Ethics Theory, TLP-UPSC Mains Answer Writing
Q. 2. What is quantum technology? Examine its potential applications and outline the steps taken by India to harness its benefits. (150 words, 10 marks)
Introduction
Quantum technology uses the rules of quantum physics—like particles being in two states at once—to build powerful tools for computing, communication, and sensing. It is set to transform science, industry, and governance.
Body
What is Quantum Technology?
- Based on quantum mechanics: It operates on the laws of quantum physics, which govern the behavior of particles at atomic and subatomic scales.
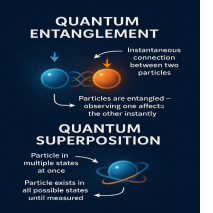
- Superposition and entanglement: It exploits quantum properties—superposition (being in multiple states at once) and entanglement (instant connection between particles)—for superior performance over classical systems.
- Beyond classical limitations: Quantum devices can process vast computations simultaneously, detect minute changes in the environment, and ensure ultra-secure communication.
- Emerging interdisciplinary field: It combines physics, engineering, mathematics, and computer science to build next-gen technologies like quantum computers, sensors, and networks.
Potential Applications of Quantum Technology
- Quantum Computing: Solves complex problems in seconds that classical computers would take years to process. Example: Drug discovery simulations by Google’s quantum computer promise breakthroughs in medicine.
- Quantum Communication: Enables ultra-secure data transfer using quantum key distribution (QKD). Example: China’s Micius satellite demonstrated QKD-based quantum-encrypted communication between ground stations.
- Quantum Sensing: Offers ultra-precise measurements of time, gravity, and magnetic fields. Example: Quantum sensors are being tested for underground mineral detection and early earthquake prediction.
- Quantum Cryptography: Revolutionizes cybersecurity by creating unbreakable encryption methods. Example: Companies like ID Quantique in Switzerland offer commercial quantum encryption solutions for banks.
- Material Science & Chemistry: Simulates molecular interactions with high accuracy for designing advanced materials. Example: IBM’s quantum simulations help in developing better catalysts and battery technologies.
- Financial Modeling & Optimization: Handles vast datasets for risk analysis and optimization in real-time. Example: JPMorgan Chase is experimenting with quantum algorithms to improve investment strategies.
Steps Taken by India to Harness Quantum Technology
- National Quantum Mission (NQM): Launched in 2023 with ₹6,003 crore outlay to develop quantum computers, sensors, and secure communication networks over 8 years.
- Centre for Quantum Technologies: Institutions like IISc Bengaluru and IIT Madras are setting up quantum research hubs and laboratories.
- International Collaborations: India has partnered with global leaders like the US, Israel, and France to enhance quantum R&D and exchange expertise.
- Quantum Communication Projects: DRDO successfully demonstrated secure quantum communication over 100+ km between two labs in 2020.
- Quantum Education Initiatives: IITs and IISERs are introducing quantum engineering and computing courses to build a skilled workforce.
- Industry Participation: Indian startups like QNu Labs are building indigenous quantum encryption tools, while TCS and Infosys are investing in quantum research.
Conclusion
Quantum technology holds the key to future breakthroughs in computing, security, and sensing. The 2022 Nobel Prize in Physics, awarded for quantum entanglement research, highlights its global importance.











