IASbaba Daily Prelims Quiz
For Previous Daily Quiz (ARCHIVES) – CLICK HERE
The Current Affairs questions are based on sources like ‘The Hindu’, ‘Indian Express’ and ‘PIB’, which are very important sources for UPSC Prelims Exam. The questions are focused on both the concepts and facts. The topics covered here are generally different from what is being covered under ‘Daily Current Affairs/Daily News Analysis (DNA) and Daily Static Quiz’ to avoid duplication. The questions would be published from Monday to Saturday before 2 PM. One should not spend more than 10 minutes on this initiative.
This is a part of our recently launched, NEW INITIATIVE IASbaba’s INTEGRATED REVISION PLAN (IRP) 2020 – Road Map for the next 100 Days! FREE INITIATIVE!
We will make sure, in the next 4 months not a single day is wasted. All your energies are channelized in the right direction. Trust us! This will make a huge difference in your results this time, provided that you follow this plan sincerely every day without fail.
Gear up and Make the Best Use of this initiative.
Do remember that, “the difference between Ordinary and EXTRA-Ordinary is PRACTICE!!”
To Know More about the Initiative -> CLICK HERE
SCHEDULE/DETAILED PLAN – > CLICK HERE
Important Note:
- Don’t forget to post your marks in the comment section. Also, let us know if you enjoyed today’s test 🙂
- After completing the 5 questions, click on ‘View Questions’ to check your score, time taken and solutions.
Test-summary
0 of 5 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Information
To view Solutions, follow these instructions:
- Click on – ‘Start Test’ button
- Solve Questions
- Click on ‘Test Summary’ button
- Click on ‘Finish Test’ button
- Now click on ‘View Questions’ button – here you will see solutions and links.
You have already completed the test before. Hence you can not start it again.
Test is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the test.
You have to finish following test, to start this test:
Results
0 of 5 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have scored 0 points out of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 5
1. Question
Mahadayi water dispute tribunal adjudicates the water dispute between which of the following two states?
Correct
Solution (a)
The Mahadayi Water Disputes Tribunal (MWDT), is a tribunal that adjudicates the dispute over River Mhadei water allocation. The sharing of the waters of this river is a cause of dispute between the governments of Karnataka and Goa
It originates in the Belagavi district of Karnataka, briefly passes through Maharashtra and flows through Goa (where its known as Mandovi), and drains to the Arabian Sea.
Since the eighties, Karnataka has been was contemplating linking of Mahadayi with Malaprabha river, a tributary of Krishna.
In 2002, Karnataka gave the idea a shape in the form of the Kalasa-Bhanduri project.
Goa strongly opposed it as Mahadayi is one of the two rivers the State is dependent on and thus Mahadayi Water Disputes Tribunal was set up in 2010.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
The Mahadayi Water Disputes Tribunal (MWDT), is a tribunal that adjudicates the dispute over River Mhadei water allocation. The sharing of the waters of this river is a cause of dispute between the governments of Karnataka and Goa
It originates in the Belagavi district of Karnataka, briefly passes through Maharashtra and flows through Goa (where its known as Mandovi), and drains to the Arabian Sea.
Since the eighties, Karnataka has been was contemplating linking of Mahadayi with Malaprabha river, a tributary of Krishna.
In 2002, Karnataka gave the idea a shape in the form of the Kalasa-Bhanduri project.
Goa strongly opposed it as Mahadayi is one of the two rivers the State is dependent on and thus Mahadayi Water Disputes Tribunal was set up in 2010.
-
Question 2 of 5
2. Question
Change in our DNA base pair sequence due to various environmental factors such as UV light, or mistakes during DNA replication is called as:
Correct
Solution (d)
In news: While novel coronavirus is undergoing many mutations, one particular mutation called D614G, according to a study, has become the dominant variant in the global COVID-19 pandemic.
Mutation is the change in our DNA base pair sequence due to various environmental factors such as UV light, or mistakes during DNA replication.
D614G mutation
- When the virus enters an individual’s body, it aims at creating copies of itself. When it makes an error in this copying process, we get a mutation.
- In this case, the virus replaced the aspartic acid (D) in the 614th position of the amino acid with glycine (G). Hence the mutation is called the D614G.
- This mutated form of the virus was first identified in China and then in Europe. Later it spread to other countries like the U.S. and Canada and was eventually reported in India.
Incorrect
Solution (d)
In news: While novel coronavirus is undergoing many mutations, one particular mutation called D614G, according to a study, has become the dominant variant in the global COVID-19 pandemic.
Mutation is the change in our DNA base pair sequence due to various environmental factors such as UV light, or mistakes during DNA replication.
D614G mutation
- When the virus enters an individual’s body, it aims at creating copies of itself. When it makes an error in this copying process, we get a mutation.
- In this case, the virus replaced the aspartic acid (D) in the 614th position of the amino acid with glycine (G). Hence the mutation is called the D614G.
- This mutated form of the virus was first identified in China and then in Europe. Later it spread to other countries like the U.S. and Canada and was eventually reported in India.
-
Question 3 of 5
3. Question
Consider the following statements:
- Winter solstice is the day when the North Pole is most tilted towards the Sun.
- Summer solstice is the day when the North Pole is most tilted away from the Sun.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (d)
In news: 21st December or the Winter Solstice marks the shortest day of the year in the Northern Hemisphere. The same day marks the Summer Solstice, the year’s longest day, in the Southern Hemisphere.
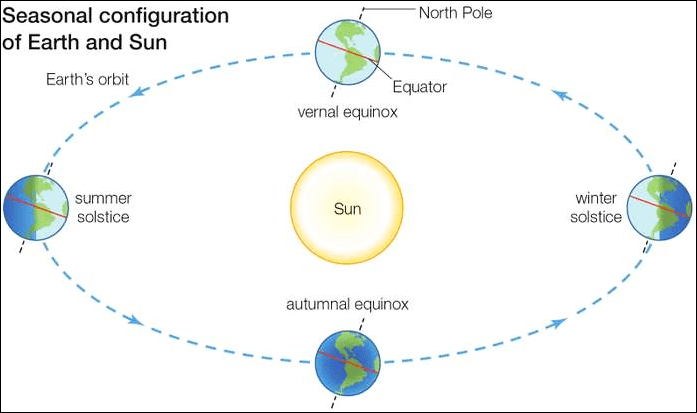
It is the shortest day and longest night of the year in the Northern Hemisphere and is also known as the ‘first day of winter’ in the Northern Hemisphere as well as ‘Hiemal solstice or Hibernal solstice’.
During this, countries in the Northern Hemisphere are farthest from the Sun and the Sun shines overhead on the Tropic of Capricorn (23.5° south).
This situation will be reversed on 21st June, when the Northern Hemisphere will see the Summer Solstice, the year’s longest day and the Southern Hemisphere will see the year’s shortest day.
Incorrect
Solution (d)
In news: 21st December or the Winter Solstice marks the shortest day of the year in the Northern Hemisphere. The same day marks the Summer Solstice, the year’s longest day, in the Southern Hemisphere.

It is the shortest day and longest night of the year in the Northern Hemisphere and is also known as the ‘first day of winter’ in the Northern Hemisphere as well as ‘Hiemal solstice or Hibernal solstice’.
During this, countries in the Northern Hemisphere are farthest from the Sun and the Sun shines overhead on the Tropic of Capricorn (23.5° south).
This situation will be reversed on 21st June, when the Northern Hemisphere will see the Summer Solstice, the year’s longest day and the Southern Hemisphere will see the year’s shortest day.
-
Question 4 of 5
4. Question
Consider the following statements with respect to Pradhan Mantri Khanij Kshetra Kalyan Yojana(PMKKKY):
- This programme meant to provide for the welfare of areas and people affected by mining related operations
- PMKKKY scheme is implemented by the District Mineral Foundations (DMFs)
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
In news: auditing and an impact assessment of utilisation of funds from the District Mineral Foundation Trust (DMFT) for the financial years 2017-2020 will be taken place in Jharkhand.
Pradhan Mantri Khanij Kshetra Kalyan Yojana(PMKKKY)
Nodal Ministry: PMKKKY is a scheme by the Ministry of Mines for the welfare of people & affected areas
Objectives:
- To implement various developmental and welfare projects/programs in mining affected areas that complement the existing ongoing schemes/projects of State and Central Government.
- To minimize/mitigate the adverse impacts, during and after mining, on the environment, health and socio-economics of people in mining districts.
- To ensure long-term sustainable livelihoods for the affected people in mining areas.
Implementation:
- The Pradhan Mantri Khanij Kshetra Kalyan Yojana (PMKKKY) will be implemented by the District Mineral Foundations (DMFs) of the respective districts using the funds accruing to the DMF.
- At least 60% the fund will be utilized for “High Priority Areas” like Drinking water supply, Environment preservation & pollution control measure, Health care, Education, etc.
- Rest of the fund will be utilized for “Other Priority Areas”, such as Physical infrastructure, Irrigation, Energy & watershed development and Measures for enhancing environmental quality.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
In news: auditing and an impact assessment of utilisation of funds from the District Mineral Foundation Trust (DMFT) for the financial years 2017-2020 will be taken place in Jharkhand.
Pradhan Mantri Khanij Kshetra Kalyan Yojana(PMKKKY)
Nodal Ministry: PMKKKY is a scheme by the Ministry of Mines for the welfare of people & affected areas
Objectives:
- To implement various developmental and welfare projects/programs in mining affected areas that complement the existing ongoing schemes/projects of State and Central Government.
- To minimize/mitigate the adverse impacts, during and after mining, on the environment, health and socio-economics of people in mining districts.
- To ensure long-term sustainable livelihoods for the affected people in mining areas.
Implementation:
- The Pradhan Mantri Khanij Kshetra Kalyan Yojana (PMKKKY) will be implemented by the District Mineral Foundations (DMFs) of the respective districts using the funds accruing to the DMF.
- At least 60% the fund will be utilized for “High Priority Areas” like Drinking water supply, Environment preservation & pollution control measure, Health care, Education, etc.
- Rest of the fund will be utilized for “Other Priority Areas”, such as Physical infrastructure, Irrigation, Energy & watershed development and Measures for enhancing environmental quality.
-
Question 5 of 5
5. Question
Consider the following statements:
- According to Status of leopards in India, 2018 report the largest number of leopards have been estimated in Karnataka
- IUCN status of leopards is Vulnerable
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
In news: As per a recent report ‘Status of leopards in India, 2018’ released by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change there has been a “60% increase in the population count of leopards in India from 2014 estimates’’.
The 2014 estimates placed the population of leopards at nearly 8,000 which has increased to 12,852.
The largest number of leopards have been estimated in Madhya Pradesh (3,421) followed by Karnataka (1,783) and Maharashtra (1,690).
Region wise distribution:
- Central India and Eastern Ghats have the highest number of leopards at 8,071.
- Western Ghats: 3,387 leopards
- Shivalik and Gangetic Plains: 1,253 leopards
- Northeast hills: 141 leopards
Conservation Status:
- International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN): Vulnerable
- Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES): Appendix I
- Wildlife Protection Act 1972: Schedule 1
Incorrect
Solution (b)
In news: As per a recent report ‘Status of leopards in India, 2018’ released by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change there has been a “60% increase in the population count of leopards in India from 2014 estimates’’.
The 2014 estimates placed the population of leopards at nearly 8,000 which has increased to 12,852.
The largest number of leopards have been estimated in Madhya Pradesh (3,421) followed by Karnataka (1,783) and Maharashtra (1,690).
Region wise distribution:
- Central India and Eastern Ghats have the highest number of leopards at 8,071.
- Western Ghats: 3,387 leopards
- Shivalik and Gangetic Plains: 1,253 leopards
- Northeast hills: 141 leopards
Conservation Status:
- International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN): Vulnerable
- Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES): Appendix I
- Wildlife Protection Act 1972: Schedule 1














