IASbaba Prelims 60 Days Plan, Rapid Revision Series (RaRe)
Archives
Hello Friends
The 60 Days Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series is IASbaba’s Flagship Initiative recommended by Toppers and loved by the aspirants’ community every year.
It is the most comprehensive program which will help you complete the syllabus, revise and practice tests on a daily basis. The Programme on a daily basis includes
Daily Prelims MCQs from Static (Monday – Saturday)
- Daily Static Quiz will cover all the topics of static subjects – Polity, History, Geography, Economics, Environment and Science and technology.
- 20 questions will be posted daily and these questions are framed from the topics mentioned in the schedule.
- It will ensure timely and streamlined revision of your static subjects.
Daily Current Affairs MCQs (Monday – Saturday)
- Daily 5 Current Affairs questions, based on sources like ‘The Hindu’, ‘Indian Express’ and ‘PIB’, would be published from Monday to Saturday according to the schedule.
Daily CSAT Quiz (Monday – Friday)
- CSAT has been an Achilles heel for many aspirants.
- Daily 5 CSAT Questions will be published.
Note – Daily Test of 20 static questions, 10 current affairs, and 5 CSAT questions. (35 Prelims Questions) in QUIZ FORMAT will be updated on a daily basis.
To Know More about 60 Days Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series – CLICK HERE
60 Day Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series Schedule – CLICK HERE
Important Note
- Comment your Scores in the Comment Section. This will keep you accountable, responsible and sincere in days to come.
- It will help us come out with the Cut-Off on a Daily Basis.
- Let us know if you enjoyed today’s test 🙂
- You can post your comments in the given format
- (1) Your Score
- (2) Matrix Meter
- (3) New Learning from the Test
Test-summary
0 of 35 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
Information
The following Test is based on the syllabus of 60 Days Plan-2023 for UPSC IAS Prelims 2022.
To view Solutions, follow these instructions:
- Click on – ‘Start Test’ button
- Solve Questions
- Click on ‘Test Summary’ button
- Click on ‘Finish Test’ button
- Now click on ‘View Questions’ button – here you will see solutions and links.
You have already completed the test before. Hence you can not start it again.
Test is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the test.
You have to finish following test, to start this test:
Results
0 of 35 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have scored 0 points out of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 35
1. Question
Consider the following statements with respect to the Indus Valley Civilization/Harappan Civilization:
- Imprint of a dog’s paw on a brick is found in Dholavira.
- Methods of field ploughing were in prevalence.
- Wells and canals were used to irrigate agricultural lands.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Incorrect Correct Correct Imprint of a dog’s paw on a brick is found in Chanhudaro. It is the only city without a citadel. Inkpot and lipstick is also found here. A Terracotta model of a bullock cart and Bronze toy cart is also found at Chanhudaro. Terracotta models of the plough have been found at sites in Cholistan and at Banawali (Haryana). Archaeologists have also found evidence of a ploughed field at Kalibangan (Rajasthan). Archaeologists have been able to reconstruct dietary practices from the finds of charred grains and seeds. These are studied by archaeo-botanists, who are specialists in ancient plant remains. Grains found at Harappan sites include wheat, barley, lentil, chickpea and sesame. Millets are found from sites in Gujarat. Finds of rice are relatively rare.
Traces of canals have been found at the Harappan site of Shortughai in Afghanistan, but not in Punjab or Sind. Therefore it can be said that wells and canals were used to irrigate agricultural lands.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Incorrect Correct Correct Imprint of a dog’s paw on a brick is found in Chanhudaro. It is the only city without a citadel. Inkpot and lipstick is also found here. A Terracotta model of a bullock cart and Bronze toy cart is also found at Chanhudaro. Terracotta models of the plough have been found at sites in Cholistan and at Banawali (Haryana). Archaeologists have also found evidence of a ploughed field at Kalibangan (Rajasthan). Archaeologists have been able to reconstruct dietary practices from the finds of charred grains and seeds. These are studied by archaeo-botanists, who are specialists in ancient plant remains. Grains found at Harappan sites include wheat, barley, lentil, chickpea and sesame. Millets are found from sites in Gujarat. Finds of rice are relatively rare.
Traces of canals have been found at the Harappan site of Shortughai in Afghanistan, but not in Punjab or Sind. Therefore it can be said that wells and canals were used to irrigate agricultural lands.
-
Question 2 of 35
2. Question
Consider the following pairs about Rig Vedic rivers:
Ancient names Modern names 1. Parushini Jhelum 2. Vipasha Beas 3. Askini Chenab How many of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
Correct
Solution (b)
- Parushini
- Vipasha
- Askini
Incorrect Correct Correct Parushini – Ravi Vipasha – Beas Askini – Chenab Note:
Ancient Names Modern Names Kubhu Kubha
Vitasta
Askini
Purushni
Shatudri
Vipasha
Sadanira
Drishdvati
Gomti
Suwastu
Sindhu
Kurram Kabul
Jhelum
Chenab
Ravi
Satluj
Beas
Gandak
Ghaggar
Gomal/Gomati
Swat
Indus
There is a verse in Nadistuti sukta of Rigveda, hymn of praise of rivers which mentions the following 10 rivers: Ganga, Yamuna, Saraswati, Sutudri, Parusni, Asikni, Marudvrdha, Vitasta, Arjikiya, Susoma.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
- Parushini
- Vipasha
- Askini
Incorrect Correct Correct Parushini – Ravi Vipasha – Beas Askini – Chenab Note:
Ancient Names Modern Names Kubhu Kubha
Vitasta
Askini
Purushni
Shatudri
Vipasha
Sadanira
Drishdvati
Gomti
Suwastu
Sindhu
Kurram Kabul
Jhelum
Chenab
Ravi
Satluj
Beas
Gandak
Ghaggar
Gomal/Gomati
Swat
Indus
There is a verse in Nadistuti sukta of Rigveda, hymn of praise of rivers which mentions the following 10 rivers: Ganga, Yamuna, Saraswati, Sutudri, Parusni, Asikni, Marudvrdha, Vitasta, Arjikiya, Susoma.
-
Question 3 of 35
3. Question
Consider the following statements about potteries of India:
- Only geometrical patterns were painted on Harappan pottery.
- Ochre colored pottery was found at sites in the upper Ganga Valley of India.
- Glazed Pottery came into being with the advent of Arab influence.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Incorrect Correct Correct Geometrical patterns, circles, squares and triangles and figures of animals, birds, snakes or fish are frequent motifs found in Harappan pottery. The Ochre Coloured Pottery culture (OCP) is a 2nd millennium BC Bronze Age culture of the Indo-Gangetic Plain, extending from eastern Punjab to northeastern Rajasthan and western Uttar Pradesh. It is considered a candidate for association with the early Indo-Aryan or Vedic culture. The pottery had a red slip but gave off an ochre color on the fingers of archaeologists who excavated it, hence the name. It was sometimes decorated with black painted bands and incised patterns. The phase of glazed pottery started in the 12th century AD, when Turkic Muslim rulers encouraged potters from Persia, Central Asia and elsewhere. Incorrect
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Incorrect Correct Correct Geometrical patterns, circles, squares and triangles and figures of animals, birds, snakes or fish are frequent motifs found in Harappan pottery. The Ochre Coloured Pottery culture (OCP) is a 2nd millennium BC Bronze Age culture of the Indo-Gangetic Plain, extending from eastern Punjab to northeastern Rajasthan and western Uttar Pradesh. It is considered a candidate for association with the early Indo-Aryan or Vedic culture. The pottery had a red slip but gave off an ochre color on the fingers of archaeologists who excavated it, hence the name. It was sometimes decorated with black painted bands and incised patterns. The phase of glazed pottery started in the 12th century AD, when Turkic Muslim rulers encouraged potters from Persia, Central Asia and elsewhere. -
Question 4 of 35
4. Question
Consider the following statements regarding the Rig Vedic period:
- Habitation was mostly confined to the Indus region.
- Kula was the basic unit of political organization.
- Sabha was a general assembly of the entire people, while Samiti was a council of the elders.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Correct Incorrect During the Rig Vedic period, the Aryans were mostly confined to the Indus region. The Rig Veda refers to ‘Saptasindhu’ or the land of seven rivers. The basic unit of political organization was Kula or family. Several families joined together on the basis of their kinship to form a village or Grama. The Rig Vedic polity was normally monarchical and the succession was hereditary. The king was assisted by the Purohita or the priest and the Senani or the commander of the army in his administration. There were two popular bodies, called the Sabha and the Samiti. The former seems to have been a council of the elders and the latter, a general assembly of the entire people. Incorrect
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Correct Incorrect During the Rig Vedic period, the Aryans were mostly confined to the Indus region. The Rig Veda refers to ‘Saptasindhu’ or the land of seven rivers. The basic unit of political organization was Kula or family. Several families joined together on the basis of their kinship to form a village or Grama. The Rig Vedic polity was normally monarchical and the succession was hereditary. The king was assisted by the Purohita or the priest and the Senani or the commander of the army in his administration. There were two popular bodies, called the Sabha and the Samiti. The former seems to have been a council of the elders and the latter, a general assembly of the entire people. -
Question 5 of 35
5. Question
Consider the following statements:
- The domestication of animals began in the Neolithic period.
- Cultivation of cereals first started in the Neolithic age.
- The main characteristic of the Neolithic period was large stone tools.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Correct Incorrect Adamgargh in Madhya Pradesh & Bagor in Rajasthan which are the neolithic sites has given the earliest evidence of the domestication of animals.It is a time period from which settled agriculture also began as a norm. The Neolithic age is associated with innovations in stone tool technology, specifically the making of ground, pecked, and polished stone tools and the advent of food production. Cultivation of cereals first started in the Neolithic age.
Stone tools found during Neolithic period are generally tiny and are called Microliths. Note:
- Gordon Childe defined the Neolithic-Chalcolithic culture as a self-sufficient food-producing economy.
- Domestication of plants and animals has been considered one of the main characteristic features of the Neolithic stage of culture. The beginnings of this stage of human culture are revealed by a new type of stone tools which are called Neolithic tools or tools of the New Stone Age.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Correct Incorrect Adamgargh in Madhya Pradesh & Bagor in Rajasthan which are the neolithic sites has given the earliest evidence of the domestication of animals.It is a time period from which settled agriculture also began as a norm. The Neolithic age is associated with innovations in stone tool technology, specifically the making of ground, pecked, and polished stone tools and the advent of food production. Cultivation of cereals first started in the Neolithic age.
Stone tools found during Neolithic period are generally tiny and are called Microliths. Note:
- Gordon Childe defined the Neolithic-Chalcolithic culture as a self-sufficient food-producing economy.
- Domestication of plants and animals has been considered one of the main characteristic features of the Neolithic stage of culture. The beginnings of this stage of human culture are revealed by a new type of stone tools which are called Neolithic tools or tools of the New Stone Age.
-
Question 6 of 35
6. Question
Consider the following statements with reference to trade in Harappan Civilisation:
- Trade was generally, based on the exchange of goods without the use of money.
- Harappans did not have knowledge of the sea.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Incorrect The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC) was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form from 2600 BCE to 1900 BCE. The Harappans carried on a considerable trade in stone, metal, shell, etc., within the Indus culture zone. However, the cities did not possess basic raw materials for the commodities they produced. In return for finished goods and possibly food grains, they procured metals from the neighboring areas by boats and bullock-carts.
Metal money was not used and trade was carried by barter systems.
The Harappan people used to trade with foreign lands traveling through seas. They practised navigation on the coast of the Arabian Sea. The Harappan seal that was recovered from excavation indicates a mast & sail boat while the Mohenjo-Daro seal & a terracotta amulet show a ship with cabins & birds. Dockyard and Clay model boats were found from excavations at Lothal which was the port city of Harappan period. Incorrect
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Incorrect The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC) was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form from 2600 BCE to 1900 BCE. The Harappans carried on a considerable trade in stone, metal, shell, etc., within the Indus culture zone. However, the cities did not possess basic raw materials for the commodities they produced. In return for finished goods and possibly food grains, they procured metals from the neighboring areas by boats and bullock-carts.
Metal money was not used and trade was carried by barter systems.
The Harappan people used to trade with foreign lands traveling through seas. They practised navigation on the coast of the Arabian Sea. The Harappan seal that was recovered from excavation indicates a mast & sail boat while the Mohenjo-Daro seal & a terracotta amulet show a ship with cabins & birds. Dockyard and Clay model boats were found from excavations at Lothal which was the port city of Harappan period. -
Question 7 of 35
7. Question
With reference to craft making in the Indus Valley Civilization, consider the following statements:
- Crafts were made up of natural stones and clay only.
- Shell obtained from coastal areas was used to make bangles.
- The city of Chanhudaro was famous for bead making.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Incorrect Correct Correct Stones like carnelian (of a beautiful red color), jasper, crystal, quartz and steatite were used; metals like copper, bronze and gold; and shell, faience and terracotta or burnt clay were used for craft making. Nageshwar and Balakot settlements are near the coast. These were specialized centers for making shell objects – including bangles. Chanhudaro is almost exclusively devoted to craft production, including bead-making, shell-cutting, metal-working, seal-making and weight-making. Incorrect
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Incorrect Correct Correct Stones like carnelian (of a beautiful red color), jasper, crystal, quartz and steatite were used; metals like copper, bronze and gold; and shell, faience and terracotta or burnt clay were used for craft making. Nageshwar and Balakot settlements are near the coast. These were specialized centers for making shell objects – including bangles. Chanhudaro is almost exclusively devoted to craft production, including bead-making, shell-cutting, metal-working, seal-making and weight-making. -
Question 8 of 35
8. Question
Which of the following statements highlights the social differences among the people of the Indus Valley Civilization?
- Burial patterns showed differences in ideology or social strata.
- Luxury items were found in all towns and settlements.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Correct
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Incorrect Archaeologists used certain strategies to find out whether there were social or economic differences amongst the people living within a particular culture. These include studying burials. Some graves contain pottery and ornaments, perhaps indicating a belief that these could be used in the after-life. In Lothal, the graves sometimes had the presence of the bones of two individuals. It has been suggested that it is likely the evidence of sati.
At Mohenjo-Daro, also referred to as the mound of the dead, baskets of bones and a single skull were also found in different houses.
At Sukotda, many animal remains were found, majorly consisting of cattle like sheep and goats along with horses and dogs.
Jewelry has been found in burials of both men and women. Archaeologists assume objects were luxuries if they are rare or made from costly, non-local materials or with complicated technologies. Rare objects, made of valuable materials (luxury goods), are generally concentrated in large settlements, like Mohenjo Daro and Harappa, and are rarely found in the smaller settlements. Incorrect
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Incorrect Archaeologists used certain strategies to find out whether there were social or economic differences amongst the people living within a particular culture. These include studying burials. Some graves contain pottery and ornaments, perhaps indicating a belief that these could be used in the after-life. In Lothal, the graves sometimes had the presence of the bones of two individuals. It has been suggested that it is likely the evidence of sati.
At Mohenjo-Daro, also referred to as the mound of the dead, baskets of bones and a single skull were also found in different houses.
At Sukotda, many animal remains were found, majorly consisting of cattle like sheep and goats along with horses and dogs.
Jewelry has been found in burials of both men and women. Archaeologists assume objects were luxuries if they are rare or made from costly, non-local materials or with complicated technologies. Rare objects, made of valuable materials (luxury goods), are generally concentrated in large settlements, like Mohenjo Daro and Harappa, and are rarely found in the smaller settlements. -
Question 9 of 35
9. Question
It is an ancient Indus Valley civilization site in Rajasthan, India’s westernmost state. The site has both pre-Harappan and Harappan remains, and the transition between the two cultures may be witnessed there. It is also said to have been founded in the geographical triangle formed by the confluence of the Drishadvati and Saraswati Rivers.
The above statement describes which of the following towns of the Indus Valley civilization?
Correct
Solution (b)
Kalibangan:
- The location Kalibangan – meaning ‘black bangles’ – gets its name from the dense dispersion of black bangle shards discovered on the surface of its mounds.
- Only the lowest layers of the western mound have shown signs of pre-Harappan civilization.
- The Indus Valley civilization flourished at the site from the proto-Harappan (3500 BC – 2500 BC) through the Harappan (2500 BC – 1750 BC), according to archaeological findings.
- Although the pre-Harappan civilization worked with copper and made pottery, it lacked a written language, and its ruins lack the regular arrangement and use of baked brick observed in later Harappan sites. A cemetery and a fortified castle are among the Harappan ruins.
- Kalibangan has also provided proof of the world’s first documented “Earthquake.”
- The earthquake, which occurred around 2600 BC, is thought to have led to the collapse of the Indus Valley Civilization.
- The discovery of fire altars at Kalibangan reveals that the locals were ritualistic and believed in fire worship.
- Luigi Pio Tessitori, an Italian Indologist and linguist, found the Kalibangan site.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Kalibangan:
- The location Kalibangan – meaning ‘black bangles’ – gets its name from the dense dispersion of black bangle shards discovered on the surface of its mounds.
- Only the lowest layers of the western mound have shown signs of pre-Harappan civilization.
- The Indus Valley civilization flourished at the site from the proto-Harappan (3500 BC – 2500 BC) through the Harappan (2500 BC – 1750 BC), according to archaeological findings.
- Although the pre-Harappan civilization worked with copper and made pottery, it lacked a written language, and its ruins lack the regular arrangement and use of baked brick observed in later Harappan sites. A cemetery and a fortified castle are among the Harappan ruins.
- Kalibangan has also provided proof of the world’s first documented “Earthquake.”
- The earthquake, which occurred around 2600 BC, is thought to have led to the collapse of the Indus Valley Civilization.
- The discovery of fire altars at Kalibangan reveals that the locals were ritualistic and believed in fire worship.
- Luigi Pio Tessitori, an Italian Indologist and linguist, found the Kalibangan site.
-
Question 10 of 35
10. Question
Which among the following was/were the impact of the invention of Iron in ancient India?
- In the Ganges Valley and in the Malwa region iron led to the rise of urban areas.
- It lead to the conversion of tribal culture to Urban and imperial Mahajanapadas.
- It led to the establishment of Black and Red ware culture.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Correct Incorrect Iron brought in a change of agriculture economy. Iron brought advanced types of agriculture. In the Ganges Valley and in the Malwa region iron led to the rise of urban areas. Both Brahmanical and Buddhist texts have reference to cities at sites like Sravasti and Ujjayini with evidence of Iron Age urbanization.
Use of Iron was sparse in the beginning but by the middle of the 6th century BC it had become fairly common and was associated with the new Northern Black Polished Ware culture. Due to the discovery of iron, agriculture became the chief occupation and knowledge of manure was increased. They traded with far countries like Babylon. A class of hereditary merchants (vaniya) came into existence and this way the tribal culture was moreover converted to urban and imperial Mahajanapadas. Use of Iron was sparse in the beginning but by the middle of the 6th century BC it had become fairly common and was associated with the new Northern Black Polished Ware culture. Note:
- Use of Iron led to transition of the Janapadas or tribal kingdoms of the Vedic period to the sixteen Mahajanapadas.
- The earliest Iron Age sites in South India are Hallur, Karnataka and Adichanallur, Tamil Nadu at around 1000 BCE.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Correct Incorrect Iron brought in a change of agriculture economy. Iron brought advanced types of agriculture. In the Ganges Valley and in the Malwa region iron led to the rise of urban areas. Both Brahmanical and Buddhist texts have reference to cities at sites like Sravasti and Ujjayini with evidence of Iron Age urbanization.
Use of Iron was sparse in the beginning but by the middle of the 6th century BC it had become fairly common and was associated with the new Northern Black Polished Ware culture. Due to the discovery of iron, agriculture became the chief occupation and knowledge of manure was increased. They traded with far countries like Babylon. A class of hereditary merchants (vaniya) came into existence and this way the tribal culture was moreover converted to urban and imperial Mahajanapadas. Use of Iron was sparse in the beginning but by the middle of the 6th century BC it had become fairly common and was associated with the new Northern Black Polished Ware culture. Note:
- Use of Iron led to transition of the Janapadas or tribal kingdoms of the Vedic period to the sixteen Mahajanapadas.
- The earliest Iron Age sites in South India are Hallur, Karnataka and Adichanallur, Tamil Nadu at around 1000 BCE.
-
Question 11 of 35
11. Question
Which one of the following statements is not true about the Chalcolithic cultures of India?
Correct
Solution (d)
a) b) c) d) Correct Correct Correct Incorrect The people were mostly rural and lived near hills and rivers. The Chalcolithic culture corresponds to the farming communities, namely Kayatha, Ahar or Banas, Malwa, and Jorwe. The first metal age of India is called the Chalcolithic Age which saw the use of copper along with the stone. It was also called Stone-Copper Age. Along with the use of copper and stone, these people also used low-grade bronze to make tools and weapons. This culture was also seen in the Pre-Harappan phase, but at most places, the Chalcolithic culture appeared in the Post-Harappan phase. It was mainly found in South-Eastern Rajasthan, the Western part of Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra, and in South and East India. Incorrect
Solution (d)
a) b) c) d) Correct Correct Correct Incorrect The people were mostly rural and lived near hills and rivers. The Chalcolithic culture corresponds to the farming communities, namely Kayatha, Ahar or Banas, Malwa, and Jorwe. The first metal age of India is called the Chalcolithic Age which saw the use of copper along with the stone. It was also called Stone-Copper Age. Along with the use of copper and stone, these people also used low-grade bronze to make tools and weapons. This culture was also seen in the Pre-Harappan phase, but at most places, the Chalcolithic culture appeared in the Post-Harappan phase. It was mainly found in South-Eastern Rajasthan, the Western part of Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra, and in South and East India. -
Question 12 of 35
12. Question
Which of the following statements is/are incorrect with reference to Indus Valley Civilization?
- The Indus-Valley people were using both cotton and wool.
- Sacrifices and ritual offering constituted the main religions practices.
- Indus civilization developed the Devanagari script for writing.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Incorrect Incorrect The Indus-Valley people were well acquainted with the use of cotton and wool. The numerous specimens of pottery, seals, bracelets etc. reveal that arts and crafts flourished. Sacrifices and ritual offerings was not a main religious practice during Indus Valley Civilization. This concept was more prevelant during Rig Vedic period.
The Rigvedic practices of sacrifices included sheep, cows, buffaloes, men and horses. Men and horses were considered to have the greatest value. Offerings comprised of cow products like milk and butter and grains which were boiled, fried or made into flour balls.
Devanagari script was not related with this civilization and developed much later. Note:
John Marshall was the first scholar to use the term Indus civilization. Numerous seals have been discovered with inscriptions of the figures of animals and names in a script which is undecipherable.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Incorrect Incorrect The Indus-Valley people were well acquainted with the use of cotton and wool. The numerous specimens of pottery, seals, bracelets etc. reveal that arts and crafts flourished. Sacrifices and ritual offerings was not a main religious practice during Indus Valley Civilization. This concept was more prevelant during Rig Vedic period.
The Rigvedic practices of sacrifices included sheep, cows, buffaloes, men and horses. Men and horses were considered to have the greatest value. Offerings comprised of cow products like milk and butter and grains which were boiled, fried or made into flour balls.
Devanagari script was not related with this civilization and developed much later. Note:
John Marshall was the first scholar to use the term Indus civilization. Numerous seals have been discovered with inscriptions of the figures of animals and names in a script which is undecipherable.
-
Question 13 of 35
13. Question
Consider the following statements about the culture of Indus Valley Civilization:
- Livestock breeding was unknown in Indus civilization.
- Evidence of Elephant domestication is found.
- Camels, though rarely, were domesticated for long travels.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Incorrect Correct Correct Livestock breeding was a known and important practice in Indus culture. Animals were of the utmost importance to the Indus Valley Civilisation, with cows and buffaloes being their coveted animals. However, sheep, grazing goats, cats, and dogs were also domesticated. The animals were slaughtered for festive foods or to complement available food during failed or limited harvests. They were offered as gifts to the kin and traded with pastoralists in the expectation of generous return gifts or bartered for stored grain.
Sheep, goats, dogs, humped cattle, buffalo and elephants were domesticated. These were their coveted animals. One of the few elephant figurines from Harappa is a head with large stylized ears and red and white stripes painted across the face. Another elephant figurine has an undecorated head with two flat ears and a trunk (all broken) on a round hollow body.
The camel was rare and the horse was not known. Camel bones are known from late levels of a few sites, particularly in Gujarat, and have mainly been identified as the single-humped Arabian camel (dromedary). Current evidence suggests this was not domesticated until much later, but the people of Oman, with whom the Harappans traded, exploited wild dromedaries, so the Harappans may have obtained camel bones, meat or even captive wild camels from there.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Incorrect Correct Correct Livestock breeding was a known and important practice in Indus culture. Animals were of the utmost importance to the Indus Valley Civilisation, with cows and buffaloes being their coveted animals. However, sheep, grazing goats, cats, and dogs were also domesticated. The animals were slaughtered for festive foods or to complement available food during failed or limited harvests. They were offered as gifts to the kin and traded with pastoralists in the expectation of generous return gifts or bartered for stored grain.
Sheep, goats, dogs, humped cattle, buffalo and elephants were domesticated. These were their coveted animals. One of the few elephant figurines from Harappa is a head with large stylized ears and red and white stripes painted across the face. Another elephant figurine has an undecorated head with two flat ears and a trunk (all broken) on a round hollow body.
The camel was rare and the horse was not known. Camel bones are known from late levels of a few sites, particularly in Gujarat, and have mainly been identified as the single-humped Arabian camel (dromedary). Current evidence suggests this was not domesticated until much later, but the people of Oman, with whom the Harappans traded, exploited wild dromedaries, so the Harappans may have obtained camel bones, meat or even captive wild camels from there.
-
Question 14 of 35
14. Question
In which of the following characteristics the Indus valley civilization differed from its contemporary Mesopotamia civilization?
- The use of baked bricks in the Mesopotamia cities was absent, however, it was used to a large extent in Harappan cities.
- Harappans domesticated elephants which was not the case with Mesopotamians
- Large number of temples/religious buildings were found in Harappan cities which were predominantly absent in Mesopotamian culture.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Incorrect Correct Incorrect The use of burnt bricks in the Harappan cities is remarkable because in the contemporary buildings of Egypt dried bricks were primarily used. We find the use of baked bricks in contemporary Mesopotamia, but they were used to a much larger extent in the Harappan cities. Elephants were well known to the Harappans, who were also acquainted with the rhinoceros. The contemporary Sumerian cities in Mesopotamia produced virtually the same food grains and domesticated the same animals as did the Harappans, but the Harappans in Gujarat produced rice and domesticated elephants which was not the case with the Mesopotamians. In sharp contrast to Egypt and Mesopotamia, no temples have been found at any Harappan site. No religious structures of any kind have been excavated apart from the great bath, which may have been used for ablution. It would, therefore, be wrong to think that priests ruled in Harappa as they did in the cities of lower Mesopotamia. Incorrect
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Incorrect Correct Incorrect The use of burnt bricks in the Harappan cities is remarkable because in the contemporary buildings of Egypt dried bricks were primarily used. We find the use of baked bricks in contemporary Mesopotamia, but they were used to a much larger extent in the Harappan cities. Elephants were well known to the Harappans, who were also acquainted with the rhinoceros. The contemporary Sumerian cities in Mesopotamia produced virtually the same food grains and domesticated the same animals as did the Harappans, but the Harappans in Gujarat produced rice and domesticated elephants which was not the case with the Mesopotamians. In sharp contrast to Egypt and Mesopotamia, no temples have been found at any Harappan site. No religious structures of any kind have been excavated apart from the great bath, which may have been used for ablution. It would, therefore, be wrong to think that priests ruled in Harappa as they did in the cities of lower Mesopotamia. -
Question 15 of 35
15. Question
Arrange the following ancient cultures in chronological order:
- Northern Black Polished Ware culture (NBPW)
- Ochre Coloured Pottery Ware culture
- The Painted Grey Ware culture
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
Correct
Solution (d)
2 3 1 OCPW (2600 BCE – 1200 BCE) PGW (1100 BCE – 800 BCE) NBPW ( 700 BCE – 200 BCE) Ochre Coloured Pottery Ware culture is found in northern India dating to the Chalcolithic period. The OCP pottery has red slip and appears ochre in colour. The OCP culture dates to 2600- 1200 BCE and is found in the Indo-Gangetic plain and may have had some associations with early Vedic culture. The Iron Age in North India coincides with the Painted Grey Ware culture. The painted grey ware is dated to from 1100 to 800 BCE. The Painted Grey Ware cultural phase is followed by Northern Black Polished Ware culture (NBPW), which is associated with the Mahajanapada and Mauryan periods. Incorrect
Solution (d)
2 3 1 OCPW (2600 BCE – 1200 BCE) PGW (1100 BCE – 800 BCE) NBPW ( 700 BCE – 200 BCE) Ochre Coloured Pottery Ware culture is found in northern India dating to the Chalcolithic period. The OCP pottery has red slip and appears ochre in colour. The OCP culture dates to 2600- 1200 BCE and is found in the Indo-Gangetic plain and may have had some associations with early Vedic culture. The Iron Age in North India coincides with the Painted Grey Ware culture. The painted grey ware is dated to from 1100 to 800 BCE. The Painted Grey Ware cultural phase is followed by Northern Black Polished Ware culture (NBPW), which is associated with the Mahajanapada and Mauryan periods. -
Question 16 of 35
16. Question
Which of the following Archaeological Sites belong to the Paleolithic age?
- Bhimbetka
- Hunsgi
- Kurnool caves
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
Correct
Solution (d)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Correct Correct Bhimbetka in present-day Madhya Pradesh. The word ‘Bhimbetka’, derived from ‘Bhim Baitka’. These caves are named after ‘Bhima’, one of the five Pandavas of Mahabharata. Bhimbetka simply means “sitting place of Bhima”.
Hunsgi is located in Karnataka. On this site, many stone tools, and weapons that are made of reddish-brown chert are found. The tools found include longish blades and many other instruments for multi-purpose usage. Most of the tools were made of limestone. Kurnool Caves are located in present-day Andhra Pradesh. Traces of ashes have been found in the Kurnool caves. This shows that the people who lived there knew the use of fire. Fire might have been used for many things such as to cook meat, to get light, and to protect against animals.
Incorrect
Solution (d)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Correct Correct Bhimbetka in present-day Madhya Pradesh. The word ‘Bhimbetka’, derived from ‘Bhim Baitka’. These caves are named after ‘Bhima’, one of the five Pandavas of Mahabharata. Bhimbetka simply means “sitting place of Bhima”.
Hunsgi is located in Karnataka. On this site, many stone tools, and weapons that are made of reddish-brown chert are found. The tools found include longish blades and many other instruments for multi-purpose usage. Most of the tools were made of limestone. Kurnool Caves are located in present-day Andhra Pradesh. Traces of ashes have been found in the Kurnool caves. This shows that the people who lived there knew the use of fire. Fire might have been used for many things such as to cook meat, to get light, and to protect against animals.
-
Question 17 of 35
17. Question
Under Harappan civilization, which of the following animals is not depicted on the Pashupati Seal?
Correct
Solution (d)
Pashupati Seal:
- Archaeologists have discovered thousands of seals, the most remarkable seal is the one depicted with a figure in the center and animals around.
- This seal is generally identified as the Pashupati Seal by some scholars whereas some identify it as the female deity.
- This seal depicts a human figure seated cross legged.
- An elephant and a tiger are depicted to the right side of the seated figure, while on the left a rhinoceros and a buffalo are seen.
- In addition to these animals two antelopes are shown below the seat.
Incorrect
Solution (d)
Pashupati Seal:
- Archaeologists have discovered thousands of seals, the most remarkable seal is the one depicted with a figure in the center and animals around.
- This seal is generally identified as the Pashupati Seal by some scholars whereas some identify it as the female deity.
- This seal depicts a human figure seated cross legged.
- An elephant and a tiger are depicted to the right side of the seated figure, while on the left a rhinoceros and a buffalo are seen.
- In addition to these animals two antelopes are shown below the seat.
-
Question 18 of 35
18. Question
Which among the following places has given the earliest evidence of agriculture in the Indian Subcontinent?
Correct
Solution (b)
Mehrgarh:
- It is a Neolithic age site that was located near the Bolan Pass on the Kacchi Plains of Balochistan, Pakistan.
- Mehrgarh is situated near the west of the river Indus and between the present-day Pakistani cities of Sibi, Kalat, and Quetta.
- The earliest evidence of farming on this site has been suggesting that a civilization existed in the site of Mehrgarh as early as 7000 BCE which is 3500 years before the Harappan Civilization.
- This site discovered the new shed light on the development of agricultural technologies and the agrarian lifestyles of the ancient stone age people of South Asia.
- The site was discovered in 1974 by an Archaeological Team directed by French archaeologists Catherine Jarrige, and Jean-François Jarrige and was excavated continuously between 1974 and 1986, and again from 1997 to 2000.
- The Archaeological Survey of India Digs has unearthed some of the earliest evidence of Agricultural Farming and Husbandry in that region.
- Mehrgarh was influenced by the nearby site of the Eastern Neolithic Sites, with similarities between pottery, early phases of farming, domesticated wheat varieties, other archaeological artifacts, some domesticated herd animals and plants.
- The earliest farming in the area was developed by semi-Nomadic people using plants such as Barley and Wheat. Animals such as Cattle, Goats, and Sheep.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Mehrgarh:
- It is a Neolithic age site that was located near the Bolan Pass on the Kacchi Plains of Balochistan, Pakistan.
- Mehrgarh is situated near the west of the river Indus and between the present-day Pakistani cities of Sibi, Kalat, and Quetta.
- The earliest evidence of farming on this site has been suggesting that a civilization existed in the site of Mehrgarh as early as 7000 BCE which is 3500 years before the Harappan Civilization.
- This site discovered the new shed light on the development of agricultural technologies and the agrarian lifestyles of the ancient stone age people of South Asia.
- The site was discovered in 1974 by an Archaeological Team directed by French archaeologists Catherine Jarrige, and Jean-François Jarrige and was excavated continuously between 1974 and 1986, and again from 1997 to 2000.
- The Archaeological Survey of India Digs has unearthed some of the earliest evidence of Agricultural Farming and Husbandry in that region.
- Mehrgarh was influenced by the nearby site of the Eastern Neolithic Sites, with similarities between pottery, early phases of farming, domesticated wheat varieties, other archaeological artifacts, some domesticated herd animals and plants.
- The earliest farming in the area was developed by semi-Nomadic people using plants such as Barley and Wheat. Animals such as Cattle, Goats, and Sheep.
-
Question 19 of 35
19. Question
Consider the following statements regarding the sites of Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC):
- Chanhudaro was a city without citadel.
- Dholavira city was divided into three parts.
- Rakhigarhi is the largest Indian site of IVC.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Correct Correct Chanhudaro is an archaeological site belonging to the Indus Valley Civilization. The site is located 130 kilometers south of Mohenjodaro, in Sindh, Pakistan. The settlement was inhabited between 4000 and 1700 BCE and is considered to have been a center for manufacturing carnelian beads. This site is a group of three low mounds that excavations have shown were parts of a single settlement, approximately 5 hectares in size. Chanhudaro was the only city without a citadel in the Indus Valley civilization. The city of Dholavira was located on Khadir Beyt in the Rann of Kutch, where there was fresh water and fertile soil. Unlike some of the other Harappan cities, which were divided into two parts, Dholavira was divided into three parts, and each part was surrounded with massive stone walls, with entrances through gateways. There was also a large open area in the settlement, where public ceremonies could be held. Rakhigarhi is the site of a pre-Indus Valley Civilisation settlement going back to about 6500 BCE. Later, it was also part of the mature Indus Valley Civilisation, dating to 2600-1900 BCE. The site is located in the Saraswati/Ghaggar-Hakra River plain, some 27 km from the seasonal Ghaggar river. Rakhigarhi is the largest Indian site of IVC. Incorrect
Solution (c)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Correct Correct Chanhudaro is an archaeological site belonging to the Indus Valley Civilization. The site is located 130 kilometers south of Mohenjodaro, in Sindh, Pakistan. The settlement was inhabited between 4000 and 1700 BCE and is considered to have been a center for manufacturing carnelian beads. This site is a group of three low mounds that excavations have shown were parts of a single settlement, approximately 5 hectares in size. Chanhudaro was the only city without a citadel in the Indus Valley civilization. The city of Dholavira was located on Khadir Beyt in the Rann of Kutch, where there was fresh water and fertile soil. Unlike some of the other Harappan cities, which were divided into two parts, Dholavira was divided into three parts, and each part was surrounded with massive stone walls, with entrances through gateways. There was also a large open area in the settlement, where public ceremonies could be held. Rakhigarhi is the site of a pre-Indus Valley Civilisation settlement going back to about 6500 BCE. Later, it was also part of the mature Indus Valley Civilisation, dating to 2600-1900 BCE. The site is located in the Saraswati/Ghaggar-Hakra River plain, some 27 km from the seasonal Ghaggar river. Rakhigarhi is the largest Indian site of IVC. -
Question 20 of 35
20. Question
Which one of the following is not a Harappan site?
Correct
Solution (c)
Sohagaura is an Ashokan era copper plate inscription written in Prakrit in the Brahmi script.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Sohagaura is an Ashokan era copper plate inscription written in Prakrit in the Brahmi script.
-
Question 21 of 35
21. Question
Consider the following statements about Zika Virus:
- It is transmitted to people through the bite of an infected mosquito from the Aedes genus that transmits dengue, chikungunya, and yellow fever.
- It can migrate between humans through sexual contact and an infected mother can pass on the virus to her newborn during birth.
- There is no specific treatment or vaccine available for Zika virus infection or disease.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
- Zika Virus is transmitted to people through the bite of an infected mosquito from the Aedes genus that transmits dengue, chikungunya, and yellow fever. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- It is a mosquito-borne virus first identified in Uganda in 1947 in a Rhesus macaque monkey.
- It can migrate between humans through sexual contact and an infected mother can pass on the virus to her newborn during birth. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- Most people with Zika virus infection do not develop symptoms. People who develop symptoms of Zika virus infections have similar symptoms to other arbovirus infections such as dengue. (Arbovirus infections– infections caused by a group of viruses spread to people by the bite of infected arthropods (insects) such as mosquitoes and ticks) Some of the common symptoms are fever, skin rashes, conjunctivitis, muscle and joint pain malaise, and headache.
- There is no specific treatment or vaccine available for Zika virus infection or disease. Hence statement 3 is correct.
- People with symptoms such as rash, fever, or joint pain should get plenty of rest, drink fluids, and treat symptoms with antipyretics and/or analgesics.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
- Zika Virus is transmitted to people through the bite of an infected mosquito from the Aedes genus that transmits dengue, chikungunya, and yellow fever. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- It is a mosquito-borne virus first identified in Uganda in 1947 in a Rhesus macaque monkey.
- It can migrate between humans through sexual contact and an infected mother can pass on the virus to her newborn during birth. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- Most people with Zika virus infection do not develop symptoms. People who develop symptoms of Zika virus infections have similar symptoms to other arbovirus infections such as dengue. (Arbovirus infections– infections caused by a group of viruses spread to people by the bite of infected arthropods (insects) such as mosquitoes and ticks) Some of the common symptoms are fever, skin rashes, conjunctivitis, muscle and joint pain malaise, and headache.
- There is no specific treatment or vaccine available for Zika virus infection or disease. Hence statement 3 is correct.
- People with symptoms such as rash, fever, or joint pain should get plenty of rest, drink fluids, and treat symptoms with antipyretics and/or analgesics.
-
Question 22 of 35
22. Question
Consider the following statements regarding the Financial Action Task Force (FATF):
- It was established as an intergovernmental body by the World Trade Organisation.
- It leads global action to tackle money laundering, terrorist, and proliferation financing.
- India has been a founder member since its inception in 1989.
- Iran, North Korea, and Myanmar are the three blacklisted countries by FATF.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
- The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) was established as an intergovernmental body by G7 in 1989. Hence statement 1 is incorrect.
- It has 39 members – 37 jurisdictions and 2 regional organizations (the Gulf Cooperation Council and the European Commission).
- It leads global action to tackle money laundering, terrorist, and proliferation financing. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- The FATF Plenary is the decision-making body of the FATF. It meets three times per year.
- India joined with ‘observer’ status in 2006 and became a full member of FATF in 2010. Hence statement 3 is incorrect.
- Countries that are considered a safe haven for supporting terror funding and money laundering are put on the grey list. This inclusion serves as a warning to the country that it may enter the blacklist.
- Countries known as non-cooperative are put on the blacklist. These countries support terror funding and money laundering activities.
- Iran, North Korea, and Myanmar are the three blacklisted countries by FATF. Hence statement 4 is correct.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
- The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) was established as an intergovernmental body by G7 in 1989. Hence statement 1 is incorrect.
- It has 39 members – 37 jurisdictions and 2 regional organizations (the Gulf Cooperation Council and the European Commission).
- It leads global action to tackle money laundering, terrorist, and proliferation financing. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- The FATF Plenary is the decision-making body of the FATF. It meets three times per year.
- India joined with ‘observer’ status in 2006 and became a full member of FATF in 2010. Hence statement 3 is incorrect.
- Countries that are considered a safe haven for supporting terror funding and money laundering are put on the grey list. This inclusion serves as a warning to the country that it may enter the blacklist.
- Countries known as non-cooperative are put on the blacklist. These countries support terror funding and money laundering activities.
- Iran, North Korea, and Myanmar are the three blacklisted countries by FATF. Hence statement 4 is correct.
-
Question 23 of 35
23. Question
Consider the following statements:
- Green infrastructure refers to the restoration of natural resources like forest covers and wetlands.
- Grey infrastructure refers to human-engineered infrastructure like stormwater drains, wastewater treatment plants, and dams.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
- Green infrastructure refers to the restoration of natural resources like forest covers and wetlands, which help in the management of excess rainwater by aiding natural percolation and natural runoff. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- Grey infrastructure refers to human-engineered infrastructure like stormwater drains, wastewater treatment plants, and dams, created for the management of excess rainwater. Hence statement 2 is correct.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
- Green infrastructure refers to the restoration of natural resources like forest covers and wetlands, which help in the management of excess rainwater by aiding natural percolation and natural runoff. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- Grey infrastructure refers to human-engineered infrastructure like stormwater drains, wastewater treatment plants, and dams, created for the management of excess rainwater. Hence statement 2 is correct.
-
Question 24 of 35
24. Question
Consider the following statements about the Krishi 24/7:
- It is an artificial intelligence-powered tool designed to automatically monitor and analyze agricultural news.
- It was developed by the Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare in partnership with the Wadhwani Institute for Artificial Intelligence.
- It scans news articles in multiple languages and translates them into English.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
- The Krishi 24/7 is an artificial intelligence-powered tool designed to automatically monitor and analyze agricultural news. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- It was developed by the Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare in partnership with the Wadhwani Institute for Artificial Intelligence. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- It extracts essential information from news articles including headlines, crop name, event type, date, location, severity, summary, and source link to ensure the government receives timely updates.
- It scans news articles in multiple languages and translates them into English. Hence statement 3 is correct.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
- The Krishi 24/7 is an artificial intelligence-powered tool designed to automatically monitor and analyze agricultural news. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- It was developed by the Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare in partnership with the Wadhwani Institute for Artificial Intelligence. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- It extracts essential information from news articles including headlines, crop name, event type, date, location, severity, summary, and source link to ensure the government receives timely updates.
- It scans news articles in multiple languages and translates them into English. Hence statement 3 is correct.
-
Question 25 of 35
25. Question
Consider the following statements about Advocate on Record (AOR):
- It is a title given to an advocate who can represent a cause or pleading before the Supreme Court.
- AOR serves as the link between litigants and the highest court in the country.
- AOR system is based on the British model of barristers and solicitors.
- The Supreme Court creates the rules for the AOR system under Article 145 of the Constitution.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (d)
- Advocate on Record (AOR) is a title given to an advocate who can represent a cause or pleading before the Supreme Court. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- AOR serves as the link between litigants and the highest court in the country.
- Only these advocates are entitled to file any matter or document before the SC. They can also file an appearance or act for a party in the SC. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- AOR system is based on the British model of barristers and solicitors where barristers argue cases and solicitors handle client matters. Hence statement 3 is correct.
- The Supreme Court creates the rules for the AOR system under Article 145 of the Constitution. Hence statement 4 is correct.
- Under Article 145 of the Constitution, the Supreme Court is empowered to make rules and regulate its procedure for hearing cases.
- The Supreme Court Rules, 2013 prescribe eligibility criteria for an AOR:
- An advocate has to clear an examination set by the Supreme Court and has to meet specific criteria such as:
- An advocate must undergo training with a court-approved AOR for at least one year before taking the examination.
- The advocate should have at least four years of legal practice before beginning the training.
- An AOR must have an office located in Delhi within a 16-kilometer radius of the Supreme Court.
Incorrect
Solution (d)
- Advocate on Record (AOR) is a title given to an advocate who can represent a cause or pleading before the Supreme Court. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- AOR serves as the link between litigants and the highest court in the country.
- Only these advocates are entitled to file any matter or document before the SC. They can also file an appearance or act for a party in the SC. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- AOR system is based on the British model of barristers and solicitors where barristers argue cases and solicitors handle client matters. Hence statement 3 is correct.
- The Supreme Court creates the rules for the AOR system under Article 145 of the Constitution. Hence statement 4 is correct.
- Under Article 145 of the Constitution, the Supreme Court is empowered to make rules and regulate its procedure for hearing cases.
- The Supreme Court Rules, 2013 prescribe eligibility criteria for an AOR:
- An advocate has to clear an examination set by the Supreme Court and has to meet specific criteria such as:
- An advocate must undergo training with a court-approved AOR for at least one year before taking the examination.
- The advocate should have at least four years of legal practice before beginning the training.
- An AOR must have an office located in Delhi within a 16-kilometer radius of the Supreme Court.
-
Question 26 of 35
26. Question
Consider the following statements:
- Project 15B of guided-missile destroyer ships are built by Mazagaon Dock Limited (MDL).
- INS Surat is the fourth ship of the indigenously designed and constructed Project 15B.
Choose the correct code:
Correct
Solution (c)
- Project 15B (P-15 Bravo class) is a project that aims to construct four guided-missile destroyer ships.
- It incorporates advanced design concepts such as state-of-the-art weapons and sensors, advanced stealth features, and a high degree of automation for improved survivability.
- It was launched in 2011 and built by Mazagaon Dock Limited (MDL). Hence statement 1 is correct.
- INS Surat is the fourth ship of the indigenously designed and constructed Project 15B. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- The other three ships are – Visakhapatnam, Mormugao, and Imphal.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
- Project 15B (P-15 Bravo class) is a project that aims to construct four guided-missile destroyer ships.
- It incorporates advanced design concepts such as state-of-the-art weapons and sensors, advanced stealth features, and a high degree of automation for improved survivability.
- It was launched in 2011 and built by Mazagaon Dock Limited (MDL). Hence statement 1 is correct.
- INS Surat is the fourth ship of the indigenously designed and constructed Project 15B. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- The other three ships are – Visakhapatnam, Mormugao, and Imphal.
-
Question 27 of 35
27. Question
Consider the following statements about the Women for Water, Water for Women Campaign:
- It was launched by the Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- It aims to provide a platform for the inclusion of women in water governance.
- It was launched under the Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT).
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
- The Women for Water, Water for Women Campaign was launched by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA). Hence statement 1 is incorrect.
- It aims to provide a platform for the inclusion of women in water governance and to instill a sense of ownership and belonging among women towards water infrastructure. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- It was launched under the Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) in partnership with the National Urban Livelihood Mission (NULM). Hence statement 3 is correct.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
- The Women for Water, Water for Women Campaign was launched by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA). Hence statement 1 is incorrect.
- It aims to provide a platform for the inclusion of women in water governance and to instill a sense of ownership and belonging among women towards water infrastructure. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- It was launched under the Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) in partnership with the National Urban Livelihood Mission (NULM). Hence statement 3 is correct.
-
Question 28 of 35
28. Question
Consider the following statements about the PM Vishwakarma Scheme:
- It is a central sector scheme that aims to provide end-to-end support to artisans and craftspeople who work with their hands and tools.
- It covers artisans and craftspeople engaged in 18 trades such as carpenters, boatmakers, blacksmiths, etc.
- The beneficiary should not have availed loans under similar credit-based schemes of the central government or state government.
- The registration and benefits under the scheme can be availed to multiple members of the family.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
- The PM Vishwakarma Scheme is a central sector scheme that aims to provide end-to-end support to artisans and craftspeople who work with their hands and tools. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- The Ministry of Micro, Small & Medium Enterprise is the nodal ministry.
- It covers artisans and craftspeople engaged in 18 trades such as carpenters, boatmakers, blacksmiths, etc. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- The beneficiary should not have availed of loans under similar credit-based schemes of the central government or state government. Hence statement 3 is correct.
- The registration and benefits under the scheme shall be restricted to one member of the family. Hence statement 4 is incorrect.
- The benefits of the scheme:
- Recognition of artisans through PM Vishwakarma certificate and ID card.
- Skill Upgradation and Advanced Training
- Toolkit Incentive of up to Rs. 15,000 in the form of e-vouchers
- Collateral-free loans of up to Rs. 3 lakhs at a low rate of interest.
- Incentive for Digital Transaction
- Marketing Support in the form of quality certification, branding, and onboarding on e-commerce platforms
Incorrect
Solution (c)
- The PM Vishwakarma Scheme is a central sector scheme that aims to provide end-to-end support to artisans and craftspeople who work with their hands and tools. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- The Ministry of Micro, Small & Medium Enterprise is the nodal ministry.
- It covers artisans and craftspeople engaged in 18 trades such as carpenters, boatmakers, blacksmiths, etc. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- The beneficiary should not have availed of loans under similar credit-based schemes of the central government or state government. Hence statement 3 is correct.
- The registration and benefits under the scheme shall be restricted to one member of the family. Hence statement 4 is incorrect.
- The benefits of the scheme:
- Recognition of artisans through PM Vishwakarma certificate and ID card.
- Skill Upgradation and Advanced Training
- Toolkit Incentive of up to Rs. 15,000 in the form of e-vouchers
- Collateral-free loans of up to Rs. 3 lakhs at a low rate of interest.
- Incentive for Digital Transaction
- Marketing Support in the form of quality certification, branding, and onboarding on e-commerce platforms
-
Question 29 of 35
29. Question
Consider the following statements about the Public Gambling Act of 1867:
- It is a central law that prohibits running or operating public gaming houses.
- Any violation of the law under this act could attract a imprisonment of up to three years.
Choose the correct code:
Correct
Solution (a)
- The Public Gambling Act of 1867 is a central law that prohibits running or operating public gaming houses. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- It says that any gambling that involves the act of putting money or betting for money or any other equivalent act is illegal.
- Any violation of the law under this act could attract a fine of Rs.200 or imprisonment of up to three months. Hence statement 2 is incorrect.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
- The Public Gambling Act of 1867 is a central law that prohibits running or operating public gaming houses. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- It says that any gambling that involves the act of putting money or betting for money or any other equivalent act is illegal.
- Any violation of the law under this act could attract a fine of Rs.200 or imprisonment of up to three months. Hence statement 2 is incorrect.
-
Question 30 of 35
30. Question
The Mount Celia Gold Operation marks the first gold mine project undertaken by the National Mineral Development Corporation (NMDC) located in?
Correct
Solution (c)
The Mount Celia Gold Operation marks the first gold mine project undertaken by the National Mineral Development Corporation (NMDC) located in Western Australia. It is the project that aims to extract gold within the Laverton Tectonic Zone of Australia. The Laverton Tectonic Zone is considered to be one of the world’s most prolific gold belts. Hence option c is correct.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
The Mount Celia Gold Operation marks the first gold mine project undertaken by the National Mineral Development Corporation (NMDC) located in Western Australia. It is the project that aims to extract gold within the Laverton Tectonic Zone of Australia. The Laverton Tectonic Zone is considered to be one of the world’s most prolific gold belts. Hence option c is correct.
-
Question 31 of 35
31. Question
The sum of four consecutive integers is 210. Which one of these four integers is prime?
Correct
Solution (c)
Let x represent the smallest of the four numbers
Then we can set up the following equation:
x + (x+1) + (x+2)+ (x+3) = 210
4x + 6 = 210
4x = 204
x = 51
Therefore the four numbers are 51, 52, 53, 54.
The only prime in this list is 53.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Let x represent the smallest of the four numbers
Then we can set up the following equation:
x + (x+1) + (x+2)+ (x+3) = 210
4x + 6 = 210
4x = 204
x = 51
Therefore the four numbers are 51, 52, 53, 54.
The only prime in this list is 53.
-
Question 32 of 35
32. Question
Each person’s performance compared with all other persons is to be done to rank them subjectively. How many comparisons are needed to total, if there are 11 persons?
Correct
Solution (a)
There will be 11C2 comparisons or (11*10)/(2*1) = 55 comparisons
Hence there will be 55 comparisons.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
There will be 11C2 comparisons or (11*10)/(2*1) = 55 comparisons
Hence there will be 55 comparisons.
-
Question 33 of 35
33. Question
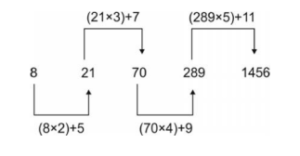
A series is given with one term missing, Select the correct alternatives from the given ones that will complete the series. 8, 21, 70, ?, 1456
Correct
Solution (c)
 Incorrect
Incorrect
Solution (c)

-
Question 34 of 35
34. Question
If ABC x DEED = ABCABC; where A, B, C, D and E are different digits, what are the values of D and E?
Correct
Solution (c)
ABC × DEED = ABCABC
Let A = 4
B = 3
C = 2
D = 1
E = 0
Then 432 x 1001 = 432432
∴ D = 1, E = 0
Incorrect
Solution (c)
ABC × DEED = ABCABC
Let A = 4
B = 3
C = 2
D = 1
E = 0
Then 432 x 1001 = 432432
∴ D = 1, E = 0
-
Question 35 of 35
35. Question
If x^2 – y^2 = 17 where x and y are positive integers then x^2 + y^2 = ?
Correct
Solution (b)
X^2 – y^2 = (x + y) (x – y)
Since 17 is a prime no.
Hence it can be uniquely factorised as 17 × 1.
So (x + y) (x – y) = 17 × 1
x + y = 17 & x – y = 1
By solving above equations, we get x = 9 & y = 8
x2 + y2 = 81 + 64 = 145
Incorrect
Solution (b)
X^2 – y^2 = (x + y) (x – y)
Since 17 is a prime no.
Hence it can be uniquely factorised as 17 × 1.
So (x + y) (x – y) = 17 × 1
x + y = 17 & x – y = 1
By solving above equations, we get x = 9 & y = 8
x2 + y2 = 81 + 64 = 145
All the Best
IASbaba











