UPSC Articles
INTERNATIONAL/ ECONOMY
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Important International institutions, agencies and fora- their structure, mandate.
COVID-19: Eurozone and challenges
Context: EU- the most progressive post-national regional arrangement was not proactive while dealing with the spread of COVID-19 pandemic. This resulted in its member states turning inward for solutions.
About European Union(EU)
- It is a political and economic union of 27 member states that are located primarily in Europe.
- Objective of EU and its policies
- Ensure the free movement of people, goods, services and capital within the internal market,
- Enact legislation in justice and home affairs and maintain common policies on trade, agriculture, fisheries and regional development
Below is the schematic representation of EU
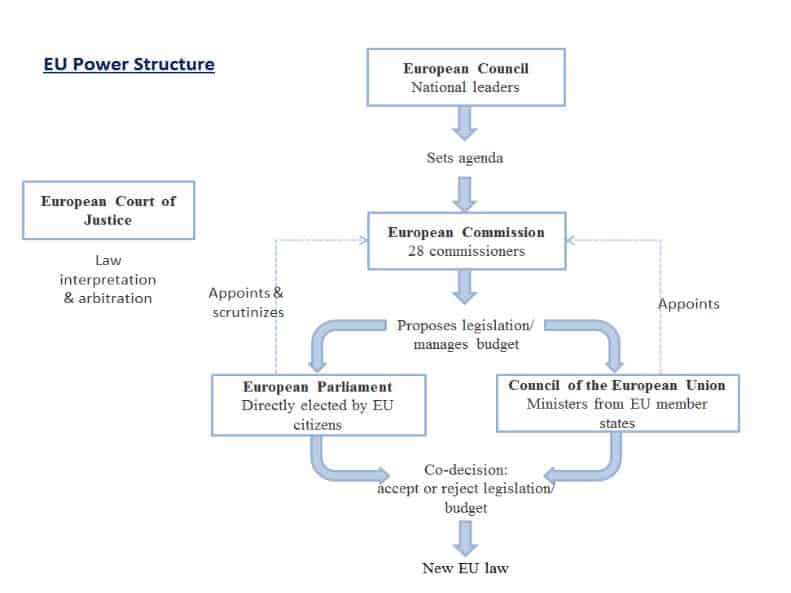
Image Source: Google
What are the recent steps taken by the EU to fight COVID-19?
- Emergency rescue package amounting to €540-billion
- Opening up of an emergency credit line for member countries
- Raise the lending capacity of the European Investment Bank
- European Commission’s €100- billion unemployment insurance scheme
- European Central Bank has decided to expand its asset purchase programme by €750-billion over the next nine months
Challenges ahead
- Apprehensions about intrusive EU inspections with regard to relief package
- Discontent with regard to burden-sharing between the richer members in the north (like Germany & France) and the poorer states in the south (like Greece & Portugal)
- Demand from Italy (worse affected) that pandemic credit to be issued by the European Stability Mechanism should not be attached with any conditionalities.
- Greece and Ireland had received financial bailouts from EU in 2009 but were accompanied by fiscal austerity measures (reduction in welfare spending)
- No progress on joint issuance of Eurobonds (dubbed corona bond).
- These are Common debt instrument which would pool borrowing among EU nations to fight the crisis.
- Implementation Challenges: Utilization of relief package would be slowed down by bureaucratic complexities
- Unsatisfied pro-European elites: The support measures by EU is considered as too little and not holistic
- Strains in National Coalition governments over the strategy to be adopted to tackle the pandemic, especially in the backdrop of EU’s less-enthusiastic role
- For instance: Netherlands’ ruling coalition unhappy over the government’s orthodox fiscal stance, where the opposition parties advocate Eurobonds.
- High Stakes: Failure to tackle the pandemic can affect European Solidarity especially after the difficulties faced in the aftermath of 2008 financial crisis and the recent Brexit.
Way Ahead
- When the pandemic hit the continent self-help and not regional coordination, was countries first instinct- which doesn’t bode well for EU.
- Therefore, bigger economies like Germany, France & Netherlands need to compromise to ensure sustainability of the grouping
Connecting the dots:
- SAARC and India’s initiative for collaboration on tackling pandemic
- Difference in structure between EU and ASEAN














