IASbaba Daily Prelims Quiz
For Previous Daily Quiz (ARCHIVES) – CLICK HERE
The Current Affairs questions are based on sources like ‘The Hindu’, ‘Indian Express’ and ‘PIB’, which are very important sources for UPSC Prelims Exam. The questions are focused on both the concepts and facts. The topics covered here are generally different from what is being covered under ‘Daily Current Affairs/Daily News Analysis (DNA) and Daily Static Quiz’ to avoid duplication. The questions would be published from Monday to Saturday before 2 PM. One should not spend more than 10 minutes on this initiative.
Gear up and Make the Best Use of this initiative.
Do remember that, “the difference between Ordinary and EXTRA-Ordinary is PRACTICE!!”
Important Note:
- Don’t forget to post your marks in the comment section. Also, let us know if you enjoyed today’s test 🙂
- After completing the 5 questions, click on ‘View Questions’ to check your score, time taken, and solutions.
Test-summary
0 of 5 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Information
To view Solutions, follow these instructions:
- Click on – ‘Start Test’ button
- Solve Questions
- Click on ‘Test Summary’ button
- Click on ‘Finish Test’ button
- Now click on ‘View Questions’ button – here you will see solutions and links.
You have already completed the test before. Hence you can not start it again.
Test is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the test.
You have to finish following test, to start this test:
Results
0 of 5 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have scored 0 points out of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 5
1. Question
Consider the following statements about Minor Forest Produce
- The Forest Rights Act (FRA), 2006 defines ‘minor forest produce’ as any non-timber forest product of plant origin.
- Minimum Support Price for the MFP scheme is Centrally Sponsored scheme started in the year 2008.
- Ministry of Tribal Affairs is the Nodal Ministry for implementation of the MSP for MFP scheme.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
Statement Analysis
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Incorrect Correct · The Scheduled Tribe and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006, or Forest Rights Act (FRA), defines ‘minor forest produce’ as any non-timber forest product of plant origin. · This includes various items such as bamboo, brush wood, stumps, cane, tussar, cocoons, honey, wax, lac, kendu leaves, medicinal plants, herbs, roots, tubers and similar items.
· In simple terms, it encompasses all other forest products, excluding timber.
MSP for MFP scheme: · The Minimum Support Price(MSP) for the MFP scheme was started by the Government of India in 2013 to ensure fair and remunerative prices to MFP gatherers. It is a Centrally Sponsored scheme.
Objectives:
· To provide a fair price to the MFP gatherers for the produce collected by them and enhance their income level
· To ensure sustainable harvesting of MFPs.
· The Scheme will have a huge social dividend for MFP gatherers, majority of whom are tribals.
Implementation: · Ministry of Tribal Affairs, Government of India is the Nodal Ministry for implementation of the scheme.
· TRIFED acts as the Central Nodal Agency for implementation and monitoring of the scheme through State level implementing agencies.
· Further, the State designated agencies will undertake procurement of notified MFPs directly from MFP gatherers at haats notified procurement centers at grass root level at prefixed Minimum Support Price.
Context: Tribal people in Odisha are struggling for approvals from the forest department to sell Kendu leaf which is a minor forest produce.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Statement Analysis
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Incorrect Correct · The Scheduled Tribe and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006, or Forest Rights Act (FRA), defines ‘minor forest produce’ as any non-timber forest product of plant origin. · This includes various items such as bamboo, brush wood, stumps, cane, tussar, cocoons, honey, wax, lac, kendu leaves, medicinal plants, herbs, roots, tubers and similar items.
· In simple terms, it encompasses all other forest products, excluding timber.
MSP for MFP scheme: · The Minimum Support Price(MSP) for the MFP scheme was started by the Government of India in 2013 to ensure fair and remunerative prices to MFP gatherers. It is a Centrally Sponsored scheme.
Objectives:
· To provide a fair price to the MFP gatherers for the produce collected by them and enhance their income level
· To ensure sustainable harvesting of MFPs.
· The Scheme will have a huge social dividend for MFP gatherers, majority of whom are tribals.
Implementation: · Ministry of Tribal Affairs, Government of India is the Nodal Ministry for implementation of the scheme.
· TRIFED acts as the Central Nodal Agency for implementation and monitoring of the scheme through State level implementing agencies.
· Further, the State designated agencies will undertake procurement of notified MFPs directly from MFP gatherers at haats notified procurement centers at grass root level at prefixed Minimum Support Price.
Context: Tribal people in Odisha are struggling for approvals from the forest department to sell Kendu leaf which is a minor forest produce.
-
Question 2 of 5
2. Question
Consider the following statements
- Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC) is operates directly under the chairmanship of Prime Minister of India.
- BARC is the research backbone of the Nuclear Power Corporation of India, which operates all nuclear power reactors in India.
Choose the correct statements:
Correct
Solution (b)
Statement Analysis
Statement 1 Statement 2 Incorrect Correct Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC): · It is India’s premier nuclear research facility.
· It operates under the Department of Atomic Energy, which is directly overseen by the Prime Minister of India.
History:
· Dr. Homi Jehangir Bhabha conceived the nuclear program in India.
· Dr. Bhabha established the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR) to carry out nuclear science research in 1945.
· To intensify the effort to exploit nuclear energy for the benefit of the nation, Dr. Bhabha established the Atomic Energy Establishment, Trombay (AEET), in January 1954 for a multidisciplinary research program essential for the ambitious nuclear program of India.
· After the death of Bhabha in 1966, AEET was renamed Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC).
· It is a multi-disciplinary research centre with extensive infrastructure for advanced research and development covering the entire spectrum nuclear science and engineering and related areas. · BARC is the research backbone of the Nuclear Power Corporation of India (NPCIL), which currently operates all nuclear power reactors in India.
Functions:
· It is engaged in research with the objective of generating knowledge and techniques for nuclear power production, the advancement of nuclear science, the use of radioisotopes in industry, health, and agriculture, and research in frontier areas of science and technology.
· It is responsible for the design and development of nuclear reactors, fuel cycle technologies, radiation protection, and safety systems.
· BARC also plays an important role in nuclear education and training.
Context: State-run Bharat Heavy Electricals Ltd. (BHEL) recently entered into a Technology Transfer Agreement (TTA) with the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC) for a 50-kW alkaline electrolyser system for Hydrogen production.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Statement Analysis
Statement 1 Statement 2 Incorrect Correct Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC): · It is India’s premier nuclear research facility.
· It operates under the Department of Atomic Energy, which is directly overseen by the Prime Minister of India.
History:
· Dr. Homi Jehangir Bhabha conceived the nuclear program in India.
· Dr. Bhabha established the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR) to carry out nuclear science research in 1945.
· To intensify the effort to exploit nuclear energy for the benefit of the nation, Dr. Bhabha established the Atomic Energy Establishment, Trombay (AEET), in January 1954 for a multidisciplinary research program essential for the ambitious nuclear program of India.
· After the death of Bhabha in 1966, AEET was renamed Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC).
· It is a multi-disciplinary research centre with extensive infrastructure for advanced research and development covering the entire spectrum nuclear science and engineering and related areas. · BARC is the research backbone of the Nuclear Power Corporation of India (NPCIL), which currently operates all nuclear power reactors in India.
Functions:
· It is engaged in research with the objective of generating knowledge and techniques for nuclear power production, the advancement of nuclear science, the use of radioisotopes in industry, health, and agriculture, and research in frontier areas of science and technology.
· It is responsible for the design and development of nuclear reactors, fuel cycle technologies, radiation protection, and safety systems.
· BARC also plays an important role in nuclear education and training.
Context: State-run Bharat Heavy Electricals Ltd. (BHEL) recently entered into a Technology Transfer Agreement (TTA) with the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC) for a 50-kW alkaline electrolyser system for Hydrogen production.
-
Question 3 of 5
3. Question
Consider the following statements about Sharavathi River
- Rising in the Western Ghats, it flows in a north-westerly direction to the Arabian Sea in Uttara Kannada district of Karnataka.
- The highest waterfall in India Kunchikal Falls is created by the Sharavathi River.
Choose the incorrect statements:
Correct
Solution (b)
Statement Analysis
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Incorrect Sharavathi River: · It is a river in western Karnataka state.
· It is one of the few westward-flowing rivers in India and a major part of the river basin lies in the Western Ghats.
Course:
· Rising in the Western Ghats, it flows in a northwesterly direction to the Arabian Sea at Honavar in Uttara Kannada District.
· The length of the river is 128 km, and the river basin covers 2,985 sq km.
· On its way, the Sharavathi forms the Jog Falls, one of the highest waterfalls in India, where the river falls from a height of 253 m. · Diverse geological features mark the river’s course, including rocky outcrops, fertile plains, and deep gorges.
· Major Tributaries: Nandihole, Haridravathi, Mavinahole, Hilkunji, Yennehole, Hurlihole, and Nagodihole.
· It is a vital source of hydroelectric power in Karnataka.
· Kunchikal Falls is India’s highest waterfall in India. It is created by the Varahi river in the Shimoga district of Karnataka. It is about 455 m in height.
Context: The National Green Tribunal (NGT) recently directed the State Environment Impact Assessment Authority (SEIAA) and mines and geology department to stop any unlawful/illegal sand mining in Sharavathi river coastal zone.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Statement Analysis
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Incorrect Sharavathi River: · It is a river in western Karnataka state.
· It is one of the few westward-flowing rivers in India and a major part of the river basin lies in the Western Ghats.
Course:
· Rising in the Western Ghats, it flows in a northwesterly direction to the Arabian Sea at Honavar in Uttara Kannada District.
· The length of the river is 128 km, and the river basin covers 2,985 sq km.
· On its way, the Sharavathi forms the Jog Falls, one of the highest waterfalls in India, where the river falls from a height of 253 m. · Diverse geological features mark the river’s course, including rocky outcrops, fertile plains, and deep gorges.
· Major Tributaries: Nandihole, Haridravathi, Mavinahole, Hilkunji, Yennehole, Hurlihole, and Nagodihole.
· It is a vital source of hydroelectric power in Karnataka.
· Kunchikal Falls is India’s highest waterfall in India. It is created by the Varahi river in the Shimoga district of Karnataka. It is about 455 m in height.
Context: The National Green Tribunal (NGT) recently directed the State Environment Impact Assessment Authority (SEIAA) and mines and geology department to stop any unlawful/illegal sand mining in Sharavathi river coastal zone.
-
Question 4 of 5
4. Question
Consider the following statements about Golden Rice
- It is genetically engineered crop to contain beta carotene (provitamin A).
- India became the first Asian country to approve commercial production of the rice variety in 2021.
- It is water intensive and requires special cultivation practices, unlike traditional rice.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
Correct
Solution (a)
Statement Analysis
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Incorrect Incorrect · Golden Rice is a new type of rice that contains beta carotene (provitamin A, a plant pigment that the body converts into vitamin A as needed). · This compound is what gives this grain it’s yellow-orange or golden colour, hence its name.
· Golden Rice is developed through genetic engineering.
· Philippines became the first country to approve commercial production of the rice variety in 2021. · Golden Rice is an enhanced version of ordinary rice designed to handle a specific nutrition issue, without any additional cost or difference in taste.
· While Golden Rice is expected to cost and taste the same as regular rice, its beta carotene content makes it a valuable asset in the battle against vitamin A deficiency (VAD).
· Like ordinary rice, Golden Rice does not require any special cultivation practices, and generally has the same yield and agronomic performance. Context: A court in the Philippines recently revoked biosafety permits for commercial propagation of genetically modified golden rice.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
Statement Analysis
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Incorrect Incorrect · Golden Rice is a new type of rice that contains beta carotene (provitamin A, a plant pigment that the body converts into vitamin A as needed). · This compound is what gives this grain it’s yellow-orange or golden colour, hence its name.
· Golden Rice is developed through genetic engineering.
· Philippines became the first country to approve commercial production of the rice variety in 2021. · Golden Rice is an enhanced version of ordinary rice designed to handle a specific nutrition issue, without any additional cost or difference in taste.
· While Golden Rice is expected to cost and taste the same as regular rice, its beta carotene content makes it a valuable asset in the battle against vitamin A deficiency (VAD).
· Like ordinary rice, Golden Rice does not require any special cultivation practices, and generally has the same yield and agronomic performance. Context: A court in the Philippines recently revoked biosafety permits for commercial propagation of genetically modified golden rice.
-
Question 5 of 5
5. Question
Halloween Crack, sometimes seen in the news recently, is associated with?
Correct
Solution (d)
Option d Correct · The “Halloween Crack” is a significant rift or fracture on the Brunt Ice Shelf in Antarctica. · It runs from an area known as the McDonald Ice Rumples, where the underside of the floating ice shelf is grounded on the shallow seabed.
· The McDonald Ice Rumples, where the crack originates, are formed due to ice flow over an underwater obstruction or bedrock rise that impedes the ice flow and causes pressure waves, crevasses, and rifts to form on the ice shelf’s surface.
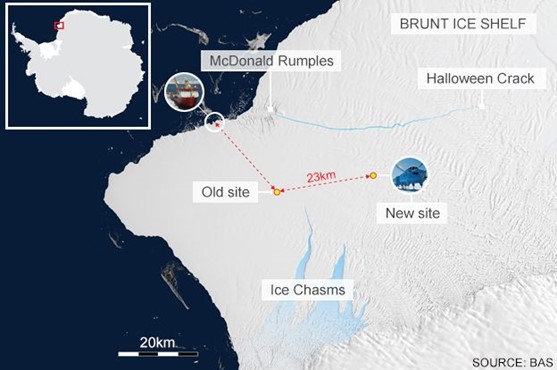
· This pinning point slows the ice flow and causes fractures on the ice surface.
· The Halloween Crack runs adjacent to the precarious tip of the Brunt Ice Shelf, which is hanging by a narrow strip of ice around 600 meters long at the northern end.
· A large iceberg measuring around 380 sq km in area has calved (broken off) from the Brunt Ice Shelf in Antarctica.
· It is the third major iceberg calving event near the Halley research base in the last three years.
· This iceberg broke off after a new 14km-long crack emerged at 90 degrees from the pre-existing “Halloween Crack” on the ice shelf.
Context: A large iceberg measuring around 380 square km in area has recently calved (broken off) from the Brunt Ice Shelf in Antarctica.
Incorrect
Solution (d)
Option d Correct · The “Halloween Crack” is a significant rift or fracture on the Brunt Ice Shelf in Antarctica. · It runs from an area known as the McDonald Ice Rumples, where the underside of the floating ice shelf is grounded on the shallow seabed.
· The McDonald Ice Rumples, where the crack originates, are formed due to ice flow over an underwater obstruction or bedrock rise that impedes the ice flow and causes pressure waves, crevasses, and rifts to form on the ice shelf’s surface.

· This pinning point slows the ice flow and causes fractures on the ice surface.
· The Halloween Crack runs adjacent to the precarious tip of the Brunt Ice Shelf, which is hanging by a narrow strip of ice around 600 meters long at the northern end.
· A large iceberg measuring around 380 sq km in area has calved (broken off) from the Brunt Ice Shelf in Antarctica.
· It is the third major iceberg calving event near the Halley research base in the last three years.
· This iceberg broke off after a new 14km-long crack emerged at 90 degrees from the pre-existing “Halloween Crack” on the ice shelf.
Context: A large iceberg measuring around 380 square km in area has recently calved (broken off) from the Brunt Ice Shelf in Antarctica.
- Current Affairs Quiz, IAS Daily Current Affairs Quiz, IAS UPSC Current Affairs Quiz, IAS UPSC Prelims Quiz, IASbaba's Current Affairs Prelims Quiz, IASbaba's Daily Quiz, IASbaba's UPSC Quiz, Prelims Current Affairs Quiz, UPSC Current Affairs Quiz, UPSC Current Affairs Quiz IASbaba, UPSC Daily Current Affair Quiz, UPSC IAS Daily Quiz











