IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS Focus)
Category: Environment and Ecology
Context:
- Law minister of Odisha recently said the state government is preparing a new action plan to protect Chilika lake’s biodiversity and develop its surrounding areas.
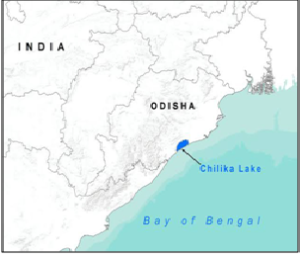
About Chilika Lake:
- Location: It is a brackish water lake and a shallow lagoon with estuarine character spread across the districts of Puri, Khurda, and Ganjam in the state of Odisha.
-
- Uniqueness: It is Asia’s largest brackish water lake.
- Associated river: Located at the mouth of the Daya River, Chilika Lake is the second-largest brackish water lagoon in the world, after the New Caledonian barrier reef in New Caledonia.
- Area: The waterspread area of Chilika varies between 900 to 1165 sq. km. during summers and monsoons, respectively.
- Linkage with Bay of Bengal: It is connected to the Bay of Bengal by a 32 km long and 1.5 km wide channel that mostly runs parallel to the Bay, separated by a narrow spit.
- Islands: Chilika Lake has several islands, such as:
- Nalabana Island – Declared a Bird Sanctuary (1987)
- Kalijai Island – Known for the Kalijai Temple
- Other islands include Honeymoon Island, Breakfast Island, Beacon Island, Satpada Island, etc.
- Significance: In 1981, Chilika Lake was designated the first Indian wetland of international importance under the Ramsar Convention.
-
- Biodiversity: It is the largest wintering ground for migratory birds on the Indian subcontinent. Birds from the Caspian Sea, Lake Baikal, Aral Sea, and other remote parts of Russia, Kirghiz steppes of Mongolia, Central and Southeast Asia, Ladakh and Himalayas come here.
- Important species: White-bellied sea eagles, Graylag Geese, Purple Moorhen, Jacana, Herons, and Flamingos are among the many species which make the lake a bird watcher’s delight. It is also home to one of the world’s largest breeding colonies of Flamingos. It is also famous for its population of Irrawaddy dolphins.
Source:
Category: Science and Technology
Context:
- Many countries across the world have initiated programmes to create awareness to prevent Spina Bifida through folic acid supplementation but India is yet to do so.
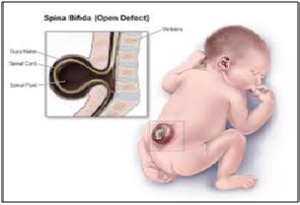
About Spina Bifida:
-
- Nature: It is a birth defect of the spinal cord that causes serious childhood paralysis. It occurs when the spine and spinal cord of a foetus do not fully develop during the embryonic period. The condition occurs during early pregnancy, and can range from mild to severe.
- Causes: The cause is not known. It’s thought that a combination of genetic, nutritional and environmental risk factors causes the condition.
- Types:
-
-
- Myelomeningocele: It is the most serious form of the condition. In this type, part of the spinal cord and nerves are exposed through a sac at the opening of the gap in the spine.
- Meningocele: It is a less common type of spina bifida that occurs when the meninges, or the protective membranes around the spinal cord, push out through the opening in a fluid-filled sac.
- Spina bifida occulta: It is the mildest form of the condition in which one or more of the vertebrae not forming properly, resulting in a small gap.
- Symptoms: These include bowel and bladder issues, back pain, weakness or lack of movement in the legs and loss of sensation in the legs.
-
- Prevention: It can be prevented largely by having folic acid in the early weeks of pregnancy.
- Treatment: There is no cure for the condition; however, treatment options are available to manage symptoms.
- Prevalence in India: In India, spina bifida occurs at a rate of approximately 1.9 per 1,000 births, significantly higher than in many Western countries.
- Steps taken by India: The Indian government promotes folic acid supplementation through the Pradhan Mantri Surakshit Matritva Abhiyan (PMSMA) and iron-folic acid (IFA) distribution under the National Health Mission.
- Awareness: October is designated as Spina Bifida Awareness Month.
Source:
Category: Government Schemes
Context:
- The Design Linked Incentive (DLI) Scheme has become critical to anchoring India in the most strategic segment of the global semiconductor value chain—chip design.

About Design Linked Incentive Scheme:
- Nature: It is a key instrument in advancing India’s ambition to develop a strong fabless capability.
- Nodal ministry: It comes under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) and is a critical component of the India Semiconductor Mission.
- Objective: The scheme aims to reduce import dependence, strengthen supply chain resilience, and enhance domestic value addition.
- Nodal Agency: C-DAC (Centre for Development of Advanced Computing) is responsible for implementation of the scheme.
- Eligibility: Start-ups and MSMEs are eligible for financial incentives and design infrastructure support for semiconductor product design & deployment. Other domestic companies are eligible for financial incentives for deploying semiconductor designs.
- Support: It provides support through three main pillars over a period of 5–6 years:
- Chip Design Infrastructure Support: Provides startups and MSMEs with remote access to the National EDA Tool Grid, IP core repositories, and post-silicon validation services through the ChipIN Centre (implemented by C-DAC).
- Product Design Linked Incentive (P-DLI): Offers reimbursement of up to 50% of eligible design expenditure, with a ceiling of ₹15 crore per application.
- Deployment Linked Incentive (DLI): Provides an incentive of 4% to 6% of net sales turnover for 5 years, capped at ₹30 crore per application, once the design is successfully deployed in electronic products.
Source:
Category: Economy
Context:
- The Allahabad High Court held that the formation of District Mineral Foundations must be construed liberally for those who are affected negatively by mining operations.
About District Mineral Foundations (DMFs):
-
- Nature: DMFs are statutory bodies in India established by the state governments by notification.
- Legal status: They derive their legal status from Section 9B of the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957, as amended on 26 March 2015 as the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Act, 2015.
-
- Establishment: In any district affected by mining-related operations, the State Government shall, by notification, establish a trust, as a non-profit body, to be called the DMF.
- Objective: It aims to work in the interest and benefit of persons and areas affected by mining-related operations in a manner as may be prescribed by the respective State Government.
- Jurisdiction: The operation of DMFs falls under the jurisdiction of the relevant State Government. Further, composition and functions of the DMF are also prescribed by the State Governments.
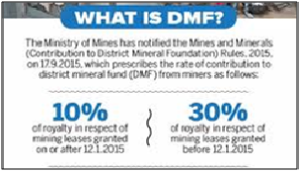
- Funding: It is funded through the contributions from the holders of major or minor mineral concessions in the district, as may be prescribed by the Central or State Government. The Central Government has notified the rates of contribution payable by miners to the DMFs.
- Changes after 2015: In the case of all mining leases executed before 12th January, 2015, miners will have to contribute an amount equal to 30% of the royalty payable by them to the DMFs. If mining leases are granted after 12.01.2015, the rate of contribution would be 10% of the royalty payable.
-
- Uses: The fund available with the Trust shall be used for:
- The overall development of the area affected by mining-related operations in the District in accordance with the Annual Action Plan prepared by the Trustees of the Foundation for the purpose.
- Uses: The fund available with the Trust shall be used for:
- Creation of local infrastructure for socio-economic purposes.
-
- Providing, maintaining, or upgrading community assets and services for the local population in the area affected by mining-related operations.
- Organising or conducting training programmes to skill development and capacity building for creating employment and self-employment capabilities.
Source:
Category: Geography
Context:
- Union Minister of Power and Housing and Urban Affairs recently directed sediment removal at the Salal Power Project to ensure maximum utilisation of water resources.

About Salal Hydroelectric Project:
-
- Location: It is located in the Reasi District of Jammu and Kashmir.
- Associated river: It is a 690 MW run-of-the-river power project on the Chenab River.
- Beginning of project: Although the plan for a water reservoir was originally conceived in pre-independent India, the planning of the project started in the 1960s. The project construction commenced in 1970 and subsequently entered into commercial operation in 1987.
- Construction: The project is developed and owned by National Hydroelectric Power Corporation (NHPC).
- Uniqueness: This was the first hydropower project, which was built by India under the Indus Water Treaty regime in Kashmir.
- Structure: Salal Dam is 130 meters high with an elevation of 1627 feet above mean sea level.
- Distribution of energy: Jammu and Kashmir receives 12.5 percent of the energy generated from the project. The rest is transmitted to the Northern Grid, where it is distributed to the states of Punjab, Haryana, Delhi, Himachal Pradesh, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh. Jammu and Kashmir also purchases additional power at regular prices.
Source:
(MAINS Focus)
GS-II: Government policies and interventions; transparency and accountability in governance; regulatory institutions.
Context (Introduction)
The crash of Air India flight AI-171 in June 2025 has exposed serious weaknesses in India’s aviation safety governance. The issue is not merely technical failure but a deeper credibility deficit arising from lack of transparency, regulatory capture, and weak institutional accountability in accident investigation and safety oversight.
Core Idea
Aviation safety is fundamentally a governance issue where credibility, transparency, and institutional integrity are as critical as technology. India’s obligations under ICAO Annex 13 require independent, transparent, and technically robust accident investigations. Delays, vague reporting, and politicisation undermine public trust and global confidence in India’s aviation ecosystem.
Key Governance Failures Highlighted
- Transparency Deficit: The preliminary report on the AI-171 crash was vague, despite availability of CVR and DFDR data, fostering speculation and misinformation.
- Weak Institutional Capacity: India lacked the technical expertise to decode flight data independently, relying on foreign agencies like the NTSB.
- Regulatory Capture: Repeated dilution and extension of DGCA safety requirements under airline pressure have compromised safety standards.
- Accountability Gaps: Past incidents (Mangalore 2010, Kozhikode 2020) reveal a pattern of delayed action and weak enforcement.
- Poor Crisis Management: Unsecured crash sites, premature reopening of airports, and delayed emergency response reflect systemic administrative lapses.
Why Credibility Matters in Aviation Governance
- Passenger Safety: Weak oversight directly endangers lives in a high-risk, technology-intensive sector.
- International Standing: Credibility in safety investigations affects India’s reputation with ICAO, FAA, and global aviation markets.
- Rule-Based Governance: Politicisation of technical findings erodes the principle of independent regulation.
- Information Integrity: Delays and opacity allow social media narratives to substitute for authoritative communication, weakening trust.
Way Forward
- Ensure statutory and functional independence of the Aircraft Accident Investigation Bureau (AAIB)
- Mandate strict timelines and full disclosure norms aligned with ICAO standards
- Strengthen DGCA’s autonomy, staffing, and enforcement powers
- Institutionalise coordination with global safety agencies without compromising transparency
- Adopt a safety-first governance culture prioritising public interest over commercial or political considerations
Conclusion
The AI-171 crash underscores that aviation safety failures are ultimately governance failures. Restoring credibility requires transparent investigations, independent regulators, and unwavering commitment to safety norms. In a sector where one failure is one too many, governance reform is not optional but imperative for protecting lives and sustaining India’s global aviation standing.
Mains Question
Recent aviation accidents have raised concerns about India’s safety oversight and regulatory credibility. Analyse the governance challenges in India’s civil aviation safety framework and suggest measures to restore institutional trust and transparency. (250 words, 15 marks)
GS-II: India and its bilateral relations; geopolitical developments and their impact on India’s foreign policy interests.
Context (Introduction)
Recent political churn in Latin America, triggered by renewed U.S. intervention in Venezuela and the potential end of the Maduro era, signals a broader geopolitical reordering in the region. These developments open a strategic window for India to correct its prolonged neglect of Latin America and recalibrate its regional engagement.
Core Idea
The post-Maduro transition could dilute the long-standing axis of anti-American politics backed by extra-regional powers like China and Russia, creating space for diversified partnerships. For India, the moment offers an opportunity to deepen political, economic, and diplomatic engagement in a region undergoing internal churn and restructured great-power relations.
Challenges in India’s Latin America Policy
-
- Strategic Marginalisation: Latin America has remained peripheral to India’s foreign policy priorities compared to the immediate neighbourhood and Indo-Pacific.
- Limited Economic Footprint: India’s annual trade with the region (~$45 billion) is modest relative to China’s ~$500 billion.
- Diplomatic Thinness: Sparse high-level visits and institutional mechanisms limit sustained engagement.
- Over-dependence on China-centric Trade: Indian exports remain concentrated in few markets, increasing vulnerability to global shocks.
Why the Moment Matters for India
-
- Geopolitical Flux: U.S. reassertion in the Western Hemisphere and declining left-wing populism reduce ideological barriers to engagement.
- Economic Diversification: Latin America’s $5.5 trillion economy and 650 million population offer scope for trade diversification amid global protectionism.
- Strategic Balancing: Regional states seek alternatives to excessive Chinese capital, technology, and market dependence.
- South–South Synergy: Shared developmental challenges allow cooperation in pharmaceuticals, digital public infrastructure, energy transition, and agriculture.
Way Forward
-
- Institutionalise political engagement through regular summits and strategic dialogues
- Expand trade agreements and promote Indian private sector presence
- Strengthen development cooperation and capacity-building initiatives
- Invest in cultural, educational, and people-to-people linkages to sustain long-term influence
Conclusion
The unfolding changes in Latin America are not merely regional disturbances but part of a larger reconfiguration of global power. For India, moving beyond episodic diplomacy to sustained engagement can convert this moment into a strategic opportunity—enhancing economic resilience, geopolitical reach, and the credibility of its global ambitions.
Mains Question
- The evolving geopolitical churn in Latin America presents India with strategic and economic opportunities. Examine why this moment is significant for India and discuss the constraints that have limited India’s engagement with the region so far. (250 words, 15 marks)











