The Big Picture- RSTV, UPSC Articles
COVID-19 & Herd Immunity
Archives
TOPIC: General Studies 2
- COVID-19 – Global Pandemic
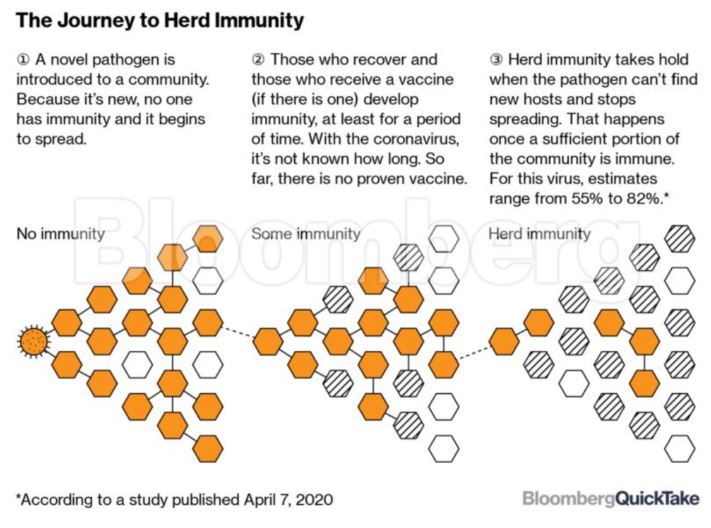
What is herd immunity?
When most of a population is immune to an infectious disease, this provides indirect protection—or herd immunity (also called herd protection)—to those who are not immune to the disease. If enough people are immune, an infected person will likely come into contact only with people who are already immune rather than spreading the virus to someone who is susceptible.
For example, if 80% of a population is immune to a virus, four out of every five people who encounter someone with the disease won’t get sick (and won’t spread the disease any further). In this way, the spread of infectious diseases is kept under control.
How do we get Herd Immunity?
There are two ways to achieve herd immunity: A large proportion of the population either gets infected or gets a protective vaccine.
Based on early estimates of this virus’s infectiousness, we will likely need at least 70% of the population to be immune to have herd protection.
Herd Immunity – COVID-19
1) We do not have a vaccine. As biologist Carl Bergstrom and biostatistician Natalie Dean pointed out, without a widely available vaccine, most of the population – 60%-85% by some estimates – must become infected to reach herd immunity, and the virus’s high mortality rate means millions would die.
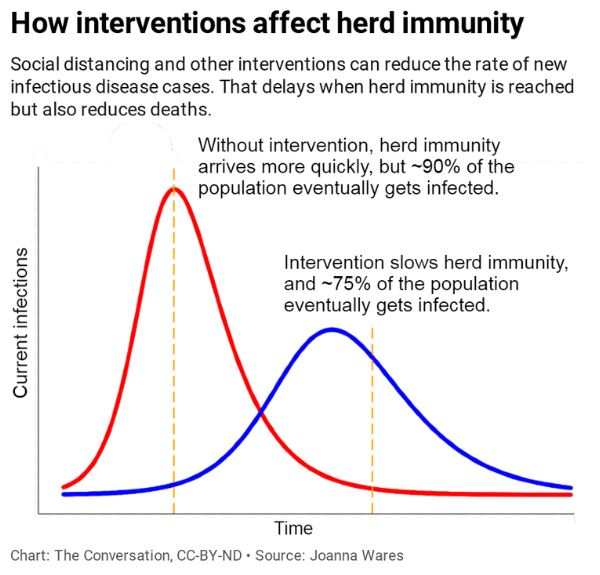
2) The virus is not currently contained. If herd immunity is reached during an ongoing pandemic, the high number of infected people will continue to spread the virus and ultimately many more people than the herd immunity threshold will become infected – likely over 90% of the population.
3) The people most vulnerable are not evenly spread across the population. Groups that have not been mixing with the “herd” will remain vulnerable even after the herd immunity threshold is reached.
Is it possible to acquire Herd Immunity during a PANDEMIC?
Herd immunity reached during a pandemic doesn’t stop the spread. An ongoing pandemic doesn’t stop as soon as the herd immunity threshold is reached. When the herd immunity threshold is reached during a pandemic, the number of new infections per day will decline, but the substantial infectious population at that point will continue to spread the virus.
The goal of any response strategy: Proactive mitigation strategies like social distancing and wearing masks flatten the curve by reducing the rate that active infections generate new cases. This delays the point at which herd immunity is reached and also reduces casualties.
Source: https://theconversation.com/herd-immunity-wont-solve-our-covid-19-problem-139724
Herd immunity does not protect the vulnerable
People who are particularly vulnerable to COVID-19, such as people over 65, have been urged to stay inside to avoid exposure. However, many of these people live and socialize in communities of people in the same cohort.
Even if the herd immunity threshold is reached by the population at large, a single infected person coming in contact with a vulnerable community can cause an outbreak.
Sweden – What happened?
With a pure herd immunity strategy in Sweden, there is no significant economic cost, but the infection spreads more rapidly, with a concomitant increase in mortality. Sweden’s public health professionals were confident about the ability of their public health system to handle the anticipated tide of infections. However, the virus has wreaked significant havoc in terms of mortality in the care homes for the elderly.
Conclusion
In the absence of a vaccine or drug, and without a clear understanding of the disease pathology, seeking to achieve herd immunity through infection is a dangerous strategy. Allow the disease to spread too quickly, it overwhelms the health system and causes many people to die “unnecessarily”; do it too slowly, and it takes that much longer for life to come back to “normal”. Therefore, for almost all countries, at this juncture, it is a cruel choice between saving lives and saving livelihoods.
Connecting the Dots:
- What is Herd Immunity? Can it be successful in a country like India?
- What are the basics of disease transmission? Explain.
- Essay: Herd Masking and Herd Immunity















