the public, academics, and politicians that they can and should evaluate development not only by economic advances but also improvements in human well-being.
Incorrect
Solution: (a)
Explanation:
The origins of the HDI are found in the annual Human Development Reports produced by the Human Development Report Office of the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). These were devised and launched by Pakistani economist Mahbub ul Haq in 1990, and had the explicit purpose “to shift the focus of development economics from national income accounting to people-centered policies”. Haq believed that a simple composite measure of human development was needed to convince the public, academics, and politicians that they can and should evaluate development not only by economic advances but also improvements in human well-being.
-
Question 10 of 30
10. Question
Consider the following pair in relation with the Approaches to Human Development
Type of Approach Meaning of Approach
1. Income Approach Level of income determines the level of Freedom which an individual enjoys 2. Welfare Approach This approach looks at human beings as beneficiaries or targets of all development activities. 3. Capability Approach Building Human capabilities in the areas of Health,Education and access to resources is the key to increasing Human development 4. Basic needs Approach In this Human choices are ignored and the emphasis is on the provision basic needs of defined sections How many of the above given pair/s is/are correct?
Correct
Solution: (d)
Explanation:
(a) Income Approach: This is one of the oldest approaches to human development. Human development is seen as being linked to income. The idea is that the level of income reflects the level of freedom an individual enjoys. Higher the level of income, the higher is the level of human development.
(b) Welfare Approach: This approach looks at human beings as beneficiaries or targets of all development activities. The approach argues for higher government expenditure on education, health, social secondary and amenities. People are not participants in development but only passive recipients. The government is responsible for increasing levels of human development by maximising expenditure on welfare.
(c) Basic Needs Approach: This approach was initial ly proposed by the International Labour Organisation (ILO). Six basic needs i.e.: health, education, food, water supply, sanitation, and housing were identified. The question of human choices is ignored and the emphasis is on the provision of basic needs of defined sections.
(d) Capability Approach: This approach is associated with Prof. Amartya Sen. Building human capabilities in the areas of health, education and access to resources is the key to increasing human development.
Incorrect
Solution: (d)
Explanation:
(a) Income Approach: This is one of the oldest approaches to human development. Human development is seen as being linked to income. The idea is that the level of income reflects the level of freedom an individual enjoys. Higher the level of income, the higher is the level of human development.
(b) Welfare Approach: This approach looks at human beings as beneficiaries or targets of all development activities. The approach argues for higher government expenditure on education, health, social secondary and amenities. People are not participants in development but only passive recipients. The government is responsible for increasing levels of human development by maximising expenditure on welfare.
(c) Basic Needs Approach: This approach was initial ly proposed by the International Labour Organisation (ILO). Six basic needs i.e.: health, education, food, water supply, sanitation, and housing were identified. The question of human choices is ignored and the emphasis is on the provision of basic needs of defined sections.
(d) Capability Approach: This approach is associated with Prof. Amartya Sen. Building human capabilities in the areas of health, education and access to resources is the key to increasing human development.
-
Question 11 of 30
11. Question
Which of the following characteristics mentioned below are observed in Intensive subsistence Agriculture?
- Capital Intensive
- Use of Family Labour
- Yield per unit is high
- Scientific method of cultivation
- Farm yard manure is used
Select the correct code :
Correct
Solution: (b)
Explanation:
Characteristics of Intensive subsistence agriculture:
(a) Dominated by rice crop,
(b) Land holdings are very small
(c) Family labor is used
(d) Less use of machine
(e) Manual labor is used
(f) Farm yard manure is used
(g) Yield per unit is high but per labor is low
Capital intensive and scientific method of cultivation are characteristics of Extensive agriculture
Incorrect
Solution: (b)
Explanation:
Characteristics of Intensive subsistence agriculture:
(a) Dominated by rice crop,
(b) Land holdings are very small
(c) Family labor is used
(d) Less use of machine
(e) Manual labor is used
(f) Farm yard manure is used
(g) Yield per unit is high but per labor is low
Capital intensive and scientific method of cultivation are characteristics of Extensive agriculture
-
Question 12 of 30
12. Question
Which of the following statement about Suburbanisation is incorrect?
Correct
Solution: (d)
Explanation:
Suburbanisation
- It is a new trend of people moving away from congested urban areas to cleaner areas outside the city in search of a better quality of living.
- Important suburbs develop around major cities and everyday thousands of people commute from their homes in the sub urbs to their work places in the city.
- Sub-urbanization is inversely related to urbanization (urbanisation), which denotes a population shift from rural areas into urban centers.
- As a consequence of the movement of households and businesses out of the city centers, low-density, peripheral urban areas grow.
- Many residents of metropolitan regions work within the central urban area, but live outside of it, in satellite communities called suburbs, and commute to work by car or mass transit.
- Others have the opportunity to work from home, due to technological advances. Suburbanization often occurs in more economically developed countries.
- The United States is believed to be the first country in which the majority of the population lived in suburbs rather than cities or rural areas.
- Proponents of containing the urban sprawl argue that the sprawl leads to urban decay and a concentration of lower-income residents in the inner city,in addition to environmental harm.
Incorrect
Solution: (d)
Explanation:
Suburbanisation
- It is a new trend of people moving away from congested urban areas to cleaner areas outside the city in search of a better quality of living.
- Important suburbs develop around major cities and everyday thousands of people commute from their homes in the sub urbs to their work places in the city.
- Sub-urbanization is inversely related to urbanization (urbanisation), which denotes a population shift from rural areas into urban centers.
- As a consequence of the movement of households and businesses out of the city centers, low-density, peripheral urban areas grow.
- Many residents of metropolitan regions work within the central urban area, but live outside of it, in satellite communities called suburbs, and commute to work by car or mass transit.
- Others have the opportunity to work from home, due to technological advances. Suburbanization often occurs in more economically developed countries.
- The United States is believed to be the first country in which the majority of the population lived in suburbs rather than cities or rural areas.
- Proponents of containing the urban sprawl argue that the sprawl leads to urban decay and a concentration of lower-income residents in the inner city,in addition to environmental harm.
-
Question 13 of 30
13. Question
These settlements are those in which large number of houses are built very close to each other. Such settlements develop along river valleys and in fertile plains. Communities are closely knit and share common occupations.
Identify the type of settlement mentioned in the above statements?
Correct
Solution: (d)
Explanation:
Types of Settlements
Settlements may also be classified by their shape, patterns types. The major types classified by shape are:
- Compact or Nucleated settlements: These settlements are those in which large number of houses are built very close to each other. Such settlements develop along river valleys and in fertile plains. Communities are closely knit and share common occupations.
- Dispersed Settlements: In these settlements, houses are spaced far apart and often interspersed with fields. A cultural feature such as a place of worship or a market, binds the settlement together.
Incorrect
Solution: (d)
Explanation:
Types of Settlements
Settlements may also be classified by their shape, patterns types. The major types classified by shape are:
- Compact or Nucleated settlements: These settlements are those in which large number of houses are built very close to each other. Such settlements develop along river valleys and in fertile plains. Communities are closely knit and share common occupations.
- Dispersed Settlements: In these settlements, houses are spaced far apart and often interspersed with fields. A cultural feature such as a place of worship or a market, binds the settlement together.
-
Question 14 of 30
14. Question
Consider the following pairs related to Rural settlement patterns
Shape of Settlement Characteristic of Settlement 1. Linear pattern Such patterns of rural settlements are found in plain areas or wide inter montane valleys. The roads are rectangular and cut each other at right angles 2. Rectangular pattern In such settlements houses are located along a road, railwayline, river, canal edge of a valley or along a levee. 3. Star like pattern Where several roads converge, star shaped settlements develop by the houses built along the roads. 4. T -shaped These settlements develop at tri-junctions of the roads
How many of the above given pair/s is/are correct?
Correct
Solution: (b)
Explanation:
Shape of Settlement Characteristic of Settlement 1. Linear pattern In such settlements houses are located along a road, railwayline, river, canal edge of a valley or along a leve 2. Rectangular pattern Such patterns of rural settlements are found in plain areas or wide inter montane valleys. The roads are rectangular and cut each other at right angle 3. Star like pattern Where several roads converge, star shaped settlements develop by the houses built along the roads. 4. T -shaped These settlements develop at tri-junctions of the roads
5. Circular pattern Circular villages develop around lakes, tanks and sometimes the village is planned in such a way that the central part remains open and is used for keeping the animals to protect them from wild animals. 6. Double village: These settlements extend on both sides of a river where there is a bridge or a ferry Incorrect
Solution: (b)
Explanation:
Shape of Settlement Characteristic of Settlement 1. Linear pattern In such settlements houses are located along a road, railwayline, river, canal edge of a valley or along a leve 2. Rectangular pattern Such patterns of rural settlements are found in plain areas or wide inter montane valleys. The roads are rectangular and cut each other at right angle 3. Star like pattern Where several roads converge, star shaped settlements develop by the houses built along the roads. 4. T -shaped These settlements develop at tri-junctions of the roads
5. Circular pattern Circular villages develop around lakes, tanks and sometimes the village is planned in such a way that the central part remains open and is used for keeping the animals to protect them from wild animals. 6. Double village: These settlements extend on both sides of a river where there is a bridge or a ferry -
Question 15 of 30
15. Question
Lahore, Baghdad and Agra are examples of which type of towns ?
Correct
Solution: (b)
Explanation:
Towns and cities are classified into the following categories.
Administrative Towns
National capitals, which house the administrative offices of central governments, such as New Delhi, Canberra, Beijing, Addis Ababa, Washington D.C., and London etc. are called administrative towns. Provincial (sub-national) towns can also have administrative functions, for example, Victoria (British Columbia), Albany (New York), Chennai (Tamil Nadu).
Trading and Commercial Towns
Agricultural market towns, such as, Winnipeg and Kansas city; banking and financial centres like Frankfurt and Amsterdam; large inland centres like Manchester and St Louis; and transport nodes such as, Lahore, Baghdad and Agra have been important trading centres.
Cultural Towns
Places of pilgrimage, such as Jerusalem, Mecca, Jagannath Puri and Varanasi etc. are considered cultural towns. These urban centres are of great religious importance.
Additional functions which the cities perform are health and recreation (Miami and Panaji ), industrial (Pittsburgh and Jamshedpur), mining and quarrying (Broken Hill and Dhanbad) and transport (Singapore and Mughal Sarai).
Incorrect
Solution: (b)
Explanation:
Towns and cities are classified into the following categories.
Administrative Towns
National capitals, which house the administrative offices of central governments, such as New Delhi, Canberra, Beijing, Addis Ababa, Washington D.C., and London etc. are called administrative towns. Provincial (sub-national) towns can also have administrative functions, for example, Victoria (British Columbia), Albany (New York), Chennai (Tamil Nadu).
Trading and Commercial Towns
Agricultural market towns, such as, Winnipeg and Kansas city; banking and financial centres like Frankfurt and Amsterdam; large inland centres like Manchester and St Louis; and transport nodes such as, Lahore, Baghdad and Agra have been important trading centres.
Cultural Towns
Places of pilgrimage, such as Jerusalem, Mecca, Jagannath Puri and Varanasi etc. are considered cultural towns. These urban centres are of great religious importance.
Additional functions which the cities perform are health and recreation (Miami and Panaji ), industrial (Pittsburgh and Jamshedpur), mining and quarrying (Broken Hill and Dhanbad) and transport (Singapore and Mughal Sarai).
-
Question 16 of 30
16. Question
Which was the first urban settlement in the world to reach a population of one million?
Correct
Solution: (a)
Explanation:
Urban Settlements
Rapid urban growth is a recent phenomenon. Until recent times, few settlements reached the population size of more than a few thousand inhabitants. The first urban settlement to reach a population of one million was the city of London by around. A.D. 1810 By 1982 approximately 175 cities in the world had crossed the one million population mark. Presently 54 per cent of the world’s population lives in urban settlements compared to only 3 per cent in the year 1800
Incorrect
Solution: (a)
Explanation:
Urban Settlements
Rapid urban growth is a recent phenomenon. Until recent times, few settlements reached the population size of more than a few thousand inhabitants. The first urban settlement to reach a population of one million was the city of London by around. A.D. 1810 By 1982 approximately 175 cities in the world had crossed the one million population mark. Presently 54 per cent of the world’s population lives in urban settlements compared to only 3 per cent in the year 1800
-
Question 17 of 30
17. Question
Arrange the following Urban settlements in the ascending order of their sizes
- Town
- City
- Conurbation
- Megalopolis
Select the correct code
Correct
Solution: (b)
Explanation:
Types of Urban Settlements
Depending on the size and the services available and functions rendered, urban centres are designated as town, city, million city, conurbation, megalopolis.
Town
The concept of ‘town’ can best be understood with reference to‘village’. Population size is not the only criterion. Functional contrasts between towns and villages may not always be clear- cut, but specific functions such as, manufacturing, retail and wholesale trade, and professional services exist in towns.
City
A city may be regarded as a leading town, which has outstripped its local or regional rivals. In the words of Lewis Mumford, “ the city is in fact the physical form of the highest and most complex type of associative life”. Cities are much larger than towns and have a greater number of economic functions. They tend to have transport terminals, major financial institutions and regional administrative offices. When the population crosses the one million mark it is designated as a million city.
Conurbation
The term conurbation was coined by Patrick Geddes in 1915 and applied to a large area of urban development that resulted from the merging of originally separate towns or cities. Greater London, Manchester, Chicago and Tokyo are examples.
Megalopolis
This Greek word meaning “great city”, was popularised by Jean Gottman (1957) and signifies ‘super- metropolitan’ region extending, as union of conurbations. The urban landscape stretching from Boston in the north to south of Washington in U.S.A. is the best known example of a megalopolis.
Incorrect
Solution: (b)
Explanation:
Types of Urban Settlements
Depending on the size and the services available and functions rendered, urban centres are designated as town, city, million city, conurbation, megalopolis.
Town
The concept of ‘town’ can best be understood with reference to‘village’. Population size is not the only criterion. Functional contrasts between towns and villages may not always be clear- cut, but specific functions such as, manufacturing, retail and wholesale trade, and professional services exist in towns.
City
A city may be regarded as a leading town, which has outstripped its local or regional rivals. In the words of Lewis Mumford, “ the city is in fact the physical form of the highest and most complex type of associative life”. Cities are much larger than towns and have a greater number of economic functions. They tend to have transport terminals, major financial institutions and regional administrative offices. When the population crosses the one million mark it is designated as a million city.
Conurbation
The term conurbation was coined by Patrick Geddes in 1915 and applied to a large area of urban development that resulted from the merging of originally separate towns or cities. Greater London, Manchester, Chicago and Tokyo are examples.
Megalopolis
This Greek word meaning “great city”, was popularised by Jean Gottman (1957) and signifies ‘super- metropolitan’ region extending, as union of conurbations. The urban landscape stretching from Boston in the north to south of Washington in U.S.A. is the best known example of a megalopolis.
-
Question 18 of 30
18. Question
Which phase in the growth of Indian demographic history has been referred as phase of Population Explosion?
Correct
Solution: (c)
Explanation:
The growth rate of population in India over the last one century has been caused by annual birth rate and death rate and rate of migration and thereby shows different trends. There are four distinct phases of growth identified within this period:
Phase I : The period from 1901-1921 is referred to as a period of stagnant or stationary phase of growth of India’s population, since in this period growth rate was very low, even recording a negative growth rate during 1911-1921. Both the birth rate and death rate were high keeping the rate of increase low. Poor health and medical services, illiteracy of people at large and inefficient distribution system of food and other basic necessities were largely responsible for a high birth and death rates in this period.
Phase II : The decades 1921-1951 are referred to as the period of steady population growth. An overall improvement in health and sanitation throughout the country brought down the mortality rate. At
the same time better transport and communication system improved distribution system. The crude birth rate remained high in this period leading to higher growth rate than the previous phase. This is impressive at the backdrop of Great Economic Depression, 1920s and World War II.
Phase III : The decades 1951-1981 are referred to as the period of population explosion in India, which was caused by a rapid fall in the mortality rate but a high fertility rate of population in the country. The average annual growth rate was as high as 2.2 per cent. It is in this period, after the Independence, that developmental activities were introduced through a centralised planning process and economy started showing up ensuring the improvement of living condition of people at large. Consequently, there was a high natural increase and higher growth rate. Besides, increased international migration bringing in Tibetans, Bangladeshis, Nepalis and even people from Pakistan contributed to the high growth rate.
Phase IV : In the post 1981 till present, the growth rate of country’s population though remained high, has started slowing down gradually . A downward trend of crude birth rate is held responsible for such a population growth. This was, in turn, affected by an increase in the mean age at marriage, improved quality of life particularly education of females in the country.
Incorrect
Solution: (c)
Explanation:
The growth rate of population in India over the last one century has been caused by annual birth rate and death rate and rate of migration and thereby shows different trends. There are four distinct phases of growth identified within this period:
Phase I : The period from 1901-1921 is referred to as a period of stagnant or stationary phase of growth of India’s population, since in this period growth rate was very low, even recording a negative growth rate during 1911-1921. Both the birth rate and death rate were high keeping the rate of increase low. Poor health and medical services, illiteracy of people at large and inefficient distribution system of food and other basic necessities were largely responsible for a high birth and death rates in this period.
Phase II : The decades 1921-1951 are referred to as the period of steady population growth. An overall improvement in health and sanitation throughout the country brought down the mortality rate. At
the same time better transport and communication system improved distribution system. The crude birth rate remained high in this period leading to higher growth rate than the previous phase. This is impressive at the backdrop of Great Economic Depression, 1920s and World War II.
Phase III : The decades 1951-1981 are referred to as the period of population explosion in India, which was caused by a rapid fall in the mortality rate but a high fertility rate of population in the country. The average annual growth rate was as high as 2.2 per cent. It is in this period, after the Independence, that developmental activities were introduced through a centralised planning process and economy started showing up ensuring the improvement of living condition of people at large. Consequently, there was a high natural increase and higher growth rate. Besides, increased international migration bringing in Tibetans, Bangladeshis, Nepalis and even people from Pakistan contributed to the high growth rate.
Phase IV : In the post 1981 till present, the growth rate of country’s population though remained high, has started slowing down gradually . A downward trend of crude birth rate is held responsible for such a population growth. This was, in turn, affected by an increase in the mean age at marriage, improved quality of life particularly education of females in the country.
-
Question 19 of 30
19. Question
Arrange the following families of Modern Indian language in the descending order of the number of speakers.
- Nishada
- Dravida
- Kirata
- Aryan
Select the correct code
Correct
Solution: (a)
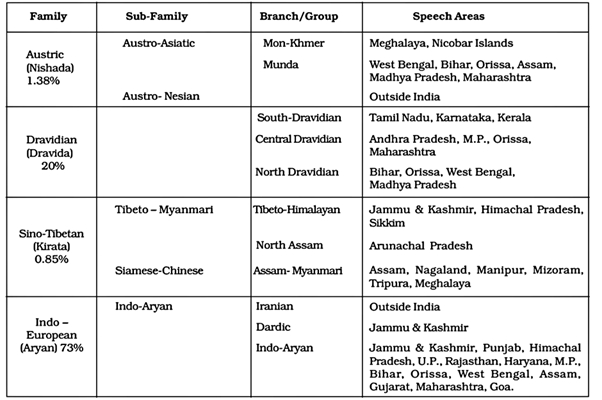
Explanation:
 Incorrect
Incorrect
Solution: (a)
Explanation:

-
Question 20 of 30
20. Question
Arrange the following religious communities of India in ascending order of their total population as proportion of total population India
- Jains
- Sikhs
- Buddhists
- Christians
Select the correct code
Correct
Solution: (a)
Explanation:
Total Population in 2011 is 121.09 crores.(Census Data)
- Hindu 96.63 crores (79.8%)
- Muslim 17.22 crores (14.2%)
- Christian 2.78 crores (2.3%)
- Sikh 2.08 crores (1.7%)
- Buddhist 0.84 crores (0.7%)
- Jain 0.45 crores (0.4%)
- Other Religions & Persuasions (ORP) 0.79 crores (0.7%)
- Religion Not Stated 0.29 crores (0.2%)
Incorrect
Solution: (a)
Explanation:
Total Population in 2011 is 121.09 crores.(Census Data)
- Hindu 96.63 crores (79.8%)
- Muslim 17.22 crores (14.2%)
- Christian 2.78 crores (2.3%)
- Sikh 2.08 crores (1.7%)
- Buddhist 0.84 crores (0.7%)
- Jain 0.45 crores (0.4%)
- Other Religions & Persuasions (ORP) 0.79 crores (0.7%)
- Religion Not Stated 0.29 crores (0.2%)
-
Question 21 of 30
21. Question
Consider the following statements with respect to ‘Seagrasses’
- Seagrasses are flowering plants that grow submerged in shallow marine waters like bays and lagoons
- The temperate waters of the Atlantic hold the highest diversity of seagrasses in the world
- Seagrasses undergo photosynthesis and manufactures their own food and produce oxygen
Choose the correct answer using the code given below
Correct
Solution (c)
Explanation:
- Seagrasses are the only flowering plants which grow in marine environments. Seagrasses are flowering plants that grow submerged in shallow marine waters like bays and lagoons. Seagrasses have roots, stems, and leaves and produce flowers and seeds. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- The tropical waters of the Indo-Pacific hold the highest diversity of seagrasses in the world, supporting 14 different species. This is probably because seagrasses evolved first in this part of the world. Hence statement 2 is not correct.
- Like all autotrophic plants, seagrasses photosynthesize, in the submerged photic zone, and most occur in shallow and sheltered coastal waters anchored in sand or mud bottoms. Like all autotrophic plants, seagrasses photosynthesize, in the submerged photic zone, and most occur in shallow and sheltered coastal waters anchored in sand or mud bottoms. Hence statement 3 is correct.
Source: CLICK HERE
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Explanation:
- Seagrasses are the only flowering plants which grow in marine environments. Seagrasses are flowering plants that grow submerged in shallow marine waters like bays and lagoons. Seagrasses have roots, stems, and leaves and produce flowers and seeds. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- The tropical waters of the Indo-Pacific hold the highest diversity of seagrasses in the world, supporting 14 different species. This is probably because seagrasses evolved first in this part of the world. Hence statement 2 is not correct.
- Like all autotrophic plants, seagrasses photosynthesize, in the submerged photic zone, and most occur in shallow and sheltered coastal waters anchored in sand or mud bottoms. Like all autotrophic plants, seagrasses photosynthesize, in the submerged photic zone, and most occur in shallow and sheltered coastal waters anchored in sand or mud bottoms. Hence statement 3 is correct.
Source: CLICK HERE
-
Question 22 of 30
22. Question
Consider the following statements about ‘Financial Stability Board (FSB)’
- The Financial Stability Board (FSB) is an international body that monitors and advises on market developments and their implications for regulatory policy
- The FSB has member institutions comprising ministries of finance, central banks, supervisory and regulatory authorities and standard-setting bodies
- The Steering Committee is the sole decision-making body of the FSB and the decisions are taken by consensus
Choose the correct answer using the code given below
Correct
Solution (a)
Explanation:
- The Financial Stability Board (FSB) is an international body that monitors and makes recommendations about the global financial system. The FSB was established to: promote coordination and information exchange among authorities responsible for financial stability, monitor and advise on market developments and their implications for regulatory policy, Monitor and advise on best practice in meeting regulatory standards among other objectives. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- The FSB has 71 member institutions, comprising ministries of finance, central banks, and supervisory and regulatory authorities from 25 jurisdictions as well as 13 international organizations and standard-setting bodies, and 6 Regional Consultative Groups reaching out to 65 other jurisdictions around the world. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- The FSB is a member-driven organisation and decisions are taken by consensus. The Plenary is the sole decision-making body of the FSB. It consists of representatives of all Members. The Steering Committee provides operational guidance between Plenary meetings to carry forward the directions of the FSB and prepare the Plenary meetings in order to allow the Plenary to efficiently fulfil its mandate. Hence statement 3 is not correct.
Source: CLICK HERE
Incorrect
Solution (a)
Explanation:
- The Financial Stability Board (FSB) is an international body that monitors and makes recommendations about the global financial system. The FSB was established to: promote coordination and information exchange among authorities responsible for financial stability, monitor and advise on market developments and their implications for regulatory policy, Monitor and advise on best practice in meeting regulatory standards among other objectives. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- The FSB has 71 member institutions, comprising ministries of finance, central banks, and supervisory and regulatory authorities from 25 jurisdictions as well as 13 international organizations and standard-setting bodies, and 6 Regional Consultative Groups reaching out to 65 other jurisdictions around the world. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- The FSB is a member-driven organisation and decisions are taken by consensus. The Plenary is the sole decision-making body of the FSB. It consists of representatives of all Members. The Steering Committee provides operational guidance between Plenary meetings to carry forward the directions of the FSB and prepare the Plenary meetings in order to allow the Plenary to efficiently fulfil its mandate. Hence statement 3 is not correct.
Source: CLICK HERE
-
Question 23 of 30
23. Question
With reference to ‘LORA (Long-Range Artillery) Weapon System’, consider the following statements
- It is a sea-to-ground and ground-to-ground system which comprises a long-range ballistic missile and an unique launcher
- Its guidance system is solely based on Inertial Navigation System (INS) and does not require Global Positioning System (GPS)
Select the correct statement(s)
Correct
Solution (a)
Explanation:
- It is a sea-to-ground and ground-to-ground system which comprises a long-range ballistic missile, a unique launcher, a command and control system, and a ground/marine support system. It provides ballistic assault capabilities for multiple ranges with a precision level of 10 meters CEP (circular error probable). The LORA uses a shaped trajectory flight mode. LORA is stored in a sealed canister, enabling very low maintenance costs. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- Its guidance system is based on both the Global Positioning System (GPS) and the Inertial Navigation System (INS), with possible in-flight maneuvering capability. Hence statement 2 is not correct.
Source: CLICK HERE
Incorrect
Solution (a)
Explanation:
- It is a sea-to-ground and ground-to-ground system which comprises a long-range ballistic missile, a unique launcher, a command and control system, and a ground/marine support system. It provides ballistic assault capabilities for multiple ranges with a precision level of 10 meters CEP (circular error probable). The LORA uses a shaped trajectory flight mode. LORA is stored in a sealed canister, enabling very low maintenance costs. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- Its guidance system is based on both the Global Positioning System (GPS) and the Inertial Navigation System (INS), with possible in-flight maneuvering capability. Hence statement 2 is not correct.
Source: CLICK HERE
-
Question 24 of 30
24. Question
Consider the following statements about ‘GST Appellate Tribunal (GSTAT)’
- It was established by the Central Government under The Central Goods and Service Tax Act, 2017
- It will serve as a forum for the first appeal in GST laws and the first common forum for dispute resolution between Centre and States.
Select the correct statement(s)
Correct
Solution (a)
Explanation:
- Section 109 of Chapter XVIII Chapter of Central Goods and Service Tax Act, 2017 Act empowers the Central Government to constitute an Appellate Tribunal known as the Goods and Services Tax Appellate Tribunal for hearing on the recommendation of Council, by notification, with effect from such date as may be specified therein on the recommendation of GST Council. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- Goods and Services Tax Appellate Tribunal is the form of the second appeal in GST laws and the first common forum of dispute resolution between Centre and States. The appeals against the orders in first appeals issued by the Appellate Authorities under the Central GST (CGST) and State GST (SGST) Acts lie before the GST Appellate Tribunal. Hence statement 2 is not correct.
Source: CLICK HERE
Incorrect
Solution (a)
Explanation:
- Section 109 of Chapter XVIII Chapter of Central Goods and Service Tax Act, 2017 Act empowers the Central Government to constitute an Appellate Tribunal known as the Goods and Services Tax Appellate Tribunal for hearing on the recommendation of Council, by notification, with effect from such date as may be specified therein on the recommendation of GST Council. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- Goods and Services Tax Appellate Tribunal is the form of the second appeal in GST laws and the first common forum of dispute resolution between Centre and States. The appeals against the orders in first appeals issued by the Appellate Authorities under the Central GST (CGST) and State GST (SGST) Acts lie before the GST Appellate Tribunal. Hence statement 2 is not correct.
Source: CLICK HERE
-
Question 25 of 30
25. Question
‘Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumanii, Staphylococcus aureus’, a group of bacterias seen in news are known for
Correct
Solution (c)
Explanation:
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumanii, Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli are proven biofilm-forming bacteria. Researchers from ARCI, an autonomous institute of the Department of Science and Technology (DST), have developed a nanocomposite coating ((named at ARCI as ATL)) by combining water repellence and biocidal property (combinatorial approach), which exhibits both hydrophobic and biocidal behaviour. ATL was deposited on different surgical sutures made of silk, nylon, and polyglactin 910 (vicryl) in addition to surgical instrument grade stainless steel 420 coupons and tested for biofilm inhibition against American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) and clinical isolate strains of proven biofilm-forming bacteria such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumanii, Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli.
Source: CLICK HERE
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Explanation:
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumanii, Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli are proven biofilm-forming bacteria. Researchers from ARCI, an autonomous institute of the Department of Science and Technology (DST), have developed a nanocomposite coating ((named at ARCI as ATL)) by combining water repellence and biocidal property (combinatorial approach), which exhibits both hydrophobic and biocidal behaviour. ATL was deposited on different surgical sutures made of silk, nylon, and polyglactin 910 (vicryl) in addition to surgical instrument grade stainless steel 420 coupons and tested for biofilm inhibition against American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) and clinical isolate strains of proven biofilm-forming bacteria such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumanii, Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli.
Source: CLICK HERE
-
Question 26 of 30
26. Question
Identify the term that will replace the “?” in the given series
14, 15, 12, 16, 9, 18, 4, 21, ?
Correct
Solution (c)
Explanation:
There are two series in the given series alternatively
1st one 14,12,9,4,…
2nd one 15,16,18,21..
The next number will belong to the 1st series.
The rule of the 1st series is 14, 14−2, 12−3, 9−5, 4−7
Next number is 4−7 = −3
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Explanation:
There are two series in the given series alternatively
1st one 14,12,9,4,…
2nd one 15,16,18,21..
The next number will belong to the 1st series.
The rule of the 1st series is 14, 14−2, 12−3, 9−5, 4−7
Next number is 4−7 = −3
-
Question 27 of 30
27. Question
You are given two identical sequences in two rows:
Sequence I: 6 14 35 111 449 2249 Sequence II: 5 A B C D E What is the entry in the place of E for the Sequence II?
Correct
Solution (a)
Explanation:
The sequence follows the rule: Term 2 = Term 1 × 1 + 8, Term 3 = Term 2 × 2 + 7, Term 4 = Term 3 × 3 + 6, Term 5 = Term 4 × 4 + 5, Term 6 = Term 5 × 5 + 4,
So, the new series is 3, 11, 29, 93, 337, and 1889
Incorrect
Solution (a)
Explanation:
The sequence follows the rule: Term 2 = Term 1 × 1 + 8, Term 3 = Term 2 × 2 + 7, Term 4 = Term 3 × 3 + 6, Term 5 = Term 4 × 4 + 5, Term 6 = Term 5 × 5 + 4,
So, the new series is 3, 11, 29, 93, 337, and 1889
-
Question 28 of 30
28. Question
What is the value of ‘X’ in the given sequence
1, 2, 7, 7, 13, 12, ?
Correct
Solution (b)
Explanation:
Given sequence consists of two series.
1, 7, 13, i.e., difference between consecutive numbers is 6.
2, 7, 12, i.e., difference between consecutive numbers is 5.
So, next number in the first series is 19.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Explanation:
Given sequence consists of two series.
1, 7, 13, i.e., difference between consecutive numbers is 6.
2, 7, 12, i.e., difference between consecutive numbers is 5.
So, next number in the first series is 19.
-
Question 29 of 30
29. Question
Select the letter-cluster that can replace the question mark (?) in the following series.
DJQC, ELTG, FNWK, GPZO, ?
Correct
Solution (a)
Explanation:
The series follows pattern as,
(D + 1)(J + 2)(Q + 3)(C + 4) = ELTG
(E + 1)(L +2)(T + 3)(G + 4) = FNWK
(F + 1)(N +2)(W + 3)(K + 4) = GPZO
(G + 1)(P +2)(Z + 3)(O + 4) = HRCS
The correct answer is option a.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
Explanation:
The series follows pattern as,
(D + 1)(J + 2)(Q + 3)(C + 4) = ELTG
(E + 1)(L +2)(T + 3)(G + 4) = FNWK
(F + 1)(N +2)(W + 3)(K + 4) = GPZO
(G + 1)(P +2)(Z + 3)(O + 4) = HRCS
The correct answer is option a.
-
Question 30 of 30
30. Question
Read the following passage and answer the item that follow. Your answer to these items should be based on the passages only
Passage 1
The dominant hypotheses in modern science believe that language evolved to allow humans to exchange factual information about the physical world. But an alternative view is that language evolved, in modern humans at least, to facilitate social bonding. It increased our ancestors’ chances of survival by enabling them to hunt more successfully or to cooperate more extensively. Language meant that things could be explained and that plans and past experiences could be shared efficiently.
Which of the following is the most logical corollary that can be drawn from the passage?
Correct
Solution (b)
Explanation:
The main idea of the paragraph is that challenging the dominant hypothesis that language evolved in order to facilitate exchange of factual information; an alternative view holds that language evolved in order to facilitate social bonding and improve chances of survival. Option b captures all key ideas.
Option a incorrectly uses the word “invented”. Option c talks about language “continuously evolving to higher forms”. The paragraph does not state this.
Option d states “experts” are challenging the “narrow” view of origin of language. The paragraph only talks about “an alternative view”.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Explanation:
The main idea of the paragraph is that challenging the dominant hypothesis that language evolved in order to facilitate exchange of factual information; an alternative view holds that language evolved in order to facilitate social bonding and improve chances of survival. Option b captures all key ideas.
Option a incorrectly uses the word “invented”. Option c talks about language “continuously evolving to higher forms”. The paragraph does not state this.
Option d states “experts” are challenging the “narrow” view of origin of language. The paragraph only talks about “an alternative view”.
All the Best
IASbaba











