IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus:
- Prelims & Mains – GEOGRAPHY
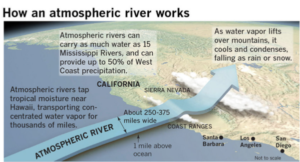
Context: Following an unusually dry January, a powerful atmospheric river known as the ‘Pineapple Express’ has been sweeping through northern and central California, bringing periods of strong winds, heavy rain, and snowfall in the hills.
Background: –
- Pineapple Express gets its name from the warm, moist air drawn into the system, originating near Hawaii, a region known for its pineapple production.
Key takeaways
- Pineapple Express is a type of atmospheric river— a narrow, fast-moving “river in the sky” that transports significant moisture over long distances. The warm air and high humidity it carries from the Pacific lead to heavy rainfall when the system reaches land.
- The atmospheric rivers are long, narrow bands in the atmosphere that transport vast amounts of water vapour from the tropics. Their size and strength can differ significantly, but on average, they carry a volume comparable to the flow of the Mississippi River at its mouth. Exceptionally strong atmospheric rivers can transport up to 15 times that amount.
- When atmospheric rivers make landfall, they typically release this moisture as rain or snow, often covering a vast region as they move inland.
- The atmospheric rivers in the sky occur often on the West Coast but can happen in other locations, including the eastern United States, where they often channel moisture from the Caribbean.When this moisture begins to interact with land, it can fall as rain or snow.
- Although atmospheric rivers come in different shapes and sizes, for one to be a “true Pineapple Express,” location matters. The tail end, where the moisture is pulled into the atmosphere, must start near Hawaii. Then the river must stretch continuously through the atmosphere to the US West Coast.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus:
- Prelims – ENVIRONMENT
Context: The International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA) has officially come into force as a treaty-based, inter-governmental organisation, becoming a fully functional international legal entity.
Background: –
- The Ministry of External Affairs (MEA), acting as the Depository for the Framework Agreement, confirmed that five countries – Nicaragua, Eswatini, India, Somalia, and Liberia – have deposited their instruments of ratification, acceptance, or approval, making them the founding members of the IBCA.
Key takeaways
- The IBCA was launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on April 9, 2023, during an event commemorating the 50th anniversary of Project Tiger.
- The initiative’s main objective is the conservation of seven major big cat species: the Tiger, Lion, Leopard, Snow Leopard, Cheetah, Jaguar, and Puma.
- Members: As of now, 27 countries have consented to join, including India, Nicaragua, Eswatini, Somalia, and Liberia.
- The membership of the IBCA is open to all UN member countries, especially those that host these species, and to non-range countries that are interested in supporting big cat conservation efforts.
- The IBCA has a framework agreement, and its headquarters is in India. It includes an Assembly of Members, a Standing Committee, and a Secretariat.
- The Union Cabinet approved a one-time budgetary support of Rs 150 crore for the IBCA for the period from 2023-24 to 2027-28.
- The IBCA aims to become self-sustaining after the initial five years through membership fees, contributions from bilateral and multilateral organizations, and the private sector.
Source: DD News
Syllabus:
- Prelims & Mains – CURRENT EVENT
Context: The Union Budget 2025 has increased the allocation for PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana (SGMBY) scheme to ₹20,000 crore, a sharp rise from the ₹11,100 crore in the FY25 Revised Estimates (RE) and ₹6,250 crore in the FY25 Budget Estimates (BE).
Background:
- According to Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) targets, India has committed to reducing the emission intensity of its GDP by 45 percent by 2030 from the 2005 level and achieving about 50 percent cumulative electric power installed capacity from non-fossil fuel-based energy resources by 2030.
Key takeaways
- The Pradhan Mantri Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana (PMSG) is a flagship initiative launched by the Government of India with the twin objectives of promoting renewable energy and ensuring affordable electricity access.
- The scheme aims to install rooftop solar systems in one crore residential households. This is expected to not only reduce household electricity bills (by providing up to 300 units of free electricity per month) but also help reduce the nation’s carbon footprint.
Key Components of the Scheme
- Residential consumers are provided with a subsidy based on their system capacity. For example, for the first 2 kW of rooftop solar capacity, a subsidy of up to 60% (at benchmark costs) is available, while for the next 1 kW (i.e. capacity between 2 and 3 kW), the subsidy is capped at 40% of the additional cost. No subsidy is provided beyond 3 kW capacity.
- Loan Facilities: In addition to the subsidy, the scheme offers access to collateral-free, low-interest loans for eligible households to finance the installation of rooftop solar systems.
- National Portal: Applications are processed through a dedicated online portal, where households register using their consumer details and select from a network of government-registered vendors.
- Vendor and DISCOM Coordination: The implementation is carried out by registered vendors and coordinated at the state level by Distribution Companies (DISCOMs) or power departments, ensuring that installations meet the technical and quality benchmarks.
- Model Solar Village Initiative: To further promote renewable energy at the grassroots, the scheme includes establishing one Model Solar Village per district.
Who are eligible to apply for the Scheme?
- The applicant must be an Indian citizen.
- Must own a house with a roof that is suitable for installing solar panels.
- The household must have a valid electricity connection.
- The household must not have availed of any other subsidy for solar panels.
Source: Moneycontrol
Syllabus:
- Prelims – SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
Context: ISRO reported the partial failure of its NVS-02 navigation satellite due to the non-firing of its engines in space. This was the latest in a series of setbacks suffered by the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), operationally referred to as the Navigation with India Constellation (NavIC) system.
Background: –
- The IRNSS was conceived in 1999 following the war in Kargil, during which India’s military could not use the American Global Positioning System (GPS) in the conflict zone.
Key takeaways
- An indigenous seven-satellite constellation serving both defence and civilian needs was proposed to be put in place by 2016, and the first satellite, IRNSS 1A, was launched on July 1, 2013.
- Eleven years later, however, only five of the 11 satellites launched in the NavIC program – including replacements for failed satellites – are fully operational.
- After IRNSS-1A in 2013, the IRNSS-1B, 1C, 1D, 1E, 1F, 1G, 1H, 1I, 1J, and 1K were launched between 2014 and January, 2025.
- Following the launch of IRNSS-1G, the seventh in the series in 2016, ISRO had said that “the successful launch of the satellite signifies the completion of the IRNSS constellation.
What went wrong with the satellites?
- Mid-2016 onward, there were reports of failures of the rubidium atomic clocks used in several navigation satellites, including ISRO’s IRNSS and the European Space Agency’s (ESA’s) Galileo Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS). There are three atomic clocks on each IRNSS satellite.
- The engine failure on the IRNSS-1K (or NVS-02) launched last month, which has left it in a sub-optimal orbit around Earth, means that six of the 11 IRNSS satellites launched so far have been partial failures.
Why is the IRNSS/ NavIC system important for India?
- The NavIC satellites provide two types of services – Standard Positioning Service which is for general and commercial use, and Restricted Service which is meant for the defence forces – over the Indian landmass and neighbouring regions.
- The system provides positioning data at all times with position accuracy better than 20 metres during all weather conditions, anywhere within India and a region extending about 1,500 km around India on dual frequencies in L5 and S band.
- A primary reason to develop an indigenous system like the IRNSS despite the existence of global systems such as the GPS (US), GLONASS (Russia), Galileo (Europe), Beidou (China), and QZSS (Japan), is the reliability that it offers in defence use.
- For NavIC to become ubiquitous in the Indian subcontinent, ISRO will have to sell its capabilities to general positioning service providers such as mobile phone and vehicle manufacturers, etc.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus:
- Prelims – SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
Context: The timeline for quantum computing’s impact remains debated, with estimates ranging from imminent to 15 years away. Regardless, its rapid computational power poses a major cybersecurity threat, as it can break traditional encryption. This underscores the need for post-quantum cryptography (PQC).
Background: –
- Quantum computers use qubits, which can represent 0, 1, or a combination of both simultaneously, allowing them to process data much faster than traditional computers. This capability makes them a potential tool for mounting lethal cyberattacks if security layers are not prepared.
Key takeaways
- Post-quantum cryptography (PQC) refers to cryptographic algorithms designed to be secure against attacks from quantum computers.
- As quantum computers advance, they pose a threat to traditional cryptographic systems such as RSA, ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography), and DH (Diffie-Hellman), which rely on the difficulty of factoring large numbers or solving discrete logarithm problems—both of which quantum computers can efficiently solve using Shor’s algorithm.
Threats Posed by Quantum Computing
- Store Now, Decrypt Later (SNDL) Attack
- In this attack, adversaries intercept and store encrypted data today with the intention of decrypting it later when quantum computers become powerful enough to break existing cryptographic systems.
- This is a major concern for long-lived sensitive data (e.g., government communications, financial transactions, military secrets).
- Even if quantum computers are not yet available, encrypted data stolen today could be compromised in the future.
- Breaking Public-Key Cryptography
- Quantum computers can use Shor’s Algorithm to efficiently factor large numbers and solve discrete logarithms, making widely used encryption protocols like RSA, ECC, and Diffie-Hellman obsolete.
- This threatens secure communications, digital signatures, and online authentication systems.
- Attacks on Symmetric Cryptography
- Grover’s Algorithm allows quantum computers to search databases and brute-force encryption keys much faster than classical computers.
- While symmetric encryption remains relatively secure, its key sizes need to double to maintain the same level of security.
- Quantum-Enhanced Cyberattacks
- Quantum computing could enhance AI-driven cyberattacks, allowing faster exploitation of vulnerabilities in software and networks.
- Quantum machine learning algorithms might optimize phishing, password cracking, or intrusion detection evasion.
- Quantum Threats to Blockchain and Digital Signatures
- Cryptographic signatures securing blockchains and cryptocurrencies are vulnerable to quantum attacks.
- A sufficiently powerful quantum computer could forge digital signatures, allowing an attacker to steal funds or manipulate transactions.
Source: Hindustan Times
Practice MCQs
Q1.) The “Store Now, Decrypt Later” (SNDL) attack in the context of quantum computing refers to:
(a) Storing encrypted data today with the aim of decrypting it later using quantum computers.
(b) Using quantum computing to break traditional passwords in real time.
(c) Developing post-quantum cryptographic algorithms for secure data transmission.
(d) Encrypting data with quantum-resistant algorithms to prevent future cyber threats.
Q2.) With reference to the ‘Pineapple Express,’ consider the following statements:
- It is a type of atmospheric river that originates near the Hawaiian region and transports moisture towards the U.S. West Coast.
- It is associated with bringing heavy rainfall and snowfall to regions where it makes landfall.
- The Pineapple Express is unique to the North American region and does not occur elsewhere in the world.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Q3.) Consider the following statements regarding the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA):
- It is an intergovernmental treaty-based organization focused on the conservation of seven big cat species.
- India is the headquarters of IBCA.
- Only range countries that host big cat species can become members of IBCA.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ Today’s – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs
ANSWERS FOR 4th February – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – d
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – b













