IASbaba's Mains Strategy
Civil Services (Mains) Examination – General Studies
Strategy for Paper 3
Total Marks: 250
The 3rd General Studies paper is considered to contain the broadest portion including a whole range of subjects encompassing a variety of topics, ranging from the Indian Economy to the External Security Issues.
A budding bureaucrat is expected to know and understand a wide range of issues, in depth as well as in breadth, with a thorough understanding with its aspects dealing with issues from its scope to implementation. Issues like economy and development, of which one or the other aspect is always in the news, can never be dealt with by studying a mere static portion and employing ‘rote memorization’ as one’s weapon in their arsenal to attack the CS(M).
This article discusses about the Preparation Strategy for General Studies-3. The strategy gives you
- Topic-wise analysis
- Book recommendations (minimum) and
- What to Read and How to read/Understand the subject.
Please note that, there are Two most important things a beginner should do, before one starts off with his/her preparation:
Firstly, memorize the syllabus.
Secondly, go through last 5 year’s UPSC (Mains) question papers.
You can (we believe, you should) follow IASbaba’s initiative Think Learn & Perform (TLP) for writing practice.
One has to be well versed with all the dimensions of the topics given in the syllabus. If you are able to understand them, then half the battle is won! While reading a newspaper or going through any material, it will help you in picking up the relevant issues from the exam perspective. While reading the newspaper ‘keep an eye on the topics mentioned in the syllabus’. Newspaper gives you more information and dimensions that you seldom find in a book. UPSC knows the ‘Art of testing Analytical Ability’ and we assure you of surprises from their end, to knock you off your chair, if you don’t study smartly!
…which implies, you need to read:
- NCERT Economics- 11th + 12th
- Economic Survey
- Mrunal: Economics + Environment
- India Year Book
- 12th Five-Year Plan
- Newspapers (Sci + Tech + Environment + other related topics)
- Stay up-to-date with Major Schemes
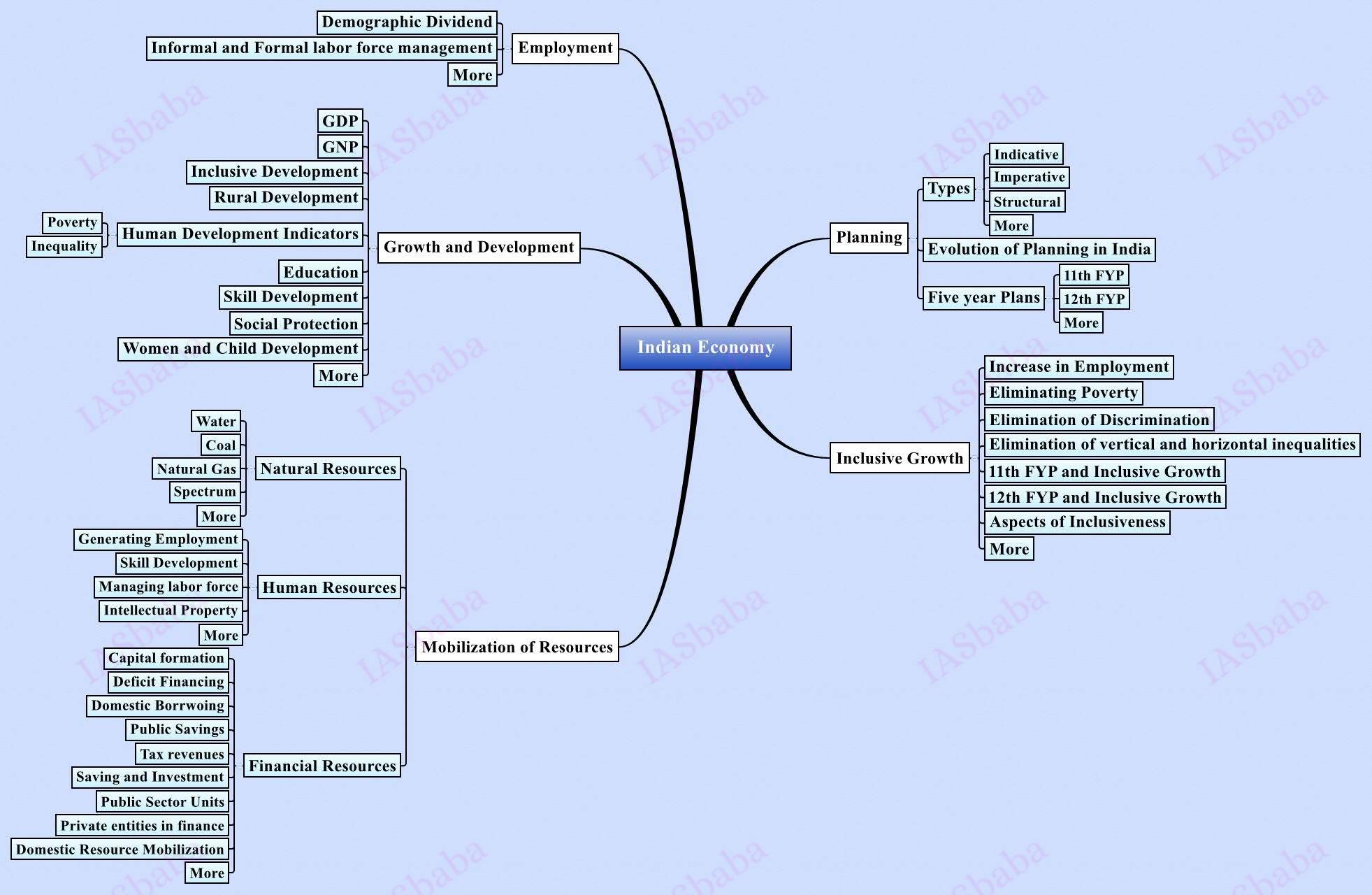
1. Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources, growth, development and employment.
- Broad economic concerns related to macro economy like inflation, BoP, GDP- Try to relate the present macro-economic situation in the economy and the steps taken by Government & RBI to deal with it
- Various sectoral contributions to GDP like primary, secondary, tertiary and issues such as employment generation and productivity concerns of each sector
- Constraints in mobilising various resources like land, capital, human and other natural resources
- Multi-dimensional issues like environmental degradation, opposition from local community etc.
- Relate it with the recent displacement issues and the stalling of the Land Bill and proclamation of the era of ‘Ordinance Raj’
- Problems in allocation of resources to various sectors
Planning:
- Historic contribution to Indian economy,
- Changing pattern of planning from centralised to decentralised,
- Relevance of planning in India for allocation of resources,
- Setting of goals coordination of various agencies
- Planning machinery in India and its weaknesses: Both Procedural and Institutional
Economic Growth & Development
- Difference between Growth and Development
- Necessity of growth for achieving development in various dimensions like social, economic and political
Read Amartya Sen’s definition of Economic Development here, to get an overall idea of development as there must be a reason for UNDP to adopt HDI 🙂
- Reasons for poor growth of economy in recent times,concentrated growth (in various sectors and in regions) and its drawbacks etc
You can easily relate it with ‘Regional Imbalance’ on which there have been various commissions working on and even Economic Survey terming it as a ‘growth inhibitor’.
Employment:
- Youth output in India,
- Sectoral composition of employment,
- Ways and means of achieving employment for youth in organised sectors with high productivity,
- Reasons for poor employment generation(jobless growth),
- Education-industry gap,
- Skill gap,
- Reasons for Informalization of economy and measures to reverse it
You must be aware of the recent initiatives for employment generation like Skill India, SETU as well as rise in the field of financial inclusion to bring about a sense of entrepreneurship to make ‘Make in India’, a reality.
Read: Newspapers: Information + Different Dimensions –> MUST–>Development of Analytical Ability
Employment: Growth
- NCERT-11th Ch 5 + 7
- NIOS: L-38 & 39
- IYB: Labour & Employment
Let us go through previous years UPSC questions
We flaunt India’s demographic dividend, we ignore the dropping rates of employability. What are we missing while doing so? Where will the jobs that India desperately needs come from? Explain.
2. Inclusive growth and issues arising from it
- Challenges of achieving inclusive growth
- Measures to achieve it
- Government schemes related to it
- Inter-relationship between Financial Inclusion-Inclusive Growth-Skilling India-Social Change
For example,
Growth in the last two decades is concentrated in few metropolis and in the educated middle class.
Ways of spreading this growth to the unreached and vulnerable like rural areas, vulnerable population like women and various sectors like agriculture etc
Geographical + Financial + Psychological Inclusion is the key
Newspapers: Information + Different Dimensions–> MUST–> Development of Analytical Ability
August, Yojana-2015- Click
Let us go through previous years UPSC questions
Capitalism has guided the world economy to unprecedented prosperity. However, it often encourages shortsightedness and contributes to wide disparities between the rich and the poor. In this light, would it be correct to believe and adopt capitalism for bringing inclusive growth in India? Discuss.
3. Government Budgeting
- Basic idea about the budgeting process and various definitions related to it like revenue deficit, fiscal deficit etc.
- Various types of budgeting like line items, zero based budget, program planning budgeting and other models.
- Types and issues in accounting and auditing government accounts
- Major sources of revenue for government and broad allocation to various sectors with effective utilisation of revenues
- Capital expenditure vs revenue expenditure and measures to curb revenue expenditure etc
Refer:
Indian Polity by LAXMIKANTH-4th Edition
Newspapers: Information + Different Dimensions–> MUST–> Development of Analytical Ability
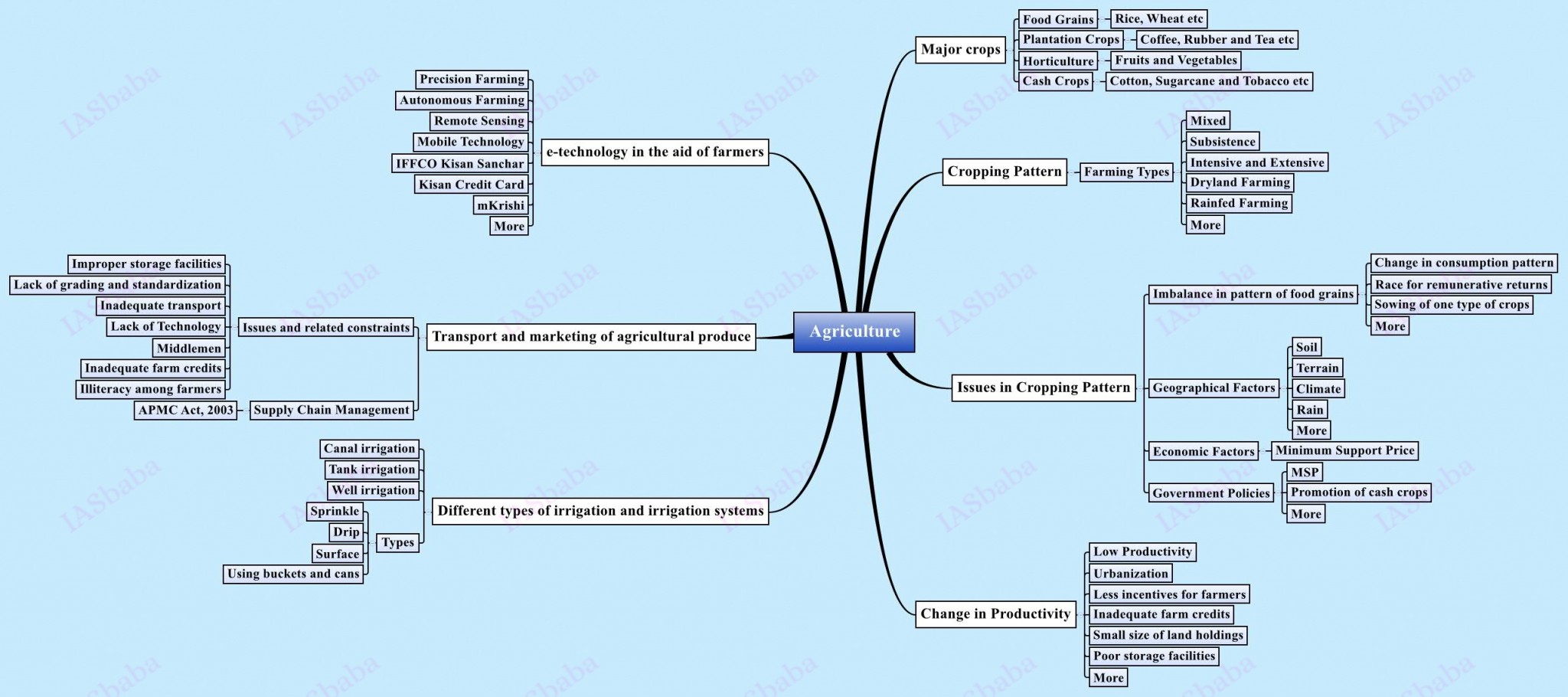
4. Major crops cropping patterns in various parts of the country, different types of irrigation and irrigation systems storage, transport and marketing of agricultural produce and issues and related constraints; e-technology in the aid of farmers.
A straight-forward syllabus putting its demands in the simplest way possible
- Details about Crops + Cropping Patterns & Irrigation Systems- Can be easily dealt with once you’ve thoroughly prepared Geography’s syllabus + A basic understanding can also help you deal with an indirect question in Paper 1.
- Infrastructural bottlenecks in agriculture in terms of transportation, storage, proper packaging (within India/exports) etc
- The indirect effects it has in poor realisation of income for farmers, increased prices for consumers and the overall inflation effect on the economy
- The reasons for fragmented markets in India and major provisions of APMC act in various states and the many bottlenecks ready to throttle the economy in it
These are some of the issues that are covered with great depth in newspapers like The Hindu, Indian Express, etc. One should make sure to go through some of the highlights of the speeches made by key Ministers. Many of the dynamic points can be lifted from our Prime Minister’s Speech itself.
- Measures taken by some states to overcome these bottlenecks for eg Apni Mandis, Rythu Bazaars, etc
- Use of technology for integration of markets
- Various initiatives in marketing like contract farming, commodity trading, entry of private agencies in marketing etc
- Recent initiatives by GOI in overcoming these through model APMC Acts, Mega Food Park scheme, warehouse receipts etc must be known.
Read:
Newspapers: Information + Different Dimensions–> MUST–> Development of Analytical Ability
Let us go through previous years UPSC questions
“In the villages itself no form of credit organisation will be suitable except the cooperative society.” – All Indian Rural Credit survey. Discuss this statement in the background of agriculture finance in India. What constraints and challenges do financial institutions supplying agricultural finance face? How can technology be used to better reach and serve rural clients?
Refer:
- It was covered in previous months of Yojana as well
- Yojana, August 2015
- Nachiket’s Recommendation
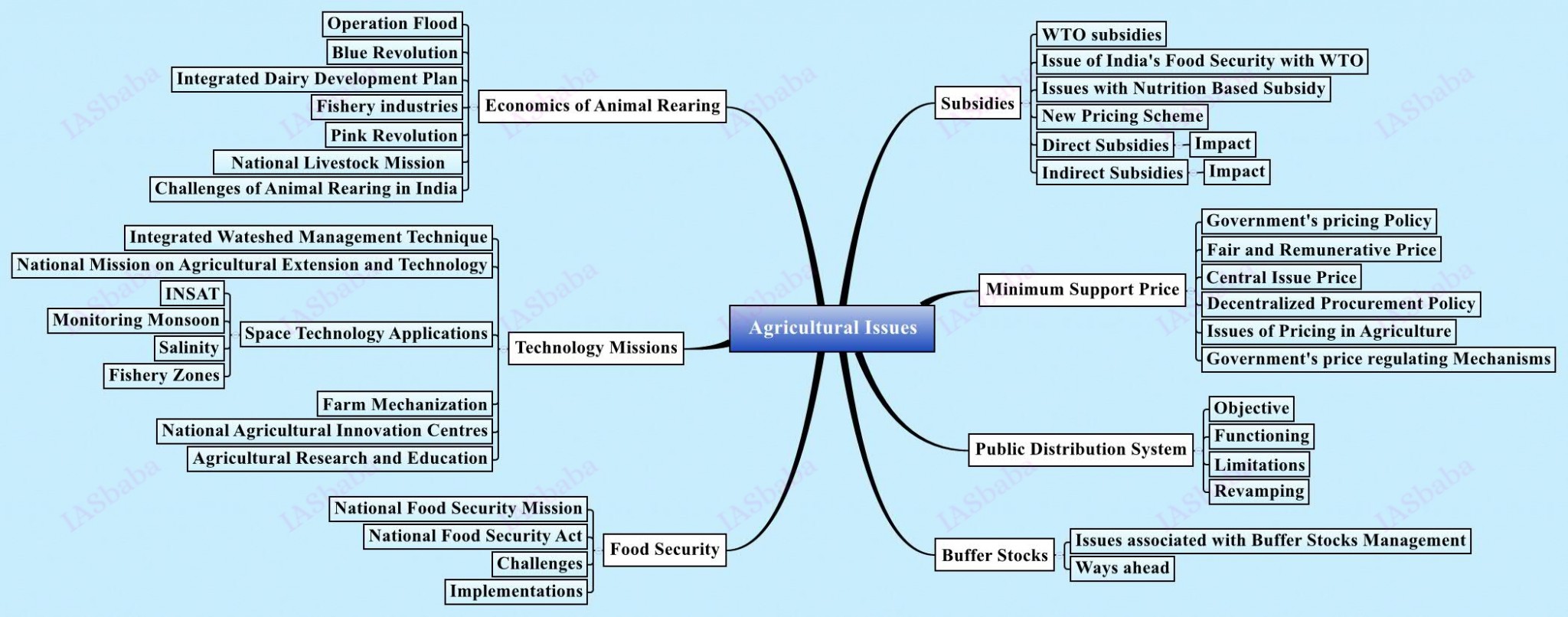
5. Issues related to direct and indirect farm subsidies and Minimum Support Prices; Public Distribution System objectives, functioning, limitations, revamping; Issues of buffer stocks and food security; Technology missions
Track down the following:
- Various forms of subsidies given by GOI and various state agencies
- Benefits + Negative Consequences on Economy, Environment, etc. One must inter-relate the benefits as well as the consequences with other discipline. Analytical discussion should be the key here.
- New methods & successful experiments adopted by States can be used as a case-study:
The “8+ Percentage Growth phenomena of Gujarat” + if it can be replicated elsewhere:
If yes: How + When + Natural Factors + Schemes that can be used + Technology, etc
If No: Why + Alternate solutions
Objectives of PDS and its evolution from mid 1960s:
- Issues of poor targeting,
- Ghostbeneficiaries,
- and
- Examples of some innovative measures adopted in few states like Tamil Nadu and Chhattisgarh PDS Model in overcoming these weaknesses
- How: Through GPS + E point of sale + Social Auditing and other measures.
Food security concerns of India:
- Measures adopted by Govt for overcoming food insecurity through various means
- Problems:
- Overstocking of food,
- Food wastage in godownsowing to poor storage,
- Excessfoodgrains vs hunger population,
- Revamping of PDS and
- The recent recommendations of Shanta Kumar committee
- Cash transfer vs kind transfer,
- WTO constraints in maintaining food stocks,
- Indian position in WTO and its obligations: Recent decisions + India’s stand on it
Questions pertaining to the above topic can be in the form of:
- Various technology missions for increasing productivity in agriculture and allied activities
- Various extension measures taken by GOI and the institutions involved in it
- The reasons for poor extension and hence the need for technology adoption in our farms
For example, if the question is:
What is the general productivity level of agriculture sector in India and various other countries and the successful measure taken to improve it?
If one has a good knowledge about the agriculture sector vis-à-vis the other countries, he/she can easily answer the first part of the question.
And, if one follows The Hindu’s Agriculture Section of Thursday’s issue, he/she can easily answer the second part of the question:
- Setting up of KVKs,
- Collaboration with Israel,
- National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture,
- ICARs National Initiative on Climate Resilient Agriculture and various models and modes adopted to reach out to our farmers.
Newspapers: Information + Different Dimensions–> MUST–> Development of Analytical Ability
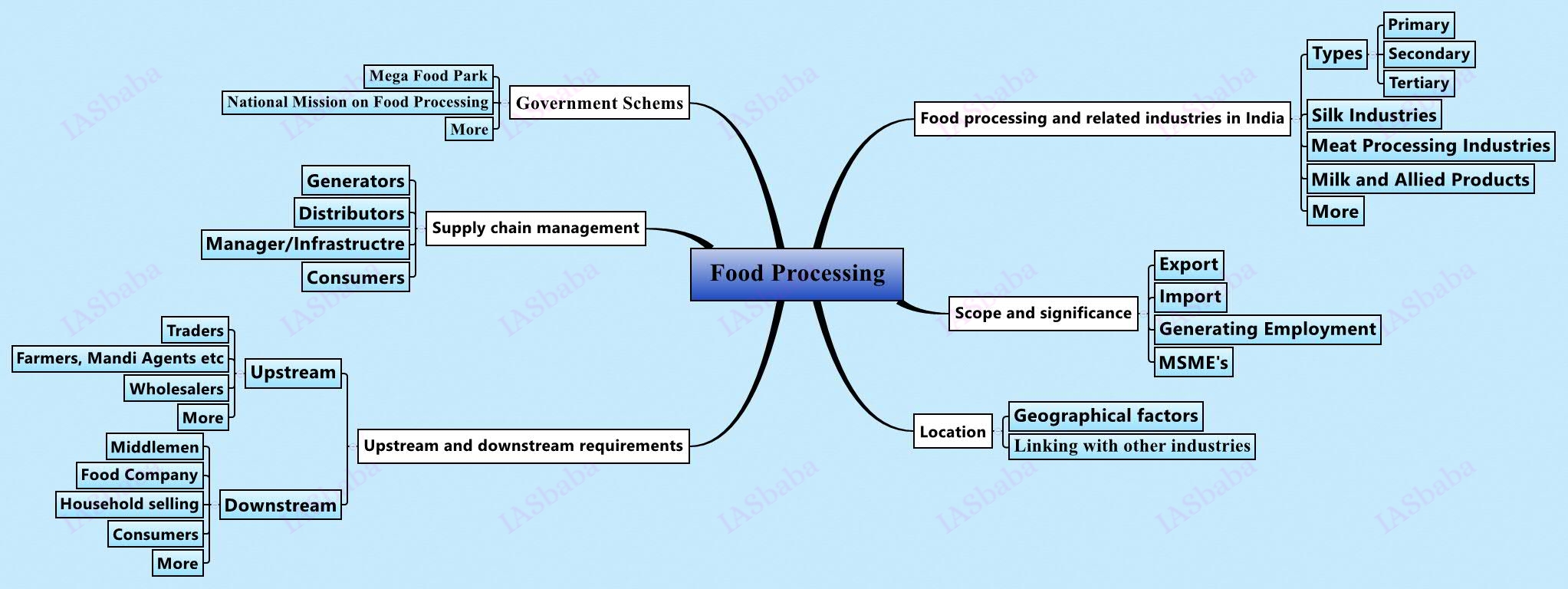
6. Economics of Animal-Rearing, Food processing and related industries in India – Scope and significance, Location, Upstream and Downstream requirements, Supply Chain Management
Mrunal – Click
Newspapers: Information + Different Dimensions–> MUST–> Development of Analytical Ability
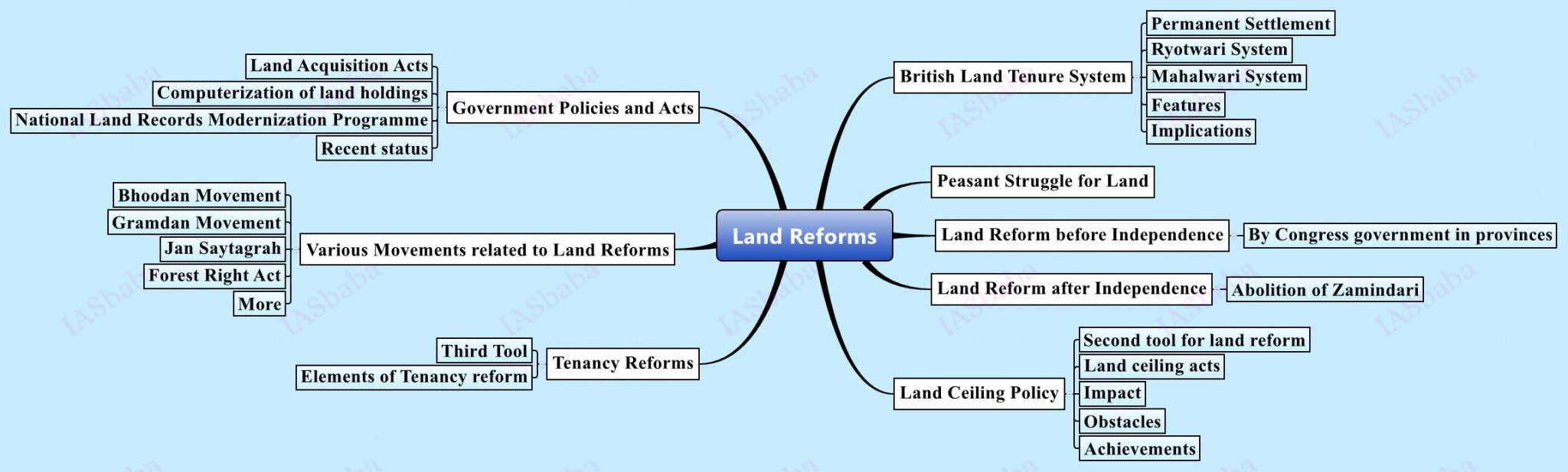
7. Land reforms in India
If an ordinance is being passed and an “Ordinance Raj” is in place, the issue must be extremely important. And UPSC, in the question given below is not only trying to understand your knowledge but also, a viewpoint of a budding officer, free of a biased mind-set and employing analytical skills to the best possible manner. Have a look:
Let us go through previous years UPSC questions
The right to fair compensation and transparency land acquisition, rehabilitation and resettlement act, 2013 has come into effect from 1 January 2014. What implication would it have on industrialization and agriculture in India?
Read:
Land Settlement Policies – Modern History
Newspapers: Information + Different Dimensions–> MUST–> Development of Analytical Ability
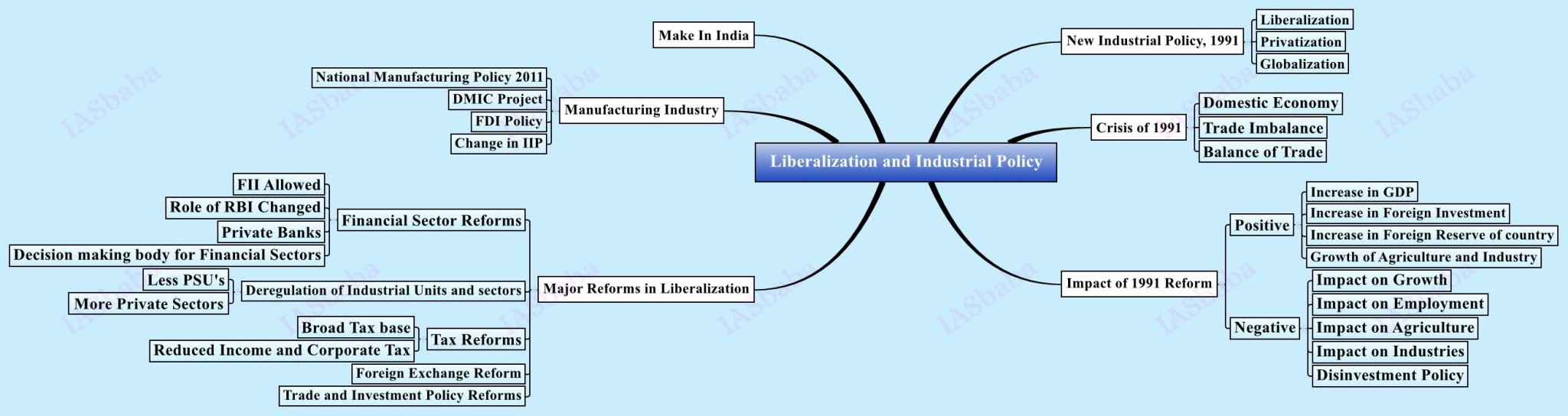
8. Effects of liberalization on the economy, changes in industrial policy and their effects on industrial growth.
Read:
- NCERT 11th :Ch 1 + 3
- NIOS- L 1+ 3 + 23 + 24 + 25 + 26 + 27 +28
- Planning + Industry + Agriculture- IYB
Newspapers: Information + Different Dimensions–> MUST–> Development of Analytical Ability
Let us go through previous years UPSC questions
Normally countries shift from agriculture to industry and then later to services, but India shifted directly from agriculture to services. What are the reasons for the huge growth of services vis-a-vis industry in the country? Can India become a developed country without a strong industrial base?
- Failure in the Development Agenda + Power Sector + Transportation facilities
- Non-translation of the growth into growth in the Manufacturing sector
- Service Sectors: One place- less demands
- Highlight the need of Manufacturing Services: Trade Balance + Employment + Make in India
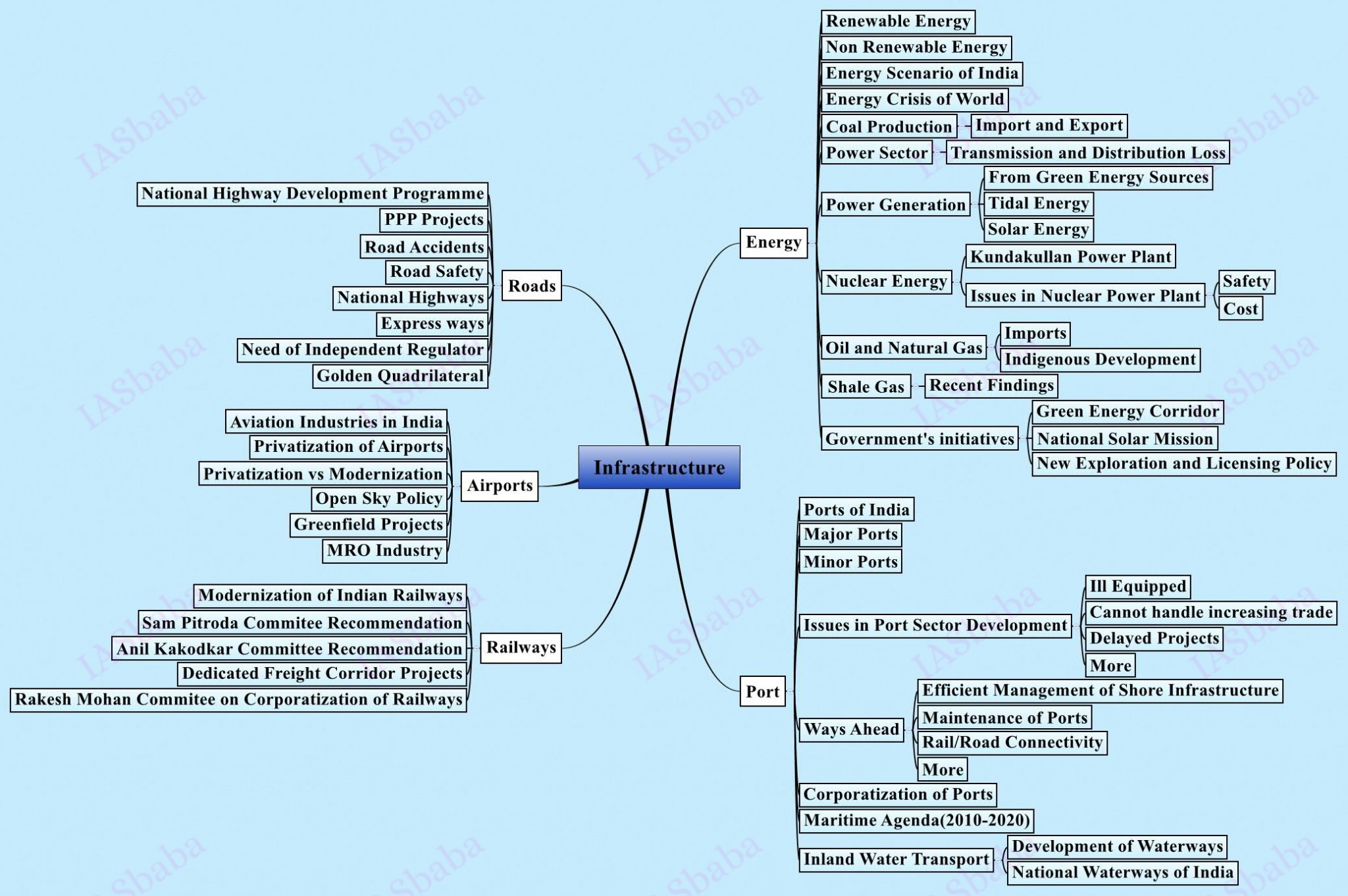
9. Infrastructure: Energy, Ports, Roads, Airports, Railways etc.
- Infrastructure financing,
- Waterways,
- Civilaviation
- Railways
Read: Infrastructure:
- NCERT-11th Ch 8
- NIOS L-29 + 30 + 32
- IYB-Energy + Transport + Water
Newspapers: Information + Different Dimensions–> MUST–> Development of Analytical Ability
Let us go through previous years UPSC questions
National urban transport policy emphasizes on moving people instead of moving vehicles. Discuss critically the success of various strategies of the government in this regard.
Let us evaluate:
- Equitable allocation of road space with people, rather than vehicles
- Unified Agency to Handle Passenger Transport
- Integrating Land Use and Transport Planning
- Importance in ‘Smart Cities’ Project
But, the need of the hour is proper implementation:
- Realignment of existing routes,
- new forms of fare structures,
- better interchange facilities
- different organisational structures
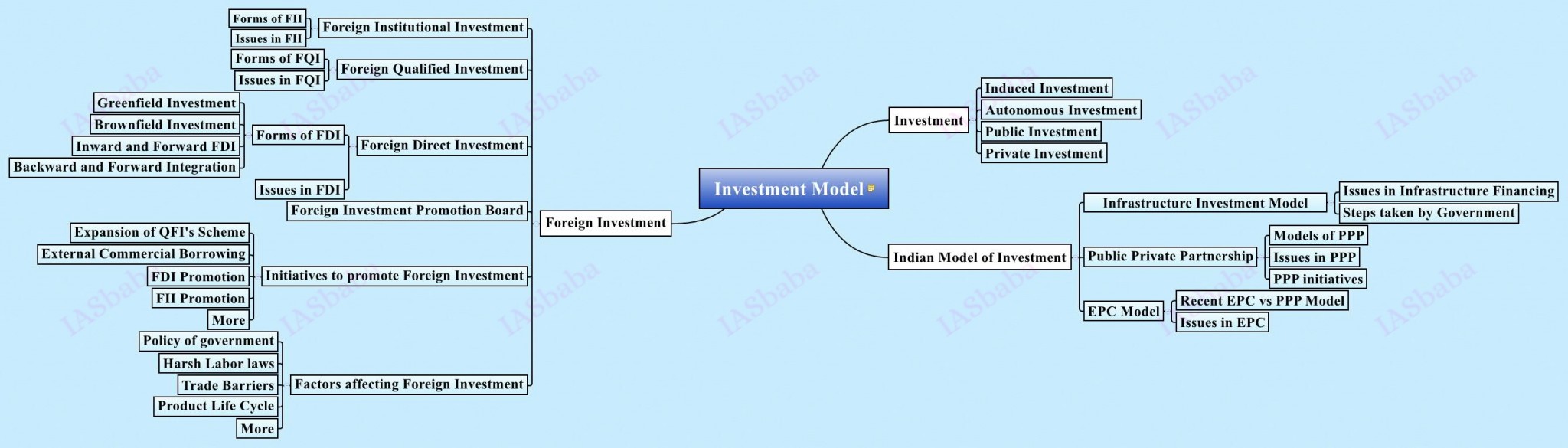
10. Investment models.
- Types of investment,
- Investment models,
- Investment strategies in India,
- PPPs,
- Controlling measures, etc.
Read about the following to get a broader picture:
- Industrial Sector,
- Public sector in India,
- Disinvestment
Newspapers: Information + Different Dimensions–> MUST–> Development of Analytical Ability
Let us go through previous years UPSC questions
Explain how private public partnership agreements, in long gestation infrastructure projects, can transfer unsustainable liabilities to the future. What arrangements need to be put in place to ensure that successive generations’ capacities are not compromised?
- Why are they stuck- Reasons?
- Solutions-Way ahead
So, here if we understand PPP and trace it through newspapers- we can write down the answers easily!
- Foreign direct investment in the defence sector is now said to be liberalized. What influence this is expected to have on Indian defence and economy in the short and long run?
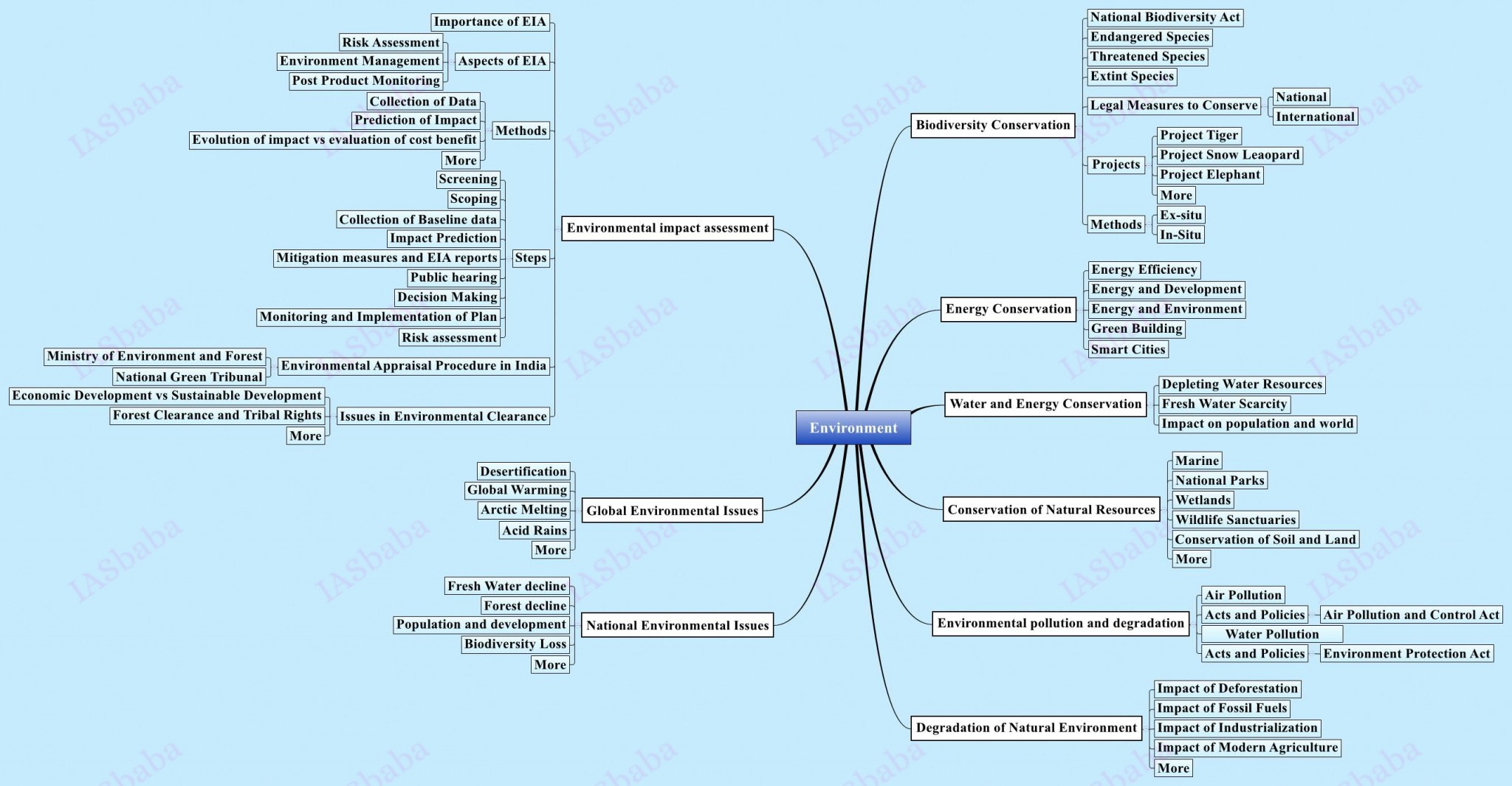
11. Biodiversity, Environment and Disaster Management
- Ecology and Natural Resources
- Biodiversity
- Environmental Pollution
- Sustainable Development, Climate Change and EIA
- Disaster Management
Read:
Newspapers: Information + Different Dimensions–> MUST–> Development of Analytical Ability
For Environment:
- NIOS (exhaustive coverage)
- Mrunal’s Environment Coverage
Disaster Management: Click & 2nd ARC Report: Crisis Management
Let us go through previous years UPSC questions
Should the pursuit of carbon credit and clean development mechanism set up under UNFCCC be maintained even through there has been a massive slide in the value of carbon credit? Discuss with respect to India’s energy needs for economic growth.
Drought has been recognized as a disaster in view of its party expense, temporal duration, slow onset and lasting effect on various vulnerable sections. With a focus on the September 2010 guidelines from the National disaster management authority, discuss the mechanism for preparedness to deal with the El Nino and La Nina fallouts in India.
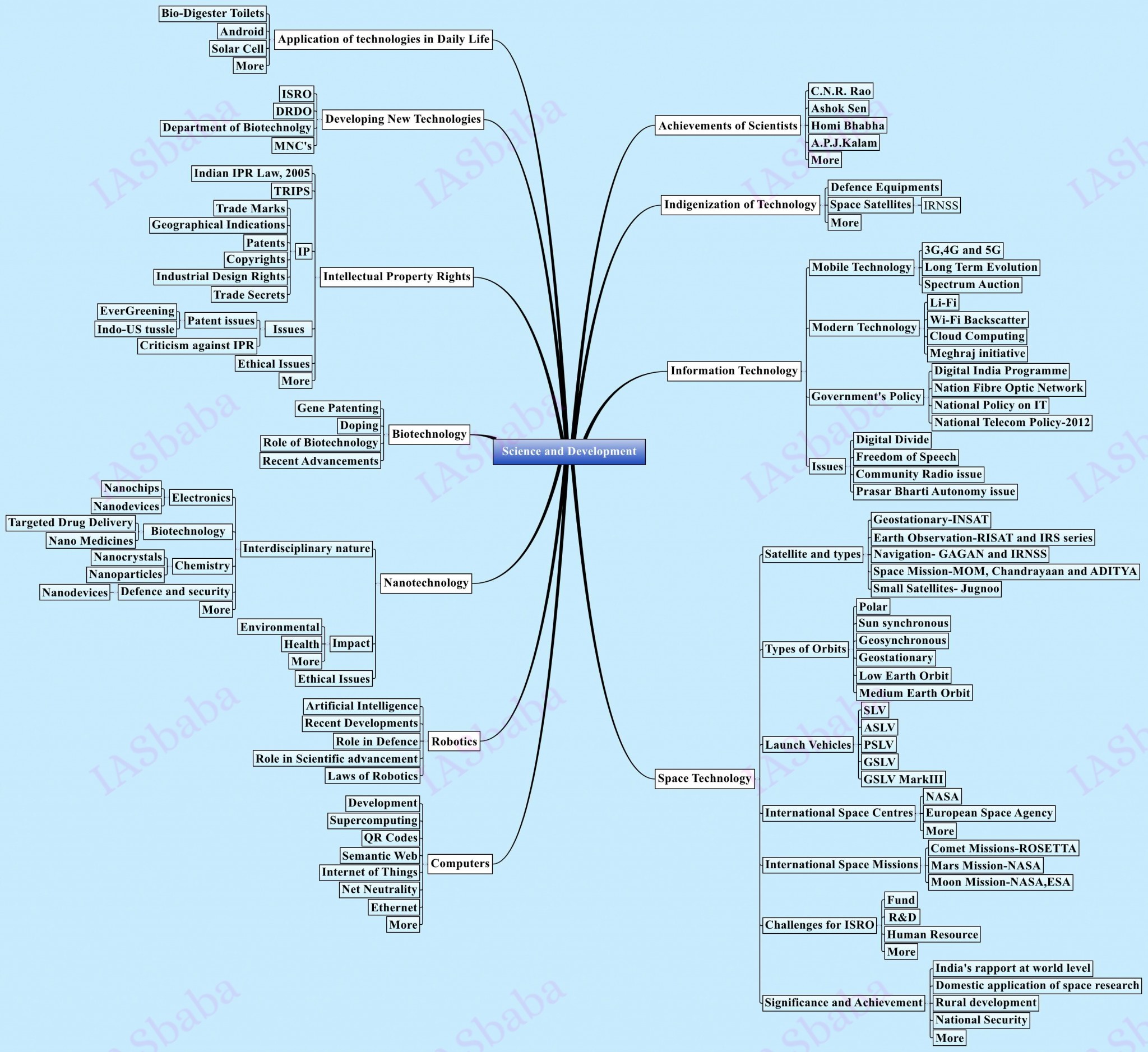
12. Science and Technology
- Developments and achievements in India
- Biotechnology
- Information Technology
- Nuclear and Defence Technology
- Space
- Robotics and Nanotechnology
- IPR issues
Newspapers: Information + Different Dimensions–> MUST–> Development of Analytical Ability
NCERT: Relevant Chapters 🙂
Let us go through previous years UPSC questions
Can overuse and the availability of antibiotics without doctor’s prescription, the contributors to the emergence of drug-resistant diseases in India? What are the available mechanisms for monitoring and control? Critically discuss the various issues involved.
Remember “Chennai Declaration”? 🙂
In a globalised world, intellectual property rights assume significance and are a source of litigation. Broadly distinguish between the terms – copyrights, patents and trade secrets.
There is a need to create a basic foundation for the issue which have continuously been in news:
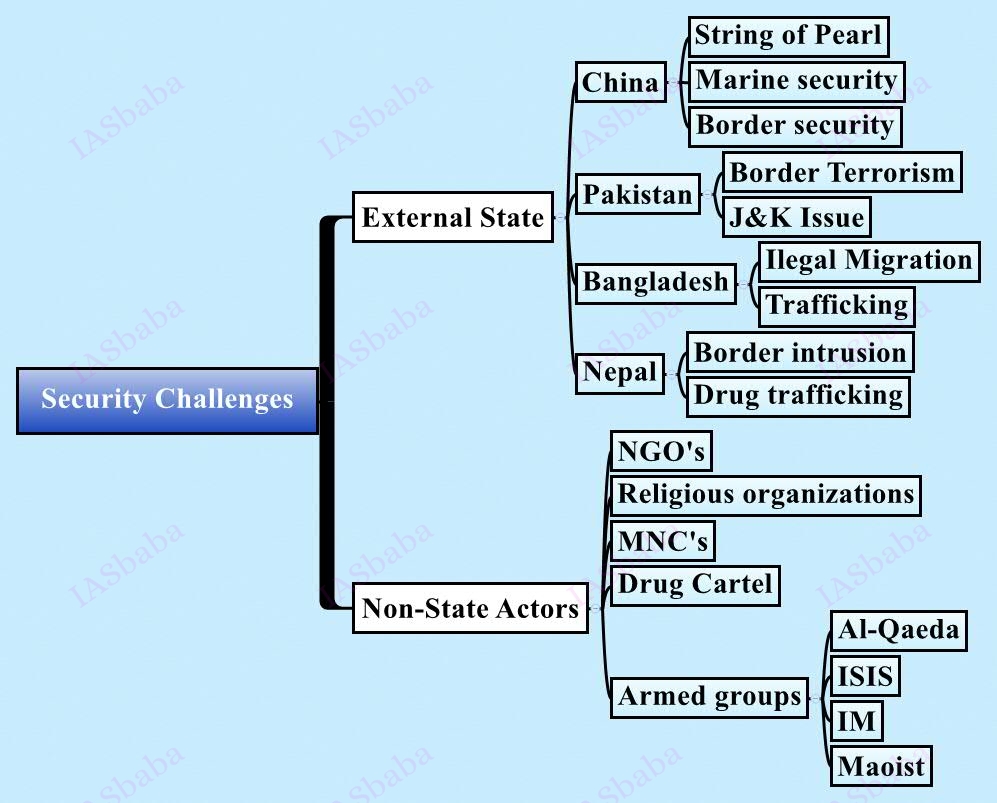
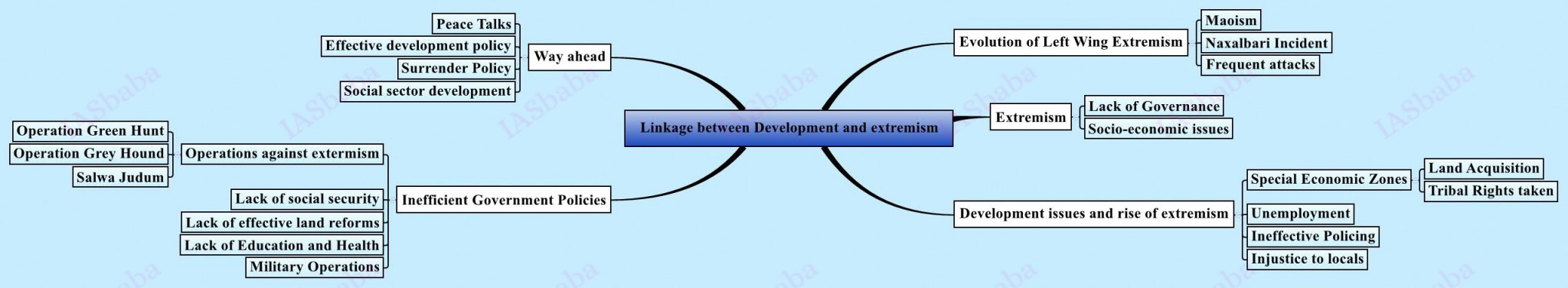
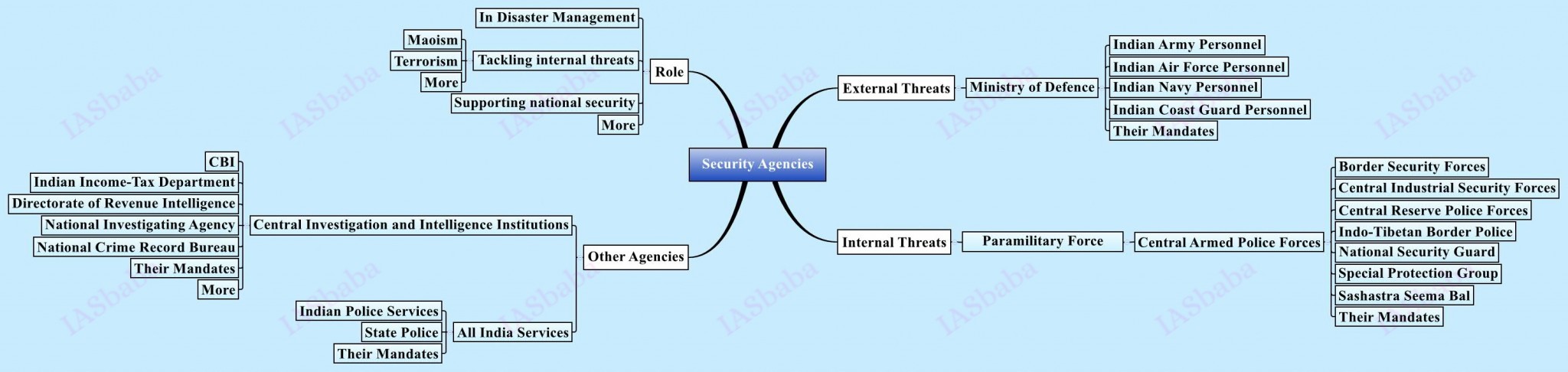
13. Security Issues
- Development, Organized crime and Extremism
- Role of external state and non-state actors
- Internal security and communication issues
- Cyber Security
- Money Laundering, border management
- Security Forces and Agencies
Read:
Newspapers: Information + Different Dimensions–> MUST–> Development of Analytical Ability
IDSA Website
2nd ARC Report: Capacity Building for Conflict Resolution
Let us go through previous years UPSC questions
International civil aviation laws provide all countries complete and exclusive severity over the airspace above the territory. What do you understand by airspace? What are the implications of these laws on the space above this airspace? Discuss the challenges which this poses and suggests ways to contain the threat.
In 2012, the longitudinal marking of the high-risk areas for piracy was moved from 65° East to 78° east in the Arabian Sea by International Maritime organisation. What impact does this have on India’s maritime security concerns?
China and Pakistan have entered into an agreement for development of an economic corridor. What threat does it pose for India’s security? Critically examine
All these topics do not require any scholar understanding. You just need basic knowledge and analytical perspective to relate the basics with contemporary developments.
End Note:
- Whole Paper 3 can be smartly covered through newspapers provided you are thorough with little basic concept.
- Any paper requires a simple reading of all the NCERTs from 6th to 12th, as it builds a basic foundation to start thinking in an objective and subjective matter.
- Reading a whole book or several sources for these topics has many disadvantages. One of them is cost benefit ratio. Second is wastage of your precious time and energy. If one plays smart here, he/she can substantially devote his/her energy for other important topics having more weightage.
- UPSC has taken a 360 degree turn and the solution to score more is “on-the-spot innovative thinking”. Mugging up is a “sheer waste of time”.
- Revision is the key to your success.Make your own plan, stick to a few resources & keep visiting them often, critically examine the issues from every possible angle and study smart: Revise again and again!!
- Start writing practice after one reading of NCERT (Beginners). One should never wait to finish off everything to start writing practice as the retention capacity is more when one writes.
Share your thoughts and Feedback 🙂