IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recently, India climbed 6 places on World Bank’s Logistic Performance Index.
About Logistic Performance Index:-
- The Logistics Performance Index (LPI), developed by the World Bank Group.
- It is an interactive benchmarking tool created to help countries identify the challenges and opportunities they face in their performance on trade logistics and what they can do to improve their performance.
- It is the weighted average of the country’s scores on the six key dimensions:
- Efficiency of the clearance process (i.e., speed, simplicity and predictability of formalities) by border control agencies, including customs.
- Quality of trade and transport-related infrastructure (e.g., ports, railroads, roads, information technology).
- Ease of arranging competitively priced shipments.
- Competence and quality of logistics services (e.g., transport operators, customs brokers).
- Ability to track and trace consignments.
- Timeliness of shipments in reaching destinations within the scheduled or expected delivery time.
- The LPI 2023 allows for comparisons across 139 countries.
- The 2023 LPI for the first time measures the speed of trade with indicators derived from big datasets tracking shipments.
- India’s new ranking on Logistics Performance Index 2023 is 38.
- India was ranked 44th on the index in 2018 and has now climbed to 38th in the 2023 listing.
- According to the report, India’s rank moved up five places in infrastructure score from 52nd in 2018 to 47th in 2023.
- It climbed to the 22nd spot for international shipments in 2023 from 44th in 2018 and moved four places up to 48th in logistics competence and equality.
MUST READ: National Logistics Policy
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Rapid Financing Instruments” and “Rapid Credit Facilities” are related to the provisions of lending by which of the following: (2022)
- Asian Development Bank
- International Monetary Fund
- United Nations Environment Programme Finance Initiative
- World Bank
Q.2) Consider the following: (2021)
- Foreign currency convertible bonds
- Foreign institutional investment with certain conditions
- Global depository receipts
- Non-resident external deposits
Which of the above can be included in Foreign Direct Investments?
- 1, 2 and 3
- 3 only
- 2 and 4
- 1 and 4
Syllabus
- Prelims –International Relations
Context: Recently, External Affairs Minister S Jaishankar, co-chaired the 4th India-CARICOM ministerial meeting with his Jamaican counterpart.
About CARICOM:-
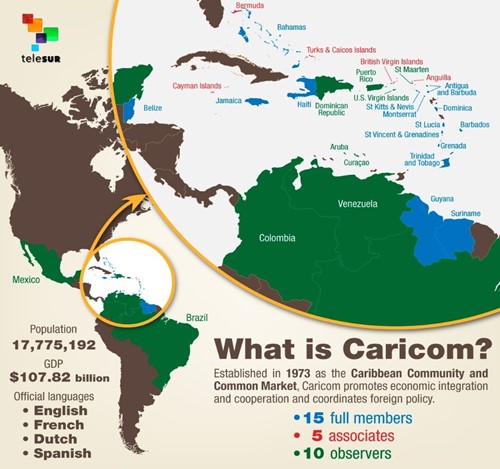
IMAGE SOURCE: What is Caricom? | Multimedia | teleSUR English
- The Caribbean Community and common market (CARICOM or CC) is an intergovernmental organisation that is a political and economic union of 15 member states (14 nation-states and one dependency) throughout the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean.
- It was established in 1973.
- CARICOM is the oldest surviving integration movement in the developing world.
- Objective: promote economic integration and cooperation among its members, to ensure that the benefits of integration are equitably shared, and to coordinate foreign policy.
- CARICOM has 15 members including Antigua and Barbuda, Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, Dominica, Grenada, Guyana, Haiti, Jamaica, Montserrat, St. Kitts and Nevis, St Lucia, St. Vincent and the Grenadines, Suriname, and Trinidad & Tobago.
- The Chairmanship of the Community is rotated every six months among the member countries.
- The CARICOM Single Market and Economy are intended to benefit the people of the region by providing more and better opportunities to produce and sell goods and services and to attract investment.
India-CARICOM :-
- Prime Minister of India had a meeting with 14 leaders of the CARICOM group of countries on the sidelines of the United Nations General Assembly in New York in 2019.
- The meeting deliberated on the steadily intensifying and deepening relations
- India provided immediate financial assistance of USD 1 million to recover from the destruction caused by Hurricane Dorian in the region and the worst-hit island of the Bahamas.
- India announced a USD 14 million grant for community development projects in the CARICOM and another 150 million Line of Credit for solar, renewable energy climate-change-related projects.
- The Government of India funded the US$ 1.166 million information technology and communication infrastructure, computer software and community studio at the CARICOM Secretariat in 2005-2006.
- India’s External Affairs Minister S Jaishankar co-chaired the 4th India-CARICOM ministerial meeting and discussed a range of issues, including trade, climate change and counterterrorism.
MUST READ: Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP)
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) In which one of the following groups are all four countries members of G20? (2020)
- Argentina Mexico, South Africa and Turkey.
- Australia Canada, Malaysia and New Zealand
- Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia and Vietnam
- Indonesia Japan Singapore and South Korea
Q.2) Which of the following adopted a law on data protection and privacy for its citizens known as the ‘General Data Protection Regulation’ in April 2016 and started the implementation of its from 25th May 2018? (2019)
- Australia
- Canada
- The European Union
- The United States of America
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: Recently, the scientific community voiced against NCERT’s decision to remove Darwin’s theory of biological evolution from Class 10 CBSE textbooks.
About Darwin’s theory of evolution:-

IMAGE SOURCE: Darwin’s theory of biological evolution info – Bing images
- Charles Darwin is known as the father of evolution due to his contribution to the establishment of the theory of evolution.
- Darwin published his concept of evolution in his book entitled “The Origin of Species”.
Ideas by Darwin on the theory of natural selection:-
- The species keep on changing or evolving with time.
- As the environment changes, the requirements of the organisms also change and they need to adapt to their new environment.
- According to the natural requirements, the phenomenon of change over a period of time is known as adaptation.
- According to Darwin’s theory, only higher changes tend to get naturally selected and lower ones are automatically eliminated.
- This leads to progressive evolution and not all the adaptations are able to contribute.
- All the organisms had a common ancestor at some point in time and this kept on diverging since then according to Darwin.
- As per Charles Darwin, evolution is a gradual and slow process.
- Darwinism consists of five principles which are:
- Over-production or prodigality of over-production: Many more individuals are born in each generation that will be able to survive and reproduce.
- Variation and Heredity: There is natural variation among individuals of the same species. Many of the favourable adaptations are hereditary and are passed on to the progeny of future generations.
- Struggle for existence: Organic beings increase by a geometrical ratio, while food production only increases in an arithmetic ratio such that in a very short time, an area will be overpopulated with any one species unless something happens to check the increase. This struggle for existence is threefold as given below:-
- Intraspecific struggle: The Intraspecific struggle is found among Individuals of the same species.
- Interspecific struggle: – It is found among organisms of different species living together.
- Struggle with the environment: Living organisms struggle with adverse environmental conditions like floods, cold waves, heat waves, and earthquakes, etc.
- Survival of the fittest or natural selection: Individuals with certain Characteristics have a better chance of surviving and reproducing than others with less favourable ones.
- Modifications of species: Gradual modification of species could have occurred over long periods of geological time through additive processes occurring in the past in the same manner as they are occurring in the present.
MUST READ: Synthetic biology
SOURCE: HINDUSTAN TIMES
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to recent developments regarding ‘Recombinant vector Vaccines’, consider the following statements: (2021)
- Genetic engineering is applied in the development of these vaccines.
- Bacteria and viruses are used as vectors.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) In the context of hereditary diseases, consider the following statements: (2021)
- Passing on mitochondrial diseases from parent to child can be prevented by mitochondrial replacement therapy either before or after in vitro fertilization of the egg.
- A child inherits mitochondrial diseases entirely from the mother and not from the father.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: India has been announced to have the 3rd-highest number of unicorns and gazelles as per the Hurun’s Global Unicorn Index 2023.
About Hurun’s Global Unicorn Index 2023:-

IMAGE SOURCE: Unicorn startups info – Bing images
- The Global Unicorn Index is taken out by HURUN.
- HURUN: It is a research, media and investments business, best known for its Hurun Rich List, a ranking of the wealthiest individuals in China.
- Hurun’s Global Unicorn Index is designed to give an insight into the economy of tomorrow, by listing out the world’s most successful startups.
- Start-ups are classified as
Key highlights:-
- According to the Global Unicorn Index, India continues to be the world’s third-largest country with the highest number of unicorns( 68 unicorns), following the US and China.
- Among these, food tech platform Swiggy, fantasy gaming company Dream11 and ed-tech firm BYJU’S are the top unicorns in the country.
- It said that the USA, especially Silicon Valley, attracted the most unicorn founders from abroad, followed by Europe.
- It revealed that India led the way for emigrant unicorn founders, followed by China, Israel and Russia.
- The report mentioned that the number of Indian unicorns established outside of India is higher than those located within India.
- The list further disclosed that India has a total of 138 unicorns, out of which 70 were established by Indian co-founders but have their headquarters located outside India, while 68 are based in India.
- Hurun’s report also revealed that India ranks third in terms of the number of gazelles.
- However, when it comes to the Hurun Global 500 companies, which is a list of the most valuable non-state-controlled businesses globally, India ranks fifth.
- According to the report, China and India have a higher proportion of gazelles and unicorns, which is expected to result in a higher number of Hurun Global 500 companies over the next five years.
- Conversely, countries such as France, Canada, and Australia, with a lower proportion, are likely to lose their positions on the Hurun Global 500 list.
- In terms of unicorn investors, Sequoia Capital, Tiger Global Management, and SoftBank are the top three, having invested in 238, 179, and 168 unicorn startups, respectively.
- The Hurun report also mentioned that 70 unicorns were started by Indian co-founders outside of India, specifically in the US (64), two in the UK, and 1 each in Germany, Singapore, Indonesia and Mexico.
MUST READ: Fund of Funds for Start-up (FFS) scheme
SOURCE: BUISINESSTODAY
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to the international trade of India at present, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2020)
- India’s merchandise exports are less than its merchandise imports.
- India’s imports of iron and steel, chemicals, fertilisers and machinery have decreased in recent years.
- India’s exports of services are more than its imports of services.
- India suffers from an overall trade/current account deficit.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 3 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
Q.2) Concerning the Indian economy, consider the following statements : (2020)
- Commercial Paper is a short-term unsecured promissory note.
- Certificate of Deposit is a long-term Instrument issued by RBI to a corporation.
- ‘Call Money’ is short-term finance used for interbank transactions.
- “Zero-Coupon Bonds’ are interest-bearing short-term bonds issued by the Scheduled Commercial Banks to corporations.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 4 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2, 3 and 4 only
Syllabus
- Prelims – Social Issues
Context: Recently, Twitter removed protection against deadnaming.
About Deadnaming:-
- A deadname is essentially the name that a trans, non-binary, and/or gender-expansive person was called before they adopted a more self-affirming name.
- The act of, intentionally or not, calling a trans, non-binary, and/or gender-expansive person by the deadname is known as deadnaming, which can lead to adverse consequences.
- Deadnaming is harmful because refusing to use a person’s chosen name or pronouns is a form of transphobia or cissexism.
- Cissexism can contribute to mental health conditions, such as depression and suicidality.
- It can also lead to physical and verbal assault and abuse.
- This might result in the person being harassed, discriminated against or assaulted.
- Deadnaming not only invalidates someone’s true identity but also may reveal information about the sex assigned to them at birth that the person concerned may not want anyone to know.
MUST READ: Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to the ‘stand up India scheme’, which of the following statement is/are correct? (2016)
- Its purpose is to promote entrepreneurship among SC/ST and women entrepreneurs.
- It provides for refinancing through SIDBI.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Rashtriya Garima Abhiyaan’ is a national campaign to (2016)
- rehabilitate the homeless and destitute persons and provide them with suitable sources of livelihood
- release the sex workers from their practice and provide them with alternative sources of livelihood
- eradicate the practice of manual scavenging and rehabilitate the manual scavengers
- release the bonded labourers from their bondage and rehabilitate them
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: Gandhisagar Wildlife Sanctuary will be developed as a second home for cheetahs in the coming times.
About Gandhisagar Wildlife Sanctuary:-
- Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary is situated in northwestern Madhya Pradesh, with one of its boundaries running along the border of Rajasthan.
- The sanctuary was notified in 1974.
- Its vast expanse lies within the Mandsaur and Neemuch districts of Madhya Pradesh.
- River Chambal flows through the sanctuary, dividing it into two parts.
- Flora: The principal tree species found in the Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary are Khair, Salai, Kardhai, Dhawda, Tendu, Palash and the like.
- Fauna: Herbivores like Chinkara, Nilgai and Spotted Deer, and carnivores like the Indian Leopard, Striped Hyena and Jackal are found in good numbers in the region.
- The reservoir also has a good population of crocodiles, fish, otters and turtles.
- Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary and the reservoir are also designated Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA) as it boasts a large bird diversity with healthy populations.
MUST READ: Tungareshwar Wildlife Sanctuary
SOURCE: HINDUSTAN TIMES
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which of the following is not a bird? (2022)
- Golden Mahseer
- Indian Nightjar
- Spoonbill
- White Ibis
Q.2) With reference to Indian laws about wildlife protection, consider the following statements :
- Wild animals are the sole property of the government.
- When a wild animal is declared protected, such animal is entitled to equal protection whether it is found in protected areas or outside.
- Apprehension of a protected wild animal becoming a danger to human life is sufficient ground for its capture or killing.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2022)
- 1 and 2
- 2 only
- 1 and 3
- 3 only
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recently, SEBI issued a procedure for vault managers to seek prior approval for the change.
About Vault managers:-
- The vault manager is regulated as a SEBI intermediary for providing vaulting services meant for gold deposited to create electronic gold receipts (EGRs).
- Electronic gold receipts: this is a gold exchange measure by SEBI, wherein the yellow metal can be traded in the form of electronic gold receipts.
- The obligations of the vault manager include accepting deposits, storage, and safekeeping of gold, creation as well as withdrawal of EGR, grievance redressal, and periodic reconciliation of physical gold with the records of the depository.
SEBI’s new procedure guidelines:-
- Under the procedure, an application should be made by the vault managers to the regulator for prior approval through the Intermediary Portal, according to a circular.
- Applications for fresh registration under a change in control shall be made to Sebi within six months from the date of prior approval.
- The matters which involve a scheme of arrangement and need sanction from the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT), the vault manager would have to ensure that the application seeking approval for the proposed change in control would be filed with Sebi before applying with NCLT.
- The validity of such in-principle approval from Sebi would be three months within which the relevant application should be made to NCLT.
- Within 15 days from the date of the order of NCLT, the vault manager would have to submit the required documents to SEBI for final approval.
- The procedure would come into force with immediate effect.
MUST READ: Sweat Equity Rules: SEBI
SOURCE: BUSINESS STANDARD
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- In India, credit rating agencies are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India.
- The rating agency popularly known as ICRA is a public limited company.
- Brickwork Ratings is an Indian credit rating agency.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to the ‘Banks Board Bureau (BBB)’, which of the following statements is correct? (2022)
- The Governor of RBI is the Chairman of BBB.
- BBB recommends the selection of heads for Public Sector Banks.
- BBB helps Public Sector Banks develop strategies and capital-raising plans.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: Recently, a rare solar eclipse, the Ningaloo Eclipse 2023 brought total darkness and a ‘ring of fire’.
About Ningaloo Eclipse 2023:-
- A solar eclipse is an astronomical event that occurs when the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun, partially blocking the Sun’s rays and creating a shadow on the Earth’s surface.
- When the Moon crosses the path of the Sun, it does not completely cover the solar disk, leaving a ring of the Sun’s outer edges visible around the Moon. This creates a spectacular ring of fire effect around the dark silhouette of the Moon.
Hybrid solar eclipse:-
- A hybrid solar eclipse looks like a total eclipse in some areas along the eclipse path, and like an annular eclipse in others and it’s all due to Earth’s curvature.
- During a hybrid solar eclipse, the Earth’s curvature brings some sections of the eclipse path into the Moon’s umbra, the darkest part of its shadow that creates total solar eclipses, while other areas remain outside the umbra’s reach, causing an annular eclipse.
- The Ningaloo Eclipse 2023 will be visible from 1:34:26 (UTC Time) to 06:59:22.
- The first location will see the partial eclipse at 01:34:26 (which is 7:04:26 in Delhi)
- The full eclipse will be visible from 02:37:08 (08:07:08 in Delhi) and the maximum eclipse will be seen at 9:46:53.
- Last location will see the full eclipse at 5:56:43 (which is 11:26:43 in Delhi).
- Australia’s Exmouth, a small resort town, will experience total darkness for 62 seconds as the moon’s shadow crosses the Exmouth Peninsula.
MUST READ: Eclipses
SOURCE: BUSINESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following is a reason why astronomical distances are measured in light-years? (2021)
- Distance among stellar bodies does not change
- The gravity of stellar bodies does not change
- Light always travels in a straight line
- Speed of light is always the same
Q.2) The experiment will employ a trio of spacecraft flying in formation in the shape of an equilateral triangle that has sides one million kilometres long, with lasers shining between the craft.” The experiment in question refers to (2020)
- Voyager-2
- New Horizons
- LISA Pathfinder
- Evolved LISA
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Security Issues)
Context: The attack on an Army truck in Poonch in Jammu highlights the continuing vulnerability of this border area in spite of tiers of security — the army at the Line of Control, the Rashtriya Rifles in areas proximate to the border and the police in the hinterland.
About Cross-Border Terrorism:
- The term ‘cross-border’ implies a movement or an activity across a border between the two countries.
- Cross-Border Terrorism is a form in which soil of one country is used to create terror in bordering countries.
- As a grey zone conflict, it is an undeclared war and considered to be highest form of strategy to bleed a nation for prolonged period by small efforts.
Cross-Border Terrorism in India:
Indo-Pakistan Border:
- Indo-Pakistan Border (3,323 Km) runs along the states of Gujarat, Rajasthan, Punjab and Jammu and Kashmir.
- Cross-Border Terrorism from Pakistan has been exacerbated due to the non-recognition of boundaries by its terrorist groups and their success in acquiring legitimacy due to religious or ethnic identity.
- Inadequate Cooperation from Pakistan has made the management of border further difficult for India.
Indo-China Border:
- India shares a long land border with China (3,488 Km) in the Indian states of Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh.
- Although this border remains relatively aloof from illegal migrations, this border remains a cause of constant vigil for Indian forces.
Indo-Bangladesh Border:
- The Indo-Bangladesh Border (4,096 Km) passes through West Bengal, Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram.
- The entire stretch consists of plains, riverine belts, hills and jungles which make illegal migration very easy.
- Illegal Migration across this border poses serious security threats and acts as a fertile ground for organisations like the Inter-Services Intelligence of Pakistan to penetrate and expand their activities.
- Also, poor law and order situation at the border, has led to smuggling of arms and drugs.
- The Supply of arms helps in sustaining any conflict.
Indo-Nepal Border:
- India-Nepal Border (1,751 Km) is an open border in the sense that people of both the countries can cross it from any point, despite the existence of border check posts at several locations.
- Anti-India organizations use this border to plant their people in the territory of India.
- Also, smuggling of gold, small arms, drugs and fake currency helps terrorists in executing an attack.
Indo-Myanmar Border:
- The northeast states of Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur and Mizoram share the border with Myanmar (1,643).
- Some of the insurgents groups like the National Socialist Council of Nagaland (NSCN) and United Liberation Front of Asom (ULFA) operate from Myanmar, which threatens the security of India as well as Myanmar.
Cross-Border Terrorism through Maritime Borders:
- Not only contiguous Border States with land borders are vulnerable to the cross-border terrorism but coastal areas are equally vulnerable.
- The Long coastline of the country remains comparatively unguarded.
- The presence of the Coast Guard is minimal.
- In 26/11 terrorists attack came from the western coast through boats.
Factors Facilitating Cross-Border Incursion:
Porous Border:
- India’s borders with most neighbours are porous (not protected) and are extremely easy to cross.
- These borders cannot be physically wired due to complex geographical features such as mountains, deserts and other landforms.
Support from Non-State Actors:
- India has a discordant political relationship with Pakistan which provide material support for secessionist militants in the border states of North-East and Jammu and Kashmir.
Internal Support:
- Sometimes the local population support and facilitate cross border movement of terrorists by providing them conveyance and safe places to hide.
Corrupt Officials:
- Sometimes officials in exchange for a few thousand rupees allow unabated entry of illegal migrants whose identities and backgrounds are little known;
- These channels provide scope to criminal elements to cross over to mainland India.
Issues in tackling Cross-border Terrorism:
- No common definition: There is no common definition for terrorism and terrorists.
- Irrational classification of terrorism: Sometimes, terrorism is classified as good or bad terrorism, small or big terrorism.
- Lack of cross–border cooperation: In many countries, cross-border terrorism and Interpol nodal agencies are different, so there is no strong and comprehensive coordination among nations.
- Complex Interdependence: Incapability of a single country to deal with this global challenge.
- Consideration of cross-border terrorism as a political problem.
Global Efforts:
- UN Global Counter-Terrorism strategy 2006: It is a unique global instrument to enhance national, regional, and international efforts to counter-terrorism.
- Through its adoption, all UN Member States agreed for the first time to a common strategic and operational approach to fighting terrorism.
- UNSC Resolution 1373: It is a counter-terrorism measure passed following the 11 September terrorist attacks on the United States.
- UNSC Resolution 1540: This resolution requires every state to criminalize various forms of non-state actor involvement in weapons of mass destruction and its related activities in its domestic legislation.
- Global Internet Forum to Counter Terrorism: It is an Internet industry initiative to share proprietary information and technology for automated content moderation.
Steps Taken by India:
- India has taken steps for setting up Joint Working Groups (JWGs) on counter-terrorism/security matters with countries.
- Bilateral treaties on Mutual Legal Assistance (MLATs) in Criminal matters to facilitate the investigation, collection of evidence, transfer of witnesses, location and action against proceeds of crime, etc. have been signed with other countries.
- In 2018, India highlighted its demand for a Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism (CCIT) at the 73rd session of the UN General Assembly (UNGA).
- In 1996, with the objective of providing a comprehensible legal framework to counter-terrorism, India proposed to the UNGA the adoption of CCIT.
- In January 2021, at the 20th anniversary of the UN Security Council (UNSC) Resolution 1373, India presented an eight-point action plan to deal with the scourge of terrorism.
- Comprehensive Integrated Border Management System: It vastly improves the capability of Border Security Force (BSF) in detecting and controlling the cross border crimes like illegal infiltration, smuggling of contraband goods, human trafficking and cross border terrorism, etc.
- Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act, 1967: It enables more effective prevention of certain unlawful activities of individuals and associations and for dealing with terrorist activities, and other related matters.
- National Investigation Agency: It is India’s counter-terrorist task force and is empowered to deal with terror related crimes across states without special permission from the states.
- Policy of Zero-Tolerance Against Terrorism: India calls for zero-tolerance against terrorism and focuses on developing a common strategy to curb it.
Various Counter-Terrorism Operations
- Operation Rakshak: Counter-insurgency and counter-terrorism operation in Jammu and Kashmir in 1990.
- Operation Sarp Vinash: Undertaken by Indian army to flush out terrorists in the areas of the Pir Panjal range in Jammu and Kashmir in 2003.
- Operation All Out: Joint offensive launched by Indian security forces to flush out militants and terrorists in Kashmir in 2017.
SourceThe Hindu
MUST READ: Left Wing Extremism + Challenges to secure India’s land border
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Economy)
Context: A recent working paper from the Centre for Social and Economic Progress (CSEP) extends the earlier minerals assessment for 23 minerals by assessing the criticality levels of 43 select minerals for India based on their economic importance.
About critical minerals:

Source: https://www.wilsoncenter.org
- Critical minerals refer to mineral resources, both primary and processed, which are essential inputs in the production process of an economy, and whose supplies are likely to be disrupted due to the risks of non-availability or unaffordable price spikes.
- To tackle such supply risks, major global economies periodically evaluate which minerals are critical for their jurisdiction through a quantitative assessment.
- Minerals such as antimony, cobalt, gallium, graphite, lithium, nickel, niobium, and strontium are among the 22 assessed to be critical for India.
Criticality of these Minerals
- As countries around the world scale up their transition towards clean energy and digital economy, these critical resources are key to the ecosystem that fuels this change.
- Any supply shock can severely imperil the economy and strategic autonomy of a country over-dependent on others to procure critical minerals.
- But these supply risks exist due to rare availability, growing demand and complex processing value chain.
- Many times the complex supply chain can be disrupted by hostile regimes, or due to politically unstable regions.
- According to the International Energy Association (IEA), the rise of low-carbon power generation is projected to triple mineral demand from this sector by 2040.
- A US government statement noted that as the world transitions to a clean energy economy, global demand for these critical minerals is set to rapidly increase by 400 per cent to 600 per cent over the next several decades, and, for minerals such as lithium and graphite used in EV batteries, demand will increase by as much as 4,000 per cent.
Applications:
- Electric vehicles: cobalt, lanthanum, lithium
- Fuel cells: platinum, palladium, rhodium
- Wind energy technologies: neodymium, dysprosium, terbium
- Aviation sector: titanium
- Photovoltaic solar technologies: cadmium, indium, gallium
Significance for India:
- Many of these are required to meet the manufacturing needs of green technologies, high-tech equipment, aviation, and national defence.
- However, while India has a significant mineral geological potential, many minerals are not readily available domestically.
- Hence, India needs to develop a national strategy to ensure resilient critical minerals supply chains, which focuses on minerals found to be critical.
India and Critical Minerals:
Lithium Agreement:
- In mid-2020, India, through a newly floated state-owned company, had signed an agreement with an Argentinian firm to jointly prospect lithium in the South American country that has the third largest reserves of the metal in the world.
India-Australia Critical Minerals Investment Partnership:
- India and Australia decided to strengthen their partnership in the field of projects and supply chains for critical minerals.
- Australia has the resources to help India fulfil its ambitions to lower emissions and meet the growing demand for critical minerals to help India’s space and defence industries, and the manufacture of solar panels, batteries and electric vehicles.
Challenges
International Challenges:
China:
- China, the most dominant player in the critical mineral supply chains, still struggles with Covid-19-related lockdowns.
- As a result, the extraction, processing and exports of critical minerals are at risk of slowdown.
Russia Ukraine war:
- Russia is one of the significant producers of nickel, palladium, titanium sponge metal, and the rare earth element scandium.
- Ukraine is one of the major producers of titanium. It also has reserves of lithium, cobalt, graphite, and rare earth elements, including tantalum, niobium, and beryllium.
- The war between the two countries has implications for these critical mineral supply chains.
Shifting Balance of power:
- As the balance of power shifts across continents and countries, the critical mineral supply chains may get affected due to the strategic partnership between China and Russia.
- As a result, developed countries have jointly drawn up partnership strategies, including the Minerals Security Partnership (MSP) and G7’s Sustainable Critical Minerals Alliance, while developing countries have missed out.
Domestic challenges:
Scarce reserves:
- Manufacturing renewable energy technologies would require increasing quantities of minerals, including copper, manganese, zinc, and indium.
- Likewise, the transition to electric vehicles would require increasing amounts of minerals, including copper, lithium, cobalt, and rare earth elements.
- However, India does not have many of these mineral reserves, or its requirements may be higher than the availability, necessitating reliance on foreign partners to meet domestic needs.
Inadequate listing:
- Many critical and strategic minerals constitute part of the list of atomic minerals in the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) (MMDR) Act, 1957.
- However, the present policy regime reserves these minerals only for public sector undertakings.
Way Forward:
Critical minerals are the possible next “Geopolitical Battleground” just as crude oil has been over the last 50 years. The Economic Survey 2022-23 has rightly prescribed a “carefully crafted multi-dimensional mineral policy”.
The skewed distribution of the resource poses a supply risk in the face of its enhanced demand. A National Critical Minerals Strategy for India, underpinned by the minerals identified, can help focus on priority concerns in supply risks, domestic policy regimes, and sustainability.
Source: Indian Express
Practice MCQs
Q.1) Gandhisagar Wildlife Sanctuary is located in
- Rajasthan
- Madhya Pradesh
- Haryana
- West Bengal
Q.2) which of the following countries are members of the Caribbean Community and common market (CARICOM):
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Bahamas
- Belize
- Guyana
- Jamaica
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 2 and 4 only
- 2 3 and 5 only
- 1 4 and 5 only
- All of the above
Q.3) Logistic Performance Index 2023 recently released by
- World Trade Organization
- World Economic Forum
- World Bank
- UNCTAD
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 24th April 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 22nd April – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – d