IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography
Context: Egyptian President Abdel Fattah al-Sisi said Monday that revenues from the Suez Canal had “decreased by 40 to 50 percent” so far this year due to attacks on shipping by Yemen’s Houthi rebels.
Background:-
- The canal is one of the main sources of foreign currency for Egypt which is gripped by a severe financial crisis.
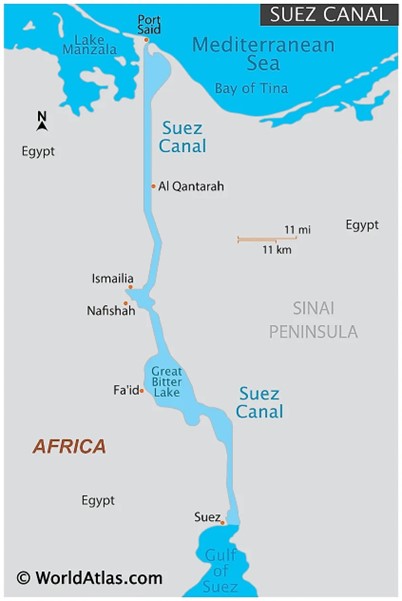
About Suez Canal:-
- The Suez Canal is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia.
- The 193.30-kilometre-long canal is a key trade route between Europe and Asia.
- It offers the shortest route between the Atlantic Ocean and lands around the Indian and western Pacific Oceans.
- The canal is one of the busiest waterways in the world, negating the need to navigate around the Cape of Good Hope in Africa and thus cutting distances by up to 7,000 km.
- Economic Lifeline: The canal continues to be the lifeline for all trade between the West and East as 12- 15 per cent of the global trade passes through it every year.
Suez Canal’s Long History
- The canal has existed in one form or the other since construction started under the reign of Senausret III, Pharao of Egypt (1887-1849 BC).
- Construction picked up pace around 300 years back as maritime trade between Europe and Asia became crucial for many economies.
- In the mid-1800s, French diplomat and engineer Ferdinand de Lesseps convinced the Egyptian viceroy Said Pasha to support the canal’s construction.
- In 1858, the Universal Suez Ship Canal Company was tasked to construct and operate the canal for 99 years, after which rights would be handed to the Egyptian government.
- Despite facing multiple problems ranging from financial difficulties and attempts by the British and Turks to halt construction, the canal was opened for international navigation in 1869.
- The French and British held most of the shares in the canal company. The British used their position to sustain their maritime and colonial interests by maintaining a defensive force along the Suez Canal Zone as part of a 1936 treaty.
Egypt takes over Suez Canal
- In 1954, facing pressure from Egyptian nationalists, the two countries signed a seven-year treaty that led to the withdrawal of British troops.
- In 1956, Egyptian President Abdel Nasser nationalised the Suez Canal to pay for the construction of a dam on the Nile. This led to the Suez Crisis with UK, France and Israel mounting an attack on Egypt.
- The conflict ended in 1957 after the United Nations got involved and was followed by the first instance of the UN Peacekeeping Forces being deployed anywhere in the world.
- In 1967, Nasser ordered the peacekeeping forces out of Sinai leading to a new conflict between the two countries. Israelis occupied Sinai and in response, Egypt closed the canal to all shipping.
- The closure lasted until 1975, when the two countries signed a disengagement accord. The canal was the focal point of the Arab-Israeli War of 1973, with the Arab coalition led by Egypt and Syria.
- Place in news:
Cape of Good Hope
- The Cape of Good Hope is a rocky headland on the Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula in South Africa.
- A common misconception is that the Cape of Good Hope is the southern tip of Africa.
- Contemporary geographic knowledge instead states the southernmost point of Africa is Cape Agulhas.
- When following the western side of the African coastline from the equator, however, the Cape of Good Hope marks the point where a ship begins to travel more eastward than southward.
Source: Reuters
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography
Context: The Israeli military said its air force on Monday struck targets of the militant Hezbollah group “deep inside Lebanon”.
Background:
- The strikes are among the deepest into Lebanon since the Israel-Hamas war began more than four months ago. They come a day after Israel’s Defense Minister vowed to step up attacks on Hezbollah even if a cease-fire is reached with Hamas in the Gaza Strip.
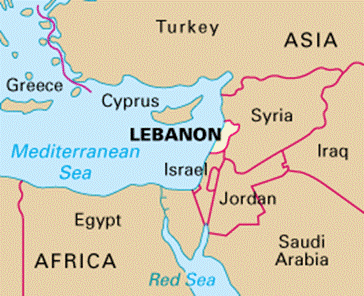
About Lebanon:
- Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia.
- It is bordered by Syria to the north and east, by Israel to the south, and by the Mediterranean Sea to the west.
- Lebanon’s capital and largest city is Beirut, followed by Tripoli and Jounieh.
- Lebanon is a founding member of the United Nations and of the Arab League and is a member of the Non-Aligned Movement and the Organization of Islamic Cooperation.
- The border with the Israeli-occupied Golan Heights is disputed by Lebanon in a small area called Shebaa Farms.
Source: Associated Press
Syllabus
- Prelims and Mains – Polity
Context: The Delhi High Court has recently stayed a single-judge order that had significant implications regarding property seized under the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA)
Background:
- The order in question held that if an investigation under the PMLA extends beyond 365 days without any related proceedings, the Enforcement Directorate (ED) must return the “seized” property to the owner. The court’s interpretation of the PMLA provisions aims to strike a balance between investigative powers and individual rights.
About Money laundering
- Money laundering is the process of concealing the origins of illegally obtained money, typically by passing it through a complex sequence of banking transfers or commercial transactions.
- The goal is to make the illicit funds appear legitimate and “clean.”
- Money laundering can involve various methods, including using shell companies, offshore accounts, and intricate financial transactions.
- The Prevention of Money-Laundering Act (PMLA) enacted in 2002 to prevent money laundering and provide for the confiscation of property derived from or involved in money laundering.
Objective of the Prevention of Money-Laundering Act (PMLA)
- The PMLA aims to prevent money laundering activities.
- It ensures the legality of financial transactions and promotes the integrity of financial systems.
Core Provisions:
- Offence of Money-Laundering: The act criminalizes disguising the origin of illegally gained money.
- Punishment: It prescribes penalties for money laundering.
- Attachment, Adjudication, and Confiscation: The act allows for the attachment of property involved in money laundering, adjudication by authorities, and the confiscation of such property.
- Obligations of Reporting Entities: Banking companies, financial institutions, and intermediaries have specific obligations under the act.
- Summonses, Searches, and Seizures: The act empowers authorities to conduct searches, seizures, and arrests related to money laundering cases.
- Appellate Tribunal and Special Courts: The act establishes an Appellate Tribunal and Special Courts for adjudication and appeals.
- The Enforcement Directorate (ED), operating under the Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance, is the primary authority responsible for investigating and prosecuting money laundering offenses under the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) at the national level.
Source: Times of India
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Event
Context: India and Japan have initiated a two-week military exercise.
Background:
- This exercise provides an opportunity for both nations to share best practices, develop inter-operability, and strengthen bilateral relations.
About The Dharma Guardian:
- The Dharma Guardian is an annual joint military exercise between the Indian Army and the Japan Ground Self Defence Force.
- The 5th edition of this exercise commenced on February 25, 2024, at the Mahajan Field Firing Ranges in Rajasthan, India.
- Inception: The exercise was initiated in 2018 as part of the growing bilateral defence cooperation between the two nations.
- Objective: The primary aim of Dharma Guardian is to enhance military interoperability and strengthen the strategic partnership between India and Japan.
- Alternating Locations: The exercise takes place alternately in India and Japan. It provides an opportunity for troops from both countries to train together, share best practices, and learn from each other.
- Focus Areas: During the exercise, soldiers engage in various tactical drills, including establishing temporary operating bases, conducting reconnaissance grids, setting up vehicle check posts, practicing cordon and search operations, and executing heliborne operations.
- Weapon Exhibition: Apart from the field exercises, there is also an exhibition of weapons and equipment. This showcases India’s ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’ initiative (self-reliant India) and highlights the country’s growing defence industrial capability.
- Mutual Benefits: Dharma Guardian fosters mutual understanding, interoperability, and camaraderie between the armed forces of India and Japan.
Source: Hindustan Times
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Event
Context: African Union imposes historic ban on cruel donkey skin trade.
Background:
- Demand for the animals’ skins is fuelled by the popularity of an ancient Chinese medicine called Ejiao, traditionally made from donkey hides.About two-thirds of world’s estimated population of 53 million donkeys are in Africa. People in the poorest, rural communities use them for transport and to carry water, food and other goods.Donkey slaughter for its skin has eroded livelihoods in Africa, robbing the continent of its culture, biodiversity and identity.
About African Union (AU)
- The African Union (AU), officially launched in 2002, is a continental body consisting of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa.
- It serves as the successor to the Organisation of African Unity (OAU), which was established from 1963 to 1999.
- The AU’s primary goal is to propel a united continent toward peace and prosperity.
- It supports political and economic integration among its 54 member nations, aiming to boost development, eradicate poverty, and bring Africa into the global economy.
- The AU’s secretariat, known as the African Union Commission, is based in Addis Ababa.
- The largest city within the AU is Lagos, Nigeria, while the largest urban agglomeration is Cairo, Egypt.
Source: BBC
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3
Context: A parliamentary panel raised concerns over the ineffective handling of plastic waste in the country, citing a report from the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG).
Background:
- Public Accounts Committee (PAC) in its 57-page report underlined the absence of effective measures that could save people from the hazards of plastic pollution.
About Plastic Pollution
- Plastic pollution refers to the accumulation of plastic waste in the environment, leading to negative impacts on ecosystems, wildlife, human health, and overall ecological balance.
Issues associated with plastic waste in India:
- Like much of the world, India is struggling to dispose of its growing quantities of plastic waste given how ubiquitous it has become-from our toothbrushes to debit cards. A little over 10,000 tonnes a day of plastic waste remains uncollected.
- India’s packaging industry is the biggest consumer of plastics. A 2020 study onpackaging in India projects a loss of almost 133 billion dollars’ worth of plastic material value over the next decade due to unsustainable packaging. Unsustainable packaging involves general packaging through single-use plastic.
- The popularity of online retail and food delivery apps, though restricted to big cities, is contributing to the rise in plastic waste. India’s biggest online delivery start-ups Swiggy and Zomato are each reportedly delivering about 28 million orders a month.
- Polluting plastics can affect the world’s tiniest organisms, such asWhen these organisms become poisoned due to plastic ingestion, this causes problems for the larger animals that depend on them for food. Larger items, such as plastic bags and straws, can choke and starve marine life, while smaller fragments (microplastics) can cause liver, reproductive, and gastrointestinal damage in animals and it can directly impact the blue economy as well.
- TheWorld Health Organisation published shocking research in 2018 that exposed the presence of microplastics in 90% of bottled water. Plastic toxicity in humans can lead to hormonal disruption and adverse reproductive and birth outcomes.
How is India addressing the concerns regarding plastic waste?
- India launched anationwide awareness campaign on single-use plastics on World Environment Day in June 2022. A mobile app for Single Use Plastics Grievance Redressal was also launched to empower citizens to check the sale/usage/manufacturing of SUP in their area and tackle the plastic menace.
- Plastic Waste Management Amendment Rules of 2022 prohibits the manufacture, import, stocking, distribution, sale, and use of several single-use plastic items as of July 1, 2022. It has also mandatedExtended Producer Responsibility (EPR) that incorporates circularity by making manufacturers of products responsible for collecting and processing their products upon the end of the product’s lifetime.
- India Plastics Pact is thefirst of its kind in Asia. The Plastics Pact is an ambitious and collaborative initiative to bring stakeholders together to reduce, reuse, and recycle plastics within the material’s value chain.
- Project REPLAN (stands for REducing PLastic in Nature)launched by the Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC) aims to reduce the consumption of plastic bags by providing a more sustainable alternative.
Sources : Times Of India
Practice MCQs
Q1.) Which among the following country rejoined African Union in 2017 despite some countries opposing it due to question over disputed territory of western sahara ?
- Algeria
- Botswana
- Morocco
- Mauritius
Q2.) Exercise Dharma Guardian is an annual joint military exercise between the Indian Army and the defence force of
- Maldives
- Australia
- France
- Japan
Q3.)With reference to the Prevention of Money-Laundering Act (PMLA), consider the following statements:
- The act criminalizes disguising the origin of illegally gained money.
- The act allows for the confiscation of property involved in money laundering.
- Enforcement Directorate (ED)is the primary authority responsible for investigating and prosecuting money laundering offenses under the PMLA.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 27th February 2024 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 26th February – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – a
Q.3) – c














