IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus:
- Prelims & Mains – POLITY
Context: After the Supreme Court’s decision to scrap electoral bonds last year, donations to political parties significantly increased through electoral trusts, as indicated by the electoral trust contribution reports released by the Election Commission of India (ECI) for the previous financial year.
Background: –
- Nearly three-fourths of the donations to the Prudent Electoral Trust, which has received the highest contribution, were made after the Supreme Court’s decision on February 15.
Key takeaways
- An Electoral Trust is a non-profit organization established in India to facilitate transparent funding to political parties.
- On 31st January, 2013, through ‘The Electoral Trusts Scheme, 2013’, the Central government specified the eligibility and procedure for registration of Electoral Trusts.
Key Features of Electoral Trusts
- Purpose:
- To collect voluntary contributions from individuals, companies, and institutions.
- To distribute these funds to registered olitical parties.
- Legal Framework:
- Governed under Section 25 of the Companies Act, 1956 (as a non-profit).
- Electoral trust can receive contribution only from permitted people/ entities as given below
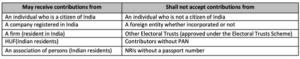
- An ET must distribute up to 95% of the voluntary contributions collected, with the surplus brought forward from the earlier year, to eligible political parties only. The remaining 5%, with a cap of ₹3 lakh, may be used for managing its own affairs.
- These trusts are not allowed to use any contribution for the direct or indirect benefit of its members or contributors.
- Eligibility Criteria for Donations:
- Only registered political parties under Section 29A of the Representation of the People Act, 1951, are eligible to receive funds.
- Donations cannot be made to independent candidates or unregistered parties.
- Transparency and Reporting:
- Trusts must file an annual contribution report with the Election Commission of India (ECI).
- The accounts of any ET must be audited and the report must be furnished to the Commissioner of Income Tax, including the list of contributors, list of parties that funds were distributed to, and the amounts disbursed.
- Tax Benefits:
- Donors receive tax benefits under Section 80GGB and Section 80GGC of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
- Electoral trusts themselves are exempt from income tax on their income.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus:
- Mains – GS 3
Context: India’s Real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is seen growing at a four-year low of 6.4 per cent in the current financial year 2024-25, the first advance estimates for FY25 released by the National Statistics Office (NSO) showed.
Background: –
- The government seems to have placed the blame for what it believes to be a cyclical slowdown largely at the door of the RBI. While the RBI’s tight monetary policy and interference with the rupee’s value have hindered export competitiveness, the issues are deeper and structural, not resolvable through interest rate cuts alone.
Key takeaways
- The high growth rates seen in the aftermath of the pandemic were driven in large part by the surge in services exports, specifically, the boom in Global Capability Centres (GCC).
- However, this growth structure is biased in favour of the highly skilled who account for a very small section. With not many moving up the income ladder, the overall consumption base hasn’t been growing.
- Limited upward mobility has, however, been a feature of the Indian economy, reflecting the inability to generate productive forms of employment for the majority. But mobility seems to have become more restricted since the pandemic. Arguably, the clearest evidence of this can be found in the car market, specifically, the low-priced, small car market.
- Take the sub Rs 10 lakh segment. Cars in this segment are bought by first-time users or those upgrading from two-wheelers or used cars. In 2014-15, this category accounted for 73 per cent of all cars sold in the country. By 2024-25, the category accounted for just 46 per cent of all cars sold.
- The labour market is just not providing enough productive employment opportunities nor are real wages growing at a fast clip.
- While millions more have joined the workforce, more are now self-employed, either as unpaid help in household establishments or in one-man roadside shops or in agriculture. Informal establishments and employment continue to witness a expansion, indicating the absence of alternatives.
- Formal employment, as per the EPFO payroll data shows, remains driven by expert services, which are nothing but manpower suppliers, normal contractors, and security services — segments that don’t require high-skill levels.
- The fallout of limited job creation and muted wage growth can be seen in the greater recourse to debt. Household debt had risen to 43 per cent by June 2024. But even this debt surge has failed to boost overall consumption significantly.
- With little demand visibility and uncertainty over government policy, investment activity continues to remain subdued. New project announcements have slowed down as per CMIE.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus:
- Prelims – ENVIRONMENT
Context: Over the past two weeks, numerous dead olive ridley turtles have washed ashore in Tamil Nadu, particularly in Chennai.
Background:
- Olive ridley turtles arrive near the Tamil Nadu coast around September-October to breed. Their nesting season begins in late November and ends in March. Although deaths during nesting season are not unusual, the large number of turtle carcasses found this early in the nesting period has sparked concerns.

Key takeaways
- Olive Ridley Sea Turtles (Lepidochelys olivacea) are one of the smallest and most abundant of all sea turtles found globally.
- Physical Characteristics:
- Size: Around 60–70 cm in length and 35–50 kg in weight.
- Shell: Olive-colored, heart-shaped, and flattened.
- Habitat:
- Found in warm waters of the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans.
- Prefer coastal and shallow marine environments but occasionally venture into open seas.
- Diet: Omnivorous; feed on algae, fish, shrimp, crabs, and jellyfish.
- Lifespan: Typically live for 50–60 years.
- These turtles are known for their unique mass nesting events called “arribadas,” where thousands of females gather on the same beach to lay eggs. Significant nesting sites include the coasts of India, Mexico, and Costa Rica.
- Olive ridley turtles lay eggs across several coastal states on India’s east coast and west coast. However, mass nesting takes place in Odisha, followed by Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
- Odisha’s Gahirmatha and Rushikulya beaches witness the arrival of lakhs of female olive ridley turtles every year.
- Olive Ridley turtles are classified as Vulnerable by the IUCN Red List.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus:
- Prelims – CURRENT EVENT
Context: Prime Minister Narendra Modi said that once property cards under the Centre’s SVAMITVA scheme have been distributed in all the villages of the country, it could unlock economic activity worth over Rs 100 lakh crore.
Background: –
- The Prime Minister was addressing an event to distribute over 65 lakh property cards to property owners in over 50,000 villages through video conferencing.
Key takeaways
- The SVAMITVA stands for Survey of Villages and Mapping with Improvised Technology in Village Areas. It aims to provide a ‘record of rights’ to those having houses in villages, and issue them a property card.
- The scheme was launched by PM Modi on National Panchayati Raj Day, on April 24, 2020.
- The plan is to survey all rural properties using drones and prepare GIS -based maps for each village.
Benefit of a SVAMITVA.
- First, property cards enables rural households to use their property as a financial asset for taking loans and other financial benefits.
- The cards help increase liquidity of land parcels in the market and increase the financial credit availability to the village.
- Second, it helps in determination of property tax, which accrues to the Gram Panchayats directly in states where they are empowered to collect such taxes.
- The scheme also paves the way for creation of accurate land records for rural planning. All the property records and maps are available at the Gram Panchayat level, which helps in taxation of villages, construction permits, elimination of encroachments, etc.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus:
- Prelims – ECONOMY
Context: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) modified guidelines related to asset reconstruction companies (ARCs) recently.
Background: –
- RBI eased norms pertaining to settlement of dues between asset reconstruction companies (ARCs) and borrowers.
Key takeaways
- Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs) are specialized financial institutions that acquire non-performing assets (NPAs) or bad loans from banks and financial institutions and help recover or restructure them. This enables banks to clean up their balance sheets and focus on lending activities.
- Regulation:
- Governed by the Securitisation and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest (SARFAESI) Act, 2002.
- Regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
Key Provisions under the SARFAESI Act:
- ARCs are empowered to take possession of secured assets of defaulters without court intervention.
- They can manage and recover loans through sale, lease, or restructuring.
Objectives of ARCs
- Resolution of Stressed Assets: Help banks and financial institutions recover bad debts.
- Financial Stability: Improve the health of the banking sector by reducing NPAs.
- Resource Allocation: Enable banks to focus on productive lending by offloading non-performing loans.
Functions of ARCs
- Acquisition of NPAs: ARCs purchase bad loans from banks at a discounted value.
- Restructuring and Recovery: Restructure the debt or recover dues through measures like asset liquidation or settlement.
- Issuance of Security Receipts (SRs): ARCs fund their operations by issuing SRs to qualified institutional buyers (QIBs).
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q1.) Which of the following statements about Olive Ridley Turtles is/are correct?
- Olive Ridley Turtles are classified as Critically Endangered under the IUCN Red List.
- Odisha’s Gahirmatha beach is one of the largest mass nesting sites for Olive Ridley Turtles.
- The unique mass nesting behavior of Olive Ridley Turtles is called “Arribadas.”
Select the correct answer using the codes below:
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Q2.) Which of the following are the benefits/objectives of the SVAMITVA Scheme?
- Issuing property cards to rural households for legal ownership of property.
- Enabling villagers to use property as a financial asset for loans.
- Improving the financial credit availability in rural areas.
- Encouraging urban migration for better economic opportunities.
Select the correct answer using the codes below:
a) 1, 2, and 3 only
b) 1 and 4 only
c) 2 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Q3.) Which of the following statements regarding Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs) is/are correct?
- ARCs are regulated under the SARFAESI Act, 2002.
- They are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- ARCs help banks improve financial stability by acquiring and resolving NPAs.
Select the correct answer using the codes below:
a) 1 and 3 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 2 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ Today’s – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs
ANSWERS FOR 20th January – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – a
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – b











