IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus:
- Prelims & Mains – CURRENT EVENT
Context: National Girl Child Day, an initiative of the Ministry of Women and Child Development, is celebrated every year on January 24.
Background: –
- The day is aimed at promoting awareness about the rights of the girl child and to increase awareness on the importance of girls’ education, their health and nutrition. It also aims at promoting the position of girls in the society to make their living better.
Key schemes for girl child
NPS Vatsalya Scheme
- The scheme was launched in 2024. It is a new pension scheme for children in the age group of 0 to 18 years.
- A parent can deposit a minimum of 1000 per month and a maximum with no limit. This account will be operated by the parents until the child turns 18, after which the account will be in the name of the children.
- Once the child turns 18, the account can be seamlessly converted into a regular NPS account or a non-NPS scheme. It is regulated and administered by the Pension Fund Regulatory Authority of India (PFRDA).
Beti Padhao, Beti Bachao:
- On January 22, the BBBP scheme completed 10 years since its launch in 2015.
- The Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao Scheme, launched to address the decline in Child Sex Ratio and related issues of empowerment of girls, is implemented by states with 100% central assistance.
- It set several targets concerning the nutritional status of girls, their attendance in schools, the provision of adequate infrastructure in schools and so on.
Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana:
- Launched in 2015 as part of the Indian government’s ‘Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao’ campaign, Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana is a small savings scheme designed to help parents of girl children accumulate a corpus for their daughter’s education and marriage.
- Parents of a girl child aged 10 years or younger can invest in this scheme. The scheme allows for a minimum and maximum annual deposit of Rs.250 and Rs.1.5 lakh, respectively.
- Deposits to the account can be made for 15 years from the account opening date. The account, however, has a lock-in period of 21 years, implying that deposits mature after 21 years.
CBSE Udaan Scheme:
- Launched in 2014 by Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) under the guidance of the Ministry of Education aims to address low enrollment of women in STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics), specifically in the Indian engineering colleges.
- The CBSE provides free tutorials for students of class 11 and class 12 to crack engineering entrance exams including the Joint Entrance Exam (JEE).
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus:
- Prelims & Mains – POLITY
Context: As India prepares to celebrate its 76th Republic Day under the theme “Swarnim Bharat: Virasat aur Vikas” (Golden India: Legacy and Progress), the day also marks a historic moment to reflect on the core values of the Indian Constitution as reflected in the preamble.
Background: –
- The idea of “constitutional patriotism,” first introduced by German social theorist Jürgen Habermas in the 1990s within a primarily European context, has taken on a unique and dynamic character in India. The Preamble, embodying the nation’s core values of justice, liberty, equality, and fraternity, holds a deeply symbolic and aspirational status, making constitutional patriotism in India a spirited and vibrant expression of loyalty to democratic principles.
Key takeaways
- The preamble begins with the words, “We, the people of India”. This invocation is significant as it stands in sharp contrast to the often unchecked and emotional invocation of “the people” by populist movements.
- The people invoked in the Preamble are presented with a sense of sobriety, as a constitutionally mediated entity, which prevents any possibility of such populist invocation of the people from easily descending into tyranny.
- Sovereign: The term refers to three aspects:
- first, sovereignty connotes a supremacy of power that the state claims and tolerates no power above it;
- second, there is no possibility or threat of insubordination below the state that could threaten its integrity;
- and third, this sovereignty is crystallised in the form of popular representation in Parliament, which represents the will of the people through universal adult franchise.
- Socialist:
- The term was not present in the original version. It was introduced into the Preamble in 1976 through the 42nd constitutional amendment along with the term “secular”.
- There has been controversy around the term socialist being part of the Preamble. Dr. B.R. Ambedkar was against the inclusion as he felt that its presence would unfairly constrain future governments.
- Secular:
- The word secular does not imply a lack or negation of religion. Instead, it simply means that in the interests of maintaining religious harmony among India’s numerous religions and belief systems, the state shall maintain a secular stance.
- Republic:
- The term republic in the Preamble of the Constitution connotes that the head of the state has to be an elected figure and not a hereditary monarch, which continues to be the case to this day in the United Kingdom.
- The landmark Keshavananda Bharati case (1973) ruled that the Preamble is a part of the Constitution.
- The Keshavananda Bharati judgement is particularly significant as it gave rise to the “basic structure” doctrine of the Constitution and included the Preamble in it.
- This judgement marked a departure from an earlier judgement in the Berubari Union Case (1960) that did not view the Preamble as part of the Constitution.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus:
- Prelims – CURRENT EVENT
Context: The Global Plastic Action Partnership (GPAP) has recently reached a significant milestone by expanding its network to include 25 countries.
Background:
- With a combined population of over 1.5 billion people, the expansion highlights a growing global effort to address the urgent issue of plastic pollution. Seven new countries — Angola, Bangladesh, Gabon, Guatemala, Kenya, Senegal, and Tanzania — have joined this collaborative effort.
Key takeaways
- The Global Plastic Action Partnership (GPAP) is a multistakeholder platform launched by the World Economic Forum in 2019.
- Its primary goal is to accelerate the transition to a circular economy for plastics and tackle plastic pollution on a global scale.
Objectives
- Reduce Plastic Pollution: GPAP aims to reduce plastic waste leakage into the environment, particularly oceans.
- Promote Circular Economy: Encourage the reuse and recycling of plastics to minimize waste and environmental impact.
- Foster Collaboration: Bring together governments, businesses, and civil society to work towards common goals.
Key Initiatives
- National Action Roadmaps: Tailored strategies for each participating country to address plastic waste management.
- Investment Mobilization: GPAP has mobilized significant investments to support sustainable plastic management.
- Job Creation: Focus on creating green jobs, especially for informal waste workers.
- Awareness and Education: Raise awareness about the impact of plastic pollution and promote sustainable practices.
Source: Down To Earth
Syllabus:
- Prelims – ENVIRONMENT
Context: The population of saltwater crocodiles in Odisha’s Bhitarkanika National Park has marginally increased in 2025. Forest officials counted 1,826 crocodiles during the recent annual reptile census whereas in 2024, they sighted 1,811 reptiles.
Background: –
- The forest department had stopped the crocodile breeding and rearing programme in 2024 in the park as the crocodile population reached a saturation point.
Key takeaways
- Bhitarkanika National Park is a prominent protected area in Odisha, known for its rich biodiversity, mangrove ecosystems, and unique wildlife.
- Situated in the delta region of the Brahmani, Baitarani, and Dhamra rivers.
- Designation: Declared a national park in 1998.
- Part of the Bhitarkanika Wildlife Sanctuary (declared in 1975).
- Designated as a Ramsar Site in 2002 for its wetland significance.
- Flora:
- One of India’s largest mangrove ecosystems.
- Supports diverse plant species such as Avicennia, Rhizophora, and Heritiera.
- Fauna:
- Known for saltwater crocodiles, with one of the largest breeding populations in India.
- Other species include Indian python, king cobra, water monitor lizard, spotted deer, and wild boar.
- Rich avian biodiversity, including migratory birds like open-billed storks and herons.
- Located within the close vicinity of the Bhitarkanika National Park is Odisha’s only Turtle Sanctuary. A part of the Gahirmatha Beach, the Turtle Sanctuary is the place where one can spot Olive Ridley Turtles.
Source: Down To Earth
Syllabus:
- Prelims – ENVIRONMENT
Context: In 2024, the yearly average level of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide (CO2) rose faster over the prior year than ever before in the 67-year-old Keeling Curve record.
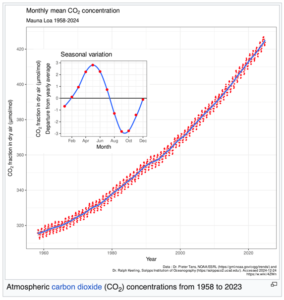
Background: –
- When researchers took the average readings for all 12 months in 2024, the average was 3.58 parts per million (ppm) higher than for 2023’s average. That broke the record for largest jump set in 2016 of 3.41 ppm. In both instances, the climate pattern El Niño played a role.
Key takeaways
- The Keeling Curve is a graphical representation of the concentration of carbon dioxide (CO₂) in Earth’s atmosphere over time.
- Origin: Named after Dr. Charles David Keeling, who began continuous monitoring of atmospheric CO₂ levels in 1958 at the Mauna Loa Observatory in Hawaii.
- The curve shows the steady increase in atmospheric CO₂ levels since 1958.
- It also captures seasonal fluctuations caused by natural processes like photosynthesis and plant respiration.
- CO₂ levels decrease during spring and summer as plants absorb CO₂ through photosynthesis, and increase during fall and winter due to plant decay.
Source: Scripps
Practice MCQs
Q1.) With reference to the Global Plastic Action Partnership (GPAP), consider the following statements:
- GPAP was launched by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) in 2019 to tackle global plastic pollution.
- One of the objectives of GPAP is to promote a circular economy for plastics by encouraging reuse and recycling.
- The recent expansion of GPAP includes countries such as Angola, Bangladesh, and Kenya.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Q2.) With reference to the Keeling Curve, consider the following statements:
- It represents the variations in global temperatures over time.
- It was developed in 1858.
- The Keeling Curve shows a steady increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO₂) levels due to human activities.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Q3.) With reference to the Bhitarkanika National Park, consider the following statements:
- It is located in the delta region of the Brahmani, Baitarani, and Dhamra rivers in Odisha.
- It is a designated Ramsar Site, recognized for its significant mangrove ecosystems and wetland biodiversity.
- Bhitarkanika is known as a major nesting site for Great Indian Bustard.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ Today’s – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs
ANSWERS FOR 23nd January – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – d
Q.3) – b











