IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Category: ART & CULTURE
Context: The Indian government has issued a legal notice to halt the “unethical” auction of ancient gem relics, which it said should be treated as the sacred body of the Buddha.
Decoding the context: The legal notice has been served on Sotheby’s Hong Kong and Chris Peppé, one of three heirs of William Claxton Peppé, a British colonial landowner who in 1898 excavated the gems on his estate in northern India, who are selling the relics.
Learning Corner:
- Piprahwa is a village in Siddharthnagar district, Uttar Pradesh, near the India-Nepal border.
- It is situated close to Kapilavastu, the ancient capital of the Shakya clan, to which Gautama Buddha belonged.
Discovery & Excavation:
- Excavated in 1898 by William Claxton Peppé, a British colonial indigo planter, on his estate. He discovered a large stupa (Buddhist burial mound) containing a stone coffer with relics and jewel-encrusted caskets.
- The stone coffer bore a Brahmi inscription in Prakrit, dated to the 3rd century BCE. It translates to: “These relics of the Blessed One (Buddha), the Lord of the Shakyas, are deposited by the Shakya brothers…”
- This is believed to indicate that these relics belonged to Gautama Buddha himself, making it a major archaeological and religious find.
- Division of Buddha’s relics among eight mahajanapadas post his Mahaparinirvana is documented in Mahaparinibbana Sutta.
- The 1971-73 excavations by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) under K.M. Srivastava found older relics (400-500 BCE) below Peppé’s level, suggesting Piprahwa as one of the original eight stupas built after Buddha’s death.
Source : Guardian
Category: POLITY
Context: The President of India, Smt Droupadi Murmu graced the launch of the Mediation Association of India and addressed the First National Mediation Conference 2025 in New Delhi.
Decoding the context: Speaking on the occasion, the President said that the Mediation Act, 2023 was the first step in consolidating the civilisational legacy. She emphasised that the dispute resolution mechanism under the Mediation Act should be effectively extended to rural areas so that the Panchayats are legally empowered to mediate and resolve the conflicts in villages.
Learning Corner:
- Mediation is a voluntary, non-binding Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) process where a neutral third party (mediator) facilitates dialogue between disputing parties to help them reach a mutually acceptable solution.
Mediation Act, 2023
- Enactment: Passed by Rajya Sabha (August 1, 2023), Lok Sabha (August 7, 2023), and received Presidential assent on September 14, 2023; notified on September 15, 2023.
- The Act aims to expand the scope and statutorily recognize pre-litigation mediation, online mediation, community mediation, conciliation under the definition of ‘mediation’. This would have the effect of dispensing with the concept of conciliation, in line with the international practice of using the terms ‘mediation’ and ‘conciliation’ interchangeably.
- Objective: Promotes institutional mediation to resolve civil and commercial disputes, aiming to reduce judicial burden and foster cost-effective, time-bound resolutions.
Key Features:
- The Act apply to mediations conducted in India. It would inter alia apply to mediations where:
- all parties habitually reside or incorporated in or have their place of business in India, or
- the mediation agreement imports the applicability of the Mediation Act, or
- there is an international mediation in relation to a commercial dispute provided one of the parties is an individual who is a national or habitually resides in a country other than India, or a body corporate/association/body of individuals having place of business outside India, or
- Further, where one of the parties is the Central/State Government or any entity/body controlled or owned by such Government, the Mediation Act will be applicable only in case of a) commercial disputes, or b) any other disputes as notified
- Exclusion: It does not apply to mediation conducted outside of India or to disputes not fit for mediation, such as those involving minors, criminal offenses, or third-party rights.
- Time Limit: Mediation must conclude within 120 days, extendable by 60 days with mutual consent.
- Mediated Settlement Agreement (MSA): Final and binding, enforceable as a court decree; can be challenged within 90 days on grounds like fraud or corruption.
- Mediation Council of India (MCI): To be established for mediator certification, training, and regulation; recognizes mediation service providers.
Differences Between Mediation, Arbitration, and Conciliation
| Aspect | Mediation | Arbitration | Conciliation |
| Nature | Voluntary; mediator facilitates dialogue. | Binding; arbitrator imposes a decision (award). | Voluntary; conciliator actively suggests solutions. |
| Outcome | Non-binding unless formalized as MSA. | Legally binding arbitral award. | Non-binding unless parties agree to terms. |
| Third Party Role | Mediator is neutral, does not impose solutions. | Arbitrator acts as a judge, decides the case. | Conciliator proposes settlements, more proactive than mediator. |
| Legal Framework | Mediation Act, 2023; includes conciliation. | Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996. | Now under Mediation Act, 2023 (previously Part III of Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996). |
| Enforceability | MSA enforceable as a court decree. | Award enforceable under Arbitration Act. | Settlement enforceable only if formalized (now as MSA). |
Source : PIB
Category: GEOGRAPHY
Context: The Indian government opened two gates at the Baglihar Hydroelectric Power Project Dam, built on the Chenab River in Ramban.
Decoding the context: The gates have reportedly been opened to manage the rising water levels caused due to the heavy rainfall in Jammu and Kashmir. This comes after the centre had shut all the dam gates to regulate the water flow to Pakistan.
Learning Corner:
- The Chenab River originates in the upper Himalayas in Himachal Pradesh’s Lahaul and Spiti district, formed by the confluence of the Chandra and Bhaga rivers near Keylong.
- The Bhaga river originates from Surya taal lake, which is situated a few kilometers west of the Bara-lacha la pass in Himachal Pradesh. The Chandra river originates from glaciers east of the same pass (near Chandra Taal)
- In the Mahabharata, the common name of the river was Chandrabhaga. The river was called Asikni (Sanskrit: असिक्नी) in the Rigveda.
- The river flows through Himachal Pradesh, then enters Jammu and Kashmir. It then enters Pakistan’s Punjab province, where it eventually merges with the Sutlej River to form the Panjnad, which ultimately flows into the Indus River.
- Drainage basin: Covers 26,155 sq km in India, primarily draining the southern slopes of the Pir Panjal Range, Jammu hills, and foothills.
Strategic and Economic Significance
- Indus Waters Treaty (IWT): Under the 1960 IWT, Chenab is a Western River allocated to Pakistan for unrestricted use, but India can build run-of-the-river projects for hydropower. The treaty was suspended in April 2025 after the Pahalgam terror attack.
- Hydropower Projects: Hosts major run-of-the-river dams in J&K like Baglihar (900 MW, Ramban) and Salal (690 MW, Reasi).
- Agricultural Dependence: Pakistan relies on Chenab for 60% of its Punjab irrigation; In India, Chenab supports J&K’s agriculture but is underutilized due to limited storage.
Source : Economic Times
Category: INTERNATIONAL
Context: India hit out strongly at the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) for its recent statement on the Pahalgam terror attack, calling it “absurd” and “politically motivated.
Decoding the context: The Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) issued a statement expressing “deep concern over the deteriorating security environment in South Asia.’ The statement also said that India’s “unfounded allegations against the Islamic Republic of Pakistan” were the factor behind escalating tensions between Delhi and Islamabad.
Learning Corner:
- The Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC), founded in 1969, is the second-largest intergovernmental organization after the UN, comprising 57 member states, primarily Muslim-majority countries, spanning four continents.
- Headquartered in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, its primary aim is to promote solidarity among Muslim nations, safeguard Islamic interests, and address global issues affecting the Muslim world.
Key Objectives
- Enhance unity and cooperation among member states.
- Protect Islamic holy sites and support the Palestinian cause.
- Promote economic, cultural, and scientific collaboration.
- Address issues like terrorism, poverty, and education.
Structure
- Summit of Heads of State: Meets every three years; highest decision-making body.
- Council of Foreign Ministers (CFM): Annual meetings to implement policies.
- General Secretariat: Led by the Secretary-General (Hissein Brahim Taha since 2020), manages daily operations.
- Specialized Organs: Includes Islamic Development Bank (IsDB) and Islamic Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (ISESCO).
OIC and India
- India’s ties with OIC remain tenuous, primarily due to Pakistan’s influence.
- India has criticized OIC resolutions on Jammu & Kashmir.
- India, despite having the third-largest Muslim population globally (over 200 million), is not a member.
Source : Hindustan Times
Category: GEOGRAPHY
Context: Recently, a large-scale blackout occurred in Spain and Portugal. There was widespread interruption in power supply in the Iberian Peninsula.
Decoding the context: An investigative commission has been launched in Spain and a request has been made by the Portuguese government for an EU agency to perform an independent audit.
Learning Corner:
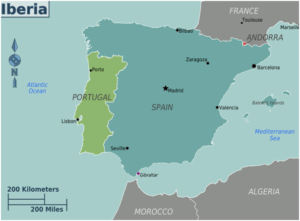
- Located in southwestern Europe, it is the third largest peninsula in Europe (after the Scandinavian and Balkan peninsulas).
- Bordered by:
- Atlantic Ocean (west and northwest)
- Mediterranean Sea (southeast)
- Pyrenees Mountains (northeast) — natural border with France.
- Countries on the peninsula:
- Spain (covers ~85% of the land area)
- Portugal
- Andorra (microstate in the Pyrenees)
- British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar
Modern Relevance:
- Spain and Portugal are EU and NATO members.
- The peninsula has strategic maritime importance, especially the Strait of Gibraltar, linking the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea.
- Plays a key role in migration routes from Africa to Europe.
Source : BBC
Practice MCQs
Q1.Which of the following statements regarding the Iberian Peninsula is/are correct?
- It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean on the west and the Mediterranean Sea on the east.
- The Pyrenees Mountains separate it from the rest of Europe.
- The countries located on the Iberian Peninsula include Spain, Portugal, Andorra, and France.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1, 2 and 3
D. 2 only
Q2.With reference to the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC), consider the following statements:
- The OIC was founded in 1969 after the arson attack on the Al-Aqsa Mosque in Jerusalem.
- India has observer status at the OIC since 2018.
- The Islamic Development Bank is a specialized institution of the OIC.
- Its headquarters is located in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1, 3 and 4 only
D. 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q3.With reference to the Chenab River, consider the following statements:
- The Chenab River is formed by the confluence of the Chandra and Bhaga rivers.
- Under the Indus Waters Treaty, the waters of the Chenab are allocated to India for unrestricted use.
- The Baglihar and Salal hydroelectric projects are located on the Chenab River.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 3 only
D. 1 and 3 only
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ Today’s – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs
ANSWERS FOR 5th May – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – b











