Science and Technology
Context: Recently Delhi Police recovered bones from the Mehrauli forest area in connection with the Shraddha Walkar murder investigation. DNA testing conducted on the bones — parts of the jaw, pelvis and lower limb — has now confirmed a positive match with Shraddha’s father.
About DNA fingerprinting:
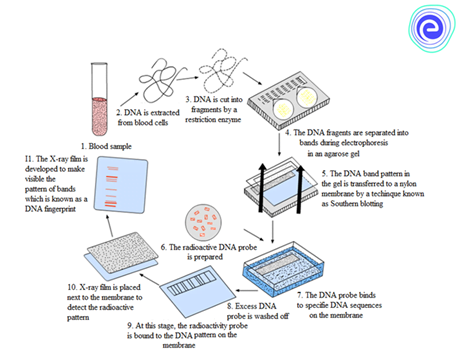
- “DNA fingerprinting is a procedure that shows the hereditary cosmetics of living things. It is a strategy for finding the distinction between the satellite DNA areas in the genome.”
- DNA profiling, DNA testing, DNA examination, Genetic profile, DNA distinguishing proof, genetic fingerprinting, and genetic investigation are a portion of the mainstream names utilized for DNA fingerprinting. This technique was invented by Alec Jeffreys in 1984.
- Sources of DNA:
- hair,
- bone,
- teeth,
- saliva,
- blood, etc.
- Because there is DNA in most cells in the human body, even a minuscule amount of bodily fluid or tissue can yield useful information.
- DNA evidence is used to solve crimes in two ways:
- If a suspect is known, that person’s DNA sample can be compared to biological evidence found at a crime scene to establish whether the suspect was at the crime scene or whether they committed the crime.
- If a suspect is not known, biological evidence from the crime scene can be analysed and compared to offender profiles in existing DNA databases to assist in identifying a suspect.
Uses of DNA Fingerprinting:
- Forensic analysis: It can be used in the identification of a (1) person involved in criminal activities, (2) for settling paternity or maternity disputes, and (3) in determining relationships for immigration purposes.
- Pedigree analysis: It can be used for inheritance pattern of genes through generations and for detecting inherited diseases such as Cystic Fibrosis, Haemophilia, Huntington’s Disease, Sickle Cell Anaemia etc.
- Personal Identification: DNA fingerprints can be used as a genetic bar code to identify individuals.
- Anthropological studies: It is useful in determining the origin and migration of human populations and genetic diversities.
- DNA Barcoding: A technique for specifying the organisms’ species using a short sequence of DNA situated in the genome is termed DNA bar-coding. The barcode DNA sequences are too short in respect to the complete genome and hence cheaper.
DNA Fingerprinting in India:
- Pioneering work was done by Lalji Singh at the Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CCMB), Hyderabad
Other centres are :
- Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (Hyderabad)
- Centre for DNA Fingerprinting & Diagnostics (Hyderabad)
- Central Forensic Science Laboratory, Kolkata
- National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resource (NBPGR), New Delhi
- National Institute of Plant and Genetic Research (NIPGR), New Delhi
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following statements: DNA Barcoding can be a tool to:
- assess the age of a plant or animal.
- distinguish among species that look alike.
- identify undesirable animal or plant materials in processed foods.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2022)
- 1 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to the recent developments in science, which one of the following statements is not correct? (2019)
- Functional chromosomes can be created by joining segments of DNA taken from cells of different species.
- Pieces of artificial functional DNA can be created in laboratories.
- A piece of DNA taken out from an animal cell can be made to replicate outside a living cell in a laboratory.
- Cells taken out from plants and animals can be made to undergo cell division in laboratory petri dishes.











