IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus:
- Prelims & Mains – CURRENT EVENT
Context: The Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) summoned the Head of Mission at the High Commission of Bangladesh to convey that fencing works on the India-Bangladesh border was being carried out in accordance with “all protocols and agreements”.
Background: –
- The conversation took place a day after Bangladesh Foreign Secretary expressed deep concern to Indian High Commissioner in Dhaka about the construction works by the Border Security Force (BSF) along the border.
Key takeaways
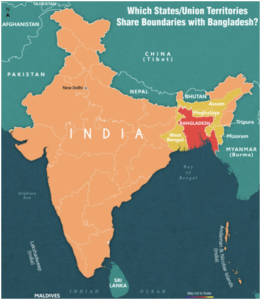
- The India-Bangladesh border is approximately 4,096.7 km, making it the longest international border that India shares with any country.
- States Sharing the Border: West Bengal (2,216.7 km), Assam (263 km), Meghalaya (443 km), Tripura (856 km), Mizoram (318 km)
- Geography:
- The border passes through plains, rivers, hills, and densely populated areas.
- Major rivers like the Ganga, Brahmaputra flow across this region.
- The border was drawn during the partition of India, based on the Radcliffe Line, dividing Bengal into West Bengal (India) and East Bengal (later East Pakistan, now Bangladesh).
The current issue
- Border Guards Bangladesh (BGB) attempted to obstruct the construction of a barbed wire fence on the international border in West Bengal’s Malda and Cooch Bihar ditsrict.
- According to the 1975 Joint India-Bangladesh Guidelines for Border Authorities, no defence structure can be constructed within 150 yards from the zero line or the international boundary by either side. India does not consider wire fencing as a defense structure, but Bangladesh and Pakistan do.
- Bangladesh’s objections to single row fencing (SRF) are essentially two pronged: the first argument, which is most commonly cited, is the 1975 agreement on no fencing within 150 yards of the international border. The second argument is that fencing causes inconvenience to residents along the international border.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus:
- Prelims – CURRENT EVENT
Context: Makar Sankranti was celebrated on January 14.
Background: –
- This festival marks the arrival of the harvest season and the end of winter. It is also associated with different traditions like flying kites and taking holy dip in rivers.
Key takeaways
- When the Sun begins its northward journey after reaching its southernmost point, it is said to enter Uttarayan. Conversely, when the Sun started travelling southward from its northernmost position, it is said to enter Daksinayana.
- Considered one of the most ancient Hindu festivals, Uttarayan is celebrated in north India as Makar Sankranti, and is dedicated to the sun god.
- In the states of Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and Rajasthan, Makar Sankranti is observed. In West Bengal and North-east region, Makar Sankranti is observed as Poush Sankranti. Tamil Nadu observes Pongal on this day, while Kerala observes this day as Makara Vilakku.
- In Assam, Makar Sankranti is observed as Magh Bihu. In Punjab, Maghi is celebrated on this day.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus:
- Prelims – CURRENT EVENT
Context: The Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying, under the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying, hosted an Entrepreneurship Development Conclave in Pune, Maharashtra, themed “Empowering Entrepreneurs: Transforming Livestock Economies.”
Background:
- Government is implementing flagship schemes such as the Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF) and National Livestock Mission (NLM). By showcasing opportunities under NLM and AHIDF, the conclave aimed to drive inclusive growth and empower rural farmers and small enterprises.
Key takeaways
- The National Livestock Mission (NLM), launched in 2014–15 by the Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying, Government of India, aims to ensure comprehensive development of the livestock sector, focusing on improving feed and fodder, breed development, and increasing per animal productivity.
Objectives of NLM:
- Employment Generation: Through entrepreneurship development in small ruminant (sheep, goats), poultry, piggery, and fodder sectors.
- Increasing Productivity: Enhancement of per animal productivity through breed improvement.
- Production Increase: Upscaling the production of meat, eggs, goat milk, wool, and fodder.
- Fodder and Feed Availability: Strengthening the fodder seed supply chain and increasing the availability of certified fodder seeds.
- Fodder Processing Units: Encouraging the establishment of fodder processing units (e.g., hay bailing, silage making) to decrease the demand-supply gap.
- Risk Management: Promotion of livestock insurance and other risk management measures.
- Applied Research: Supporting research in prioritized areas like poultry, sheep, goat, feed, and fodder.
- Capacity Building: Strengthening the extension machinery to provide quality extension services to farmers and training livestock owners in skill-based practices.
Sub-Missions under NLM:
- Breed Development of Livestock & Poultry:
- Support entrepreneurship and breed improvement in poultry, sheep, goat, and piggery sectors.
- Activities include establishing breed development farms and genetic improvement programs.
- Feed and Fodder Development:
- Enhance the availability of quality fodder seeds and promote entrepreneurial activities in feed production.
- Focus on establishing fodder block units, hay bailing, and silage making units.
- Innovation and Extension:
- Encourage research in livestock sectors, extension activities, livestock insurance, and innovative practices.
- Implementation and Funding: NLM is implemented through both Central Sector (CS) and Centrally Sponsored Schemes (CSS), with financial assistance provided to individuals, Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), Self-Help Groups (SHGs), and State Governments.
Source: PIB
Syllabus:
- Prelims – GEOGRAPHY
Context: Southern Japan was hit by a strong earthquake on Monday.
Background: –
- The Nankai Trough produces massive earthquakes about every 100-150 years. Strong quakes nearby are seen as a potential indication that a megaquake could be more likely.
Key takeaways
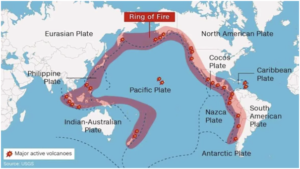
- The Nankai Trough is an undersea subduction zone located off coast of Japan. It extends approximately 900 kilometers (559 miles), running parallel to Honshu, Japan’s main island.
- Nankai Trough is where the Philippine Sea Plate is slipping under the Eurasia Plate at the bottom of the sea off the southwest coast of Japan. The accumulating tectonic strains could result in earthquakes.
- The Nankai Trough is known for generating megathrust earthquakes, some of the most powerful types of quakes. The most recent notable event was in 1946, with a magnitude 8.0 earthquake and subsequent tsunami.
- It is part of the larger Pacific “Ring of Fire.”
Additional Information
- The magnitude of an earthquake is related to the length of the fault on which it occurs, according to the United States Geological Survey. The largest earthquake ever recorded was a magnitude 9.5 on May 22, 1960 in Chile on a fault that is almost 1,000 miles long.
Source: Reuters
Syllabus:
- Prelims & Mains – GEOGRAPHY
Context: Deccan Volcanism, a major event of volcanic eruptions which occurred ~66 million years ago and led to mass extinctions of fauna, did not have such negative impact on tropical flora, says a new study.
Background: –
- The study was conducted by Birbal Sahni Institute of Palaeosciences (BSIP), an autonomous institute of Department of Science and Technology.
Key takeaways
- Deccan Volcanism, one of Earth’s most significant volcanic events, occurred about 66 million years ago in what is now west-central India. It created the Deccan Traps, a massive region of flood basalts covering around 500,000 square kilometers and reaching up to 2,000 meters thick in places.
Key Features of Deccan Volcanism:
- Formation of Deccan Traps: The Deccan Traps were formed by massive volcanic eruptions. Lava extruding through fissures created horizontal layers of basalt, forming step-like hills (hence the term “Traps,” derived from the Swedish word for stairs).
- Duration: These eruptions lasted for around 600-800,000 years during the transition between the Cretaceous and Paleogene periods.
- Volcanic Source: A mantle plume, often associated with the still-active Réunion hotspot, is believed to have triggered these extensive eruptions
Impact on Earth’s History:
- Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) Mass Extinction: Deccan Volcanism is one of the key events linked to the K-Pg mass extinction, which led to the extinction of non-avian dinosaurs.
- The eruptions released vast amounts of greenhouse gases and sulfur aerosols that altered the global climate, causing significant warming and acid rain.
What the new study says?
- The study by Birbal Sahni Institute of Palaeosciences (BSIP) suggests that despite highly devastating consequences for terrestrial faunas, the Deccan Volcanism only caused regional and short-term impacts on the flora.
- Deccan Volcanism indirectly imposed a positive impact on the development of hyper-diverse tropical flora by wiping off the large faunal community of dinosaurs along with gymnosperms and by providing nascent, undisturbed, barren yet fertile habitats within congenial warm and humid climate state ideal for angiosperms to grow and evolve.
Source: PIB
Practice MCQs
Q1.) Consider the following statements regarding the National Livestock Mission (NLM)
- The NLM aims to improve feed and fodder availability and focuses on breed development for livestock and poultry.
- It is implemented only as a Central Sector Scheme (CS).
- Promotion of livestock insurance and risk management measures is one of its objectives.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Q2.) The Nankai Trough is significant because:
- It is a tectonic subduction zone located near the Indian Ocean.
- It is responsible for generating megathrust earthquakes.
- It is part of the Pacific “Ring of Fire.”
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Q3.) Which of the following is/are associated with Deccan Volcanism?
- Formation of the Deccan Traps in west-central India.
- Linked to the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) mass extinction.
- Triggered by the collision of the Indian plate with the Eurasian plate.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ Today’s – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs
ANSWERS FOR 13th January – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – b











