IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus:
- Prelims & Mains – ECONOMY
Context: After holding the repo rate at 6.50 per cent for two years, the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) six-member Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) reduced the key policy rate by 25 basis points (bps) to 6.25 per cent on February 7.
Background: –
- This marks the first repo rate cut in nearly five years and will likely lead to a fall in interest rates and equated monthly instalments (EMIs) on home and personal loans.
Key takeaways
- The repo rate is the interest rate at which the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) lends money to commercial banks. The term “repo” stands for Repurchase Agreement or Repurchasing Option.
- Mechanism: When commercial banks need funds, they can sell securities to the RBI with an agreement to repurchase them at a predetermined price. The difference between the sale and repurchase price is the interest charged, which is the repo rate.
- The main reason behind the repo rate cut is to stimulate economic growth by making borrowing cheaper, leading to increased spending and investment, ultimately supporting job creation and employment.
How might the repo rate cut impact the economy?
- All external benchmark lending rates (EBLR) — lending rates set by the banks based on external benchmarks such as the repo rate — will come down by 25 bps, giving relief to borrowers as their equated monthly instalments (EMIs) will also fall.
- Lenders may also reduce interest rates on loans that are linked to the marginal cost of fund-based lending rate (MCLR, or the minimum lending rate below which a bank is not allowed to lend), where the full transmission of a 250-bps hike in the repo rate between May 2022 and February 2023 has not happened.
- EMIs on home and vehicle loans will come down, making it easier for individuals to repay their debts.
- A lower repo rate makes borrowing cheaper for individuals and businesses, which can lead to increased spending and investment, thereby boosting economic growth.
- However, a lower repo rate can lead to higher inflation, as increased money supply and lower interest rates can drive up prices. It can reduce the interest earned on savings, making it less attractive for individuals to save.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus:
- Prelims & Mains – ENVIRONMENT
Context: The marine heatwaves (MHWs) linked to the death of more than 30,000 fish off the coastal Western Australia in January were made up to 100 times more likely to occur due to climate change.
Background: –
- The MHWs began in September 2024 and are still ongoing in the region.
- The current MHWs are the second-worst in Western Australia’s recorded history. The region saw its most intense MHWs during the 2010–11 summer, when temperatures soared to 5 degrees Celsius above average.
Key takeaways
- A marine heatwave occurs when the surface temperature of a particular region of the sea rises to 3 or 4 degrees Celsius above the average temperature for at least five days.
- MHWs can last for weeks, months or even years.
- A 2021 report by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) said MHWs have increased by 50% over the past decade and now last longer and are more severe. MHWs have been recorded in surface and deep waters, across all latitudes, and in all types of marine ecosystems, the report said.
Why have marine heatwaves intensified?
- The primary reason is the climate crisis. As global temperatures have soared to 1.3 degrees Celsius above the pre-industrial levels, 90% of the extra heat has been absorbed by the ocean.
- Global mean SST increased close to 0.9 degrees Celsius since 1850, and the rise over the last four decades is around 0.6 degrees Celsius. As a result, MHWs have become more frequent, long-lasting, and severe.
Impact Of Marine Heatwaves
- MHWs can be devastating for marine life. For example, the 2010-11 MHWs in Western Australia caused large-scale fish kills. It also destroyed klep forests and fundamentally altered the ecosystem of the coast. Kelps usually grow in cooler waters, providing habitat and food for many marine animals.
- These heatwaves contribute to coral bleaching, which reduces the reproductivity of corals and makes them more vulnerable. Thousands of marine animals depend on coral reefs for survival and damage to corals could, in turn, threaten their existence.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus:
- Prelims – GEOGRAPHY
Context: Days after the capture of Goma, M23 rebels and allied Rwandan forces have launched a new offensive in the eastern Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC).
Background:
- The ongoing insurgency in the DRC, which is the continuation of protracted turmoil and insecurity that has plagued the region for generations, is intertwined with the region’s geography and resources.
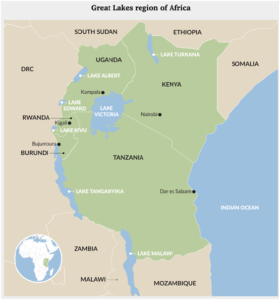
Key takeaways
The Great Lakes Region of Africa
- The Great Lakes Region of Africa, located in East and Central Africa, is a series of lakes in and around the East African Rift Valley.
- This network of large freshwater lakes in the heart of Africa is endowed with various natural resources, which give the East African Rift Valley a unique ecology and socioeconomic significance.
- These lakes include Lake Victoria, Lake Tanganyika, Lake Malawi, Lake Albert, Lake Kivu and Lake Edward. They are surrounded by ten riparian states that include Burundi, the DRC, Ethiopia, Kenya, Malawi, Mozambique, Rwanda, Tanzania, Uganda, and Zambia.
- Most of them have a traumatic past, while violent conflict is endemic in the region.
- The resource curse—whereby abundant natural wealth spurs conflict and corruption—is a recurring theme.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus:
- Prelims – GEOGRAPHY
Context: A significant temperature drop has been observed across North India due to a western disturbance currently positioned over North Pakistan, the India Meteorological Department (IMD) reported.
Background: –
- The system is gradually moving eastward, impacting weather patterns in the region.
Key takeaways
- Western Disturbances are extratropical storm systems that originate over the Mediterranean Sea/ Caspian Sea region. These systems travel eastward across the Middle East into the Indian subcontinent, particularly affecting the northern and northwestern parts of India during the winter months (November to April).
Meteorological Features:
- Moisture Transport: They carry moisture from the Mediterranean, which, upon interacting with the Himalayan barrier, leads to cloud formation and precipitation.
- Weather Impact: In the plains of northern India, they cause light to moderate rainfall, while in the higher reaches of the Himalayas, they result in significant snowfall.
Agricultural and Hydrological Importance:
- Winter Rainfall: The rainfall from Western Disturbances is critical for replenishing soil moisture and supporting the rabi (winter) cropping season. Crops such as wheat, barley, and mustard benefit from the moisture provided by these systems.
- Snowfall Contribution: Snowfall in the Himalayas not only supports winter tourism and local ecosystems but also plays a crucial role in feeding the major rivers during the melt season, which is vital for agriculture and water supply in the summer.
Source: DD News
Syllabus:
- Prelims – ENVIRONMENT
Context: Australian scientists have produced the world’s first kangaroo embryo through in vitro fertilisation (IVF), a breakthrough they say could help save other species from extinction.
Background: –
- The feat provides important insights into marsupial breeding and could aid efforts to improve the genetic diversity of endangered species such as the koala, Tasmanian devil, northern hairy-nosed wombat and Leadbeater’s possum.
Key takeaways
- Marsupials are a group of mammals characterized by premature birth and continued development of their young in a pouch (marsupium).
- They belong to the infraclass Marsupialia under the class Mammalia.
- Unlike placental mammals, marsupials give birth to underdeveloped young, which then crawl into the mother’s pouch to continue development.
Global Distribution:
- Australia & Nearby Islands – The largest diversity of marsupials, including kangaroos, koalas, wombats, and Tasmanian devils.
- South America – Home to species like the opossum.
- North America – The Virginia Opossum is the only marsupial found in the wild.
Marsupials in Evolution & Biogeography:
- They diverged from placental mammals around 160 million years ago.
- Australia’s long geographic isolation led to the dominance of marsupials over placental mammals.
- Convergent Evolution – Many marsupials resemble placental mammals due to similar ecological niches (e.g., the marsupial mole vs. placental mole).

Conservation & Ecological Importance:
- Many marsupial species face threats due to habitat destruction, invasive species, and climate change.
- Conservation efforts in Australia focus on predator control (feral cats, foxes) and habitat restoration.
- Marsupials play key ecological roles as herbivores, pollinators, and prey species in their ecosystems.
- Marsupials are considered strong evidence of continental drift, particularly in the context of the breakup of the supercontinent Gondwana.
Source: BBC
Practice MCQs
Q1.) The Great Lakes Region of Africa, frequently in the news, includes which of the following lakes?
- Lake Victoria
- Lake Baikal
- Lake Tanganyika
- Lake Malawi
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 3, and 4 only
(c) 2, 3, and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Q2.) With reference to Western Disturbances, consider the following statements:
- Western Disturbances originate over the Mediterranean Sea and move eastward toward the Indian subcontinent.
- They are most active during the summer monsoon season in India.
- Western Disturbances are responsible for winter rainfall in North India and snowfall in the Western Himalayas.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 2 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Q3.) Consider the following statements regarding Marine Heatwaves (MHWs):
- A Marine Heatwave is defined as a sea surface temperature rise of at least 1°C above the average for three consecutive days.
- MHWs have been increasing in frequency and intensity due to global warming.
- They contribute to coral bleaching, marine biodiversity loss, and ecosystem disruptions.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ Today’s – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs
ANSWERS FOR 6th February – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – b














