IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus:
- Prelims & Mains – CURRENT EVENT
Context: After 15 months of devastating war between Israel and Hamas, a ceasefire took effect on Sunday.
Background: –
- The ceasefire deal, brokered by Qatar, the US, and Egypt, promises to pause fighting for 42 days and includes the release of hostages held in Gaza in exchange for Palestinian prisoners in Israeli jails.
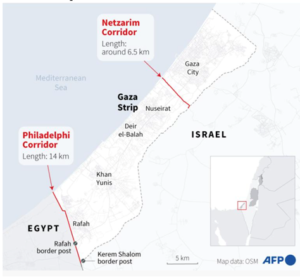
Key takeaways
- During a 42-day first phase beginning Sunday, Hamas will release 33 hostages and Israel will release between 900 and 1,650 Palestinian detainees, including all of those detained since October 7, 2023.
- The IDF will withdraw from central Gaza and the Netzarim Corridor — a 2-4-km-wide security clearing that it has created, cutting Gaza in half up to the Mediterranean — and eventually from the Philadelphi Corridor, the buffer zone along the Gaza-Egypt border.
- Negotiations for a second phase will begin on the 16th day after the ceasefire comes into effect, and is expected to produce almost a full Israeli withdrawal from the Strip, and the release of all remaining hostages by Hamas in return for a yet-to-be-decided number of Palestinian detainees.
War that reshaped the Middle East
- The war has rippled across the Middle East, triggering conflict with Hezbollah in Lebanon and drawing Israel into direct confrontation with Iran.
- Despite billions spent by Iran in building up a network of militants around Israel, its influence in the region has taken a significant hit. Hezbollah’s formidable missile arsenal has been largely destroyed, and much of its leadership has been killed.
- In Syria, the collapse of the Assad regime has further weakened Iran’s position in the region, leaving Israel militarily unchallenged but diplomatically isolated.
- Even as Israel emerges from the conflict militarily dominant, its international standing has suffered. Outrage over the humanitarian toll in Gaza has mounted, with Netanyahu now facing allegations of war crimes at the International Criminal Court (ICC) and accusations of genocide at the International Court of Justice (ICJ).
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus:
- Prelims – ART & CULTURE
Context: Maha Kumbh is progressing in Prayagraj. Kumbh mela is listed as the largest peaceful congregation of pilgrims on earth by UNESCO.
Background: –
- It is expected to have a footfall of 450 million this year, nearly twice the population of Uttar Pradesh, India’s most populous State.
Key takeaways
- Kumbh, derived from a Sanskrit word which means a pitcher, is rotationally held every three years at the four riverside cities of Prayagraj, Haridwar, Ujjain and Nasik. Its schedule is based on the planetary alignments, mainly of that of Sun and Jupiter.
- The Ardh (half) Kumbh is held every six years at Haridwar and Prayagraj while the Purna (complete) Kumbh takes place in all four cities, every 12 years.
- The Maha Kumbh happens after 12 Purna Kumbhs in Prayagraj, once in 144 years and is considered the most auspicious.
- The mythological beliefs say that drops of Amrit (essence of immortality) were spilled at these sites from an urn which came out during the Samudra Mantha (churning of the ocean) done by the gods and demons.
- The central ritual of the fair remains bathing in waters of the sacred rivers where millions immerse themselves with the belief that the act will cleanse them of their sins and liberate them from the cycle of birth and death.
A gathering of ascetics
- Religious texts also link Kumbh Mela’s origins to the 8th-century philosopher, Adi Shankaracharya, who established this practice of gatherings of ascetics from across the country, for discussion on religion.
- It was Shankaracharya who instituted the monastery system and the 13 Akharas (warrior-saint sects) — Nirvani, Atal, Niranjani, Anand, Juna, Awahan and Agni, Nirmohi, Digambar Ani and Nirvani Ani, the two Udasin Akharas (Naya and Bada) and the Nirmala Akhara. The saints from these sects are the main attraction at the Kumbh.
- The latest in the line of Akharas is the Kinnar (transgender) Akhara, established in 2015 by transgender rights activist Laxmi Narayan Tripathi.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus:
- Mains – GS 3
Context: The Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) will be using distributed ledger technology (DLT) to register spam preferences from customers, TRAI chairman said.
Background:
- The TRAI regulates the telecom industry, and its main role is in regulating Unsolicited Commercial Communications (UCC), the official name for spam.
Key takeaways
- Starting in 2007, TRAI implemented a do-not-disturb (DND) registry. If a telecom customer signs up to the DND registry, they are not supposed to get any spam calls or SMS messages.
- Under the Telecom Commercial Communication Customer Preference Regulation (TCCCPR), 2018, telemarketers who called or sent messages to DND-registered customers would receive warnings, and if enough warnings accumulate, they would be blacklisted from sending messages to telecom operators.
- In 2024, TRAI mandated that DND reporting be made available on every telecom provider’s app.
What role does blockchain play?
- In order to fight the deluge of spam messages, TRAI mandated in the TCCCPR that telcos use a blockchain ledger, also known as a distributed ledger, in order to store a constantly-updated list of approved senders of SMS messages.
- Telcos would also be required to approve specific formats of messages. For instance, an OTP message that goes, “Your OTP is 433212,” would be stored in the blockchain as “Your OTP is …” with space for a variable. These messages have been required to be sent from sender IDs, and not phone numbers.
- This has been one of the most stringent rules that have been issued to fight SMS spam.
- In 2024, the regulations were tightened to ensure “traceability” of messages. This was aimed at plugging a crucial flaw in the system that would allow anyone to register on the blockchain solutions implemented by telecom operators and send out fraudulent or spam messages.
Have these measures been effective?
- For those who have registered their DND preferences, communications from legitimate businesses that follow the rules have reduced. However, spam is constantly changing.
- Fraudulent calls have emerged, with frauds seeking to ensnare Indians in scams. Many of these operations are done outside the framework of SMS sender IDs, through disposable 10-digit phone numbers.
- There is also the issue of spam and scam calls from international numbers, which can be leased from certain online Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) providers.
Other steps taken by the government to end spam
- The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) has launched the Sanchar Saathi portal, which has a reporting site called Chakshu.
- DoT has partnered with law enforcement, banks, and other stakeholders to accept reports of suspected fraudulent calls and messages, and has moved to cancel lakhs of numbers associated with unauthorised telemarketers and scammers.
- It also set up the Telecom Security Operation Centre at its New Delhi headquarters to monitor suspicious internet traffic in real time.
- Meanwhile, firms like Airtel have taken steps to declare suspicious calls using Artificial Intelligence as “Suspected Spam,” a move that is being replicated by other telcos as well.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus:
- Prelims – GEOGRAPHY
Context: The Navies of nine Indo-Pacific countries, including India, are taking part in a multilateral exercise, La Perouse, hosted by France in the strategic straits of Malacca, Sunda, and Lombok, between the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean.
Background: –
- The three straits are critical choke points as these provide entry and exit into the Indian Ocean Region. With forays by the Chinese Navy in the region rising, the straits are under increased focus.
Key takeaways
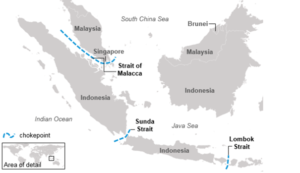
Strait of Malacca
- Strait of Malacca connects the Andaman Sea (Indian Ocean) to the South China Sea (Pacific Ocean).
- Location: Lies between Peninsular Malaysia and Sumatra (Indonesia), with its northern end near Thailand.
- Length: Approximately 930 kilometers.
- Width:
- Narrowest point: Around 2.8 kilometers at the Philips Channel near Singapore.
- Widest point: Approximately 370 kilometers.
- Depth: Varies, with shallowest points being around 25 meters, making navigation challenging for large vessels.
Sunda strait
- The Sunda Strait is a significant waterway in Southeast Asia that separates the islands of Java and Sumatra in Indonesia.
- It connects the Java Sea (part of the Pacific Ocean) to the Indian Ocean. Though less utilized than the Strait of Malacca, the Sunda Strait holds strategic and economic importance.
- Length: Approximately 130 kilometers.
- Width: Varies between 24 kilometers at its narrowest and about 150 kilometers at its widest.
- Depth: Relatively shallow, with depths ranging from 20 to 100 meters, making it less suitable for large vessels compared to other straits.
- Volcanic Activity: The strait includes several volcanic islands, the most notable being Krakatoa, which erupted catastrophically in 1883.
Lombok strait
- The Lombok Strait is a key maritime passage in Southeast Asia, situated between the Indonesian islands of Bali (to the west) and Lombok (to the east).
- It connects the Java Sea (Pacific Ocean) to the Indian Ocean and serves as a critical alternative to the congested Strait of Malacca.
- Length: Approximately 60 kilometers.
- Width: Around 20 kilometers at its narrowest point.
- Depth: Significantly deeper than the Sunda and Malacca Straits, with depths ranging from 250 to 1,300 meters.
- Part of the Wallace Line: The strait is a biogeographical boundary between Asian and Australasian flora and fauna, making it ecologically significant.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus:
- Prelims – CURRENT EVENT
Context: The World Economic Forum (WEF) is holding its Annual Meeting from January 20 to 24 in Davos, Switzerland.
Background: –
- Union Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw will head the Indian delegation. Maharashtra Chief Minister Devendra Fadnavis, Telangana Chief Minister Revanth Reddy, and Andhra Pradesh Chief Minister Chandrababu Naidu Chief will also attend.
Key takeaways
- Founded: 1971 by Klaus Schwab, originally known as the European Management Forum.
- Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
- Nature: An international, non-governmental organization.
- Objective: To improve the state of the world by fostering public-private cooperation.
- Key Focus Areas: Economic growth, sustainable development, technological innovation, social inclusion, and global governance.
- The WEF is largely funded by its partnering corporations.
Functions of the WEF
- Platform for Dialogue:
- Brings together political leaders, business executives, academicians, and civil society representatives.
- Focuses on addressing global challenges such as climate change, poverty, inequality, and economic instability.
- Annual Meetings: The Davos Agenda, held annually in Davos, Switzerland, serves as a platform for addressing pressing global issues.
- Regional and thematic meetings are also organized.
- Publishes key reports such as:
- Global Competitiveness Report
- Global Gender Gap Report
- Global Risks Report
- Future of Jobs Report
- Energy Transition Index
Source: Indian Express
Practice MCQs
Q1.) Which of the following reports is published by the World Economic Forum (WEF)?
- Global Risks Report
- World Development Report
- Global Gender Gap Report
- Human Development Report
Select the correct option:
a) 1 and 3 only
b) 2 and 4 only
c) 1, 3, and 4 only
d) 1, 2, and 3 only
Q2.) Which of the following straits is the narrowest at the Philips Channel near Singapore?
- a) Sunda Strait
b) Strait of Malacca
c) Lombok Strait
d) Makassar Strait
Q3.) The Sunda Strait connects which two water bodies?
- a) Andaman Sea and South China Sea
b) Indian Ocean and Java Sea
c) Pacific Ocean and Banda Sea
d) Timor Sea and Java Sea
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ Today’s – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs
ANSWERS FOR 17th January – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – c











