IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis, IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs December 2015, International, UPSC
Archives
IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs – 15th December, 2015
INTERNATIONAL
TOPIC: General Studies 2
- Important Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
- Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests, Indian diaspora.
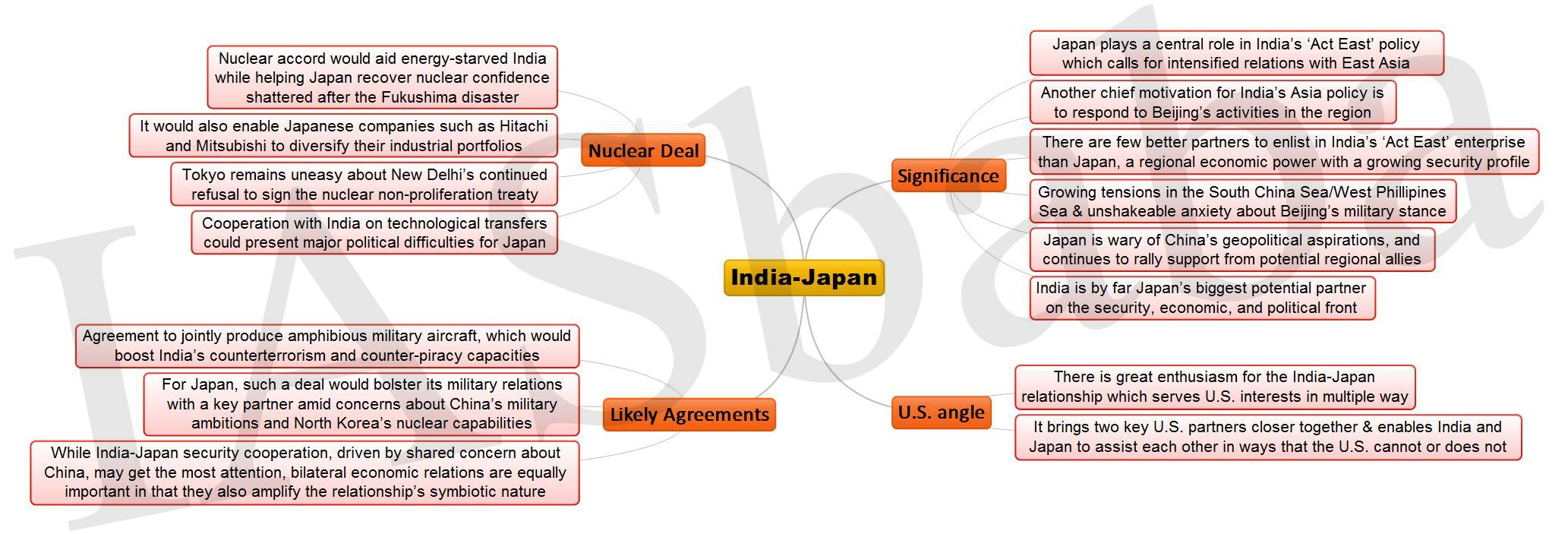
INDIA-JAPAN TIES
Background and Importance of India-Japan Ties:
- Relations between India and Japan go back to the 6th century AD. When Buddhism which was born in India was introduced in Japan. Indian culture has left a deep impact on Japanese culture.
- Indian Iron ore helped in Japan’s recovery after the World war. In return Japan started providing Yen loans at lower interest rate and Assistance to development projects and infrastructure.
- Both India and Japan are members of G4 Group of Nations with German y and Brazil, who are jointly trying to be permanent members of UN Security Council with full veto powers. The countries have realized that together they stand a better chance of making it to the high table of the UNSC, rather than separately.
- India and Japan have signed a bilateral agreement on currency swap. Such agreement will help to address short term liquidity problems of either country with objectives such as: Firstly, to help each other in case of balance of payment crisis. Secondly, to counter speculative attack on their respective currencies.
- India and Japan have come up with “Road map for New Dimensions to Strategic and Global Partnership’ which seeks to strengthen ties in civil nuclear energy, political, security, defence, economic, high technology, and disarmament.
Recent developments and Indo-Japan Summit:
- Generally, International conflicts arise due to non-transparency, suspicion and trust-deficit. But, when two leaders meet face to face, it allows personalization of relationship, adds warmth between two nations creates positive atmosphere and reduces tensions and misunderstandings.
Strategic Ties (Civil + Defence):
- In 1998: Japan had banned sale of HAL and other Indian defence companies (due to Pokhran test). After Modi visit, they lifted ban from HAL and 5 other cos.
- Abe and Modi have intensified bilateral defence cooperation, which had begun in the last decade. Besides an agreement on the sale of advanced amphibious aircraft, the US-2, Delhi and Tokyo are also likely to sign a framework agreement that will facilitate defence technology transfer and the co-production of weapons. This will be Japan’s first overseas military sale in 50 years. In line with the Modi government’s Make in India initiative, a broader defence agreement underpinning joint development of weapon systems is also in the offing.
- Japan will intensify 2+2 strategic dialogue with India, involving foreign and defence Secretaries. Japan also has similar with US, Australia, Russia and France.
- Apart from Bilateral ties, Japan is looking forward to join hands with India and US in trilateral ties in terms of its participation in India-US Malabar Naval exercise.
- Both India and Japan want urgent reforms in UNSC- for increasing no. of permanent and non-permanent members. Japan will help India get FULL membership in four international export control regimes such as: Nuclear Suppliers Group, Missile Technology Control Regime, Wassenaar Arrangement, Australia Group.
Economy and Infrastructure:
- At present, China biggest producer of rare earth and it may limit its exports to safeguard its local manufacturing units. Hence India is pitching in to supply rare earth chloride to Japan- for making defence and high tech electronics.
- Japan will be investing $35 billion in many projects such as smart cities, bullet trains, Ganga Cleaning in next five years and proposal to double the Japanese FDI in 5 years. In parallel, 50 billion yen loan to IIFCL (India Infrastructure Finance corp. ltd) for PPP projects.
- As per the recent meet between Abe and Modi, The agreement that is likely to have the biggest and most visible impact is the $12 billion loan from Japan to help India build its first high-speed railway project to connect Ahmedabad with Mumbai. The 500-kilometre-long railway line would be built within a period of seven years. The agreement provides India not just over 80 per cent of the total project cost with loan having incredibly low interest rate of 0.1 per cent over a period of 50 years, but also technical assistance to build domestic capacity to manufacture coaches and tracks before making them operational.
- Japan will help finishing the ongoing industrial corridor projects: Western Dedicated Freight Corridor (DFC), Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC), Chennai-Bengaluru Industrial Corridor (CBIC), Japan will help to setup Industrial cities / townships in Gujarat, Maharashtra, UP and Madhya Pradesh. Japanese industrial townships will give benefits similar or higher than SEZ and NIMZs in India. Japan will also help Road connectivity, Forest resource Management, water supply improvement at North East.
Nuke Deal:
Negotiations on civil nuclear deal have been completed. If signed, India will become the first non-NPT country with which Japan has signed a nuclear deal. Issues like, should/can India conduct another nuclear test like Pokhran after the deal, are yet to be addressed.
Why should Japan sign nuclear deal with a non-NPT country?
Japan has got about 54 nuclear reactors. Most of the reactors are shut after the recent events of Tsunami, earthquake and radiation leak from Fukushima. They are shut due to internal protests and for safety reasons. Now, the PM Shinzo Abe has been attempting to open one or two of them. Besides, the Japanese economy is slowing down. It needs exports and can transfer nuclear technology. India is the potential country where it can export.
Why does India want nuke deal with Japan?
- Japanese companies supply critical components to nuclear power plants and if we can get these Japanese components and technology, it will be great in terms of increase in nuclear-electricity generation.
- In parallel, Japan has huge stockpile of reprocessed plutonium which will be of greater use in the long run.
Energy-Environment:
- Tie up in oil-gas exploration, Coal-fired power generation technology; Clean Coal Technology (CCT); Super-critical coal-fired power project in Meja, UP; Super critical thermal power plant in Barauni, Bihar; Assisting Gujarat in development of Canal top solar power plants and Mega Solar Power project at Neemrana, Rajasthan.
Science-Space-Healthcare
- Japan will help in Outer space exploration via Asia-Pacific Regional Space Agency Forum (APRSAF); internet security; Joint ocean studies; Science Fellowship programs for youth.
People 2 People contact:
- Kyoto-Varanasi partnership agreement: to develop Varanasi just like Japan’s historical city Kyoto;
- JENESYS 2.0 program: Exchanging approximately 1500 youth;
- Japan Overseas Cooperation Volunteer (JOCV) – will send nurses and medical help to Mizoram.
Japan will also promote Tourism which is a potential domain to generate Forex and employment in India; youth exchange; It also help in skill development of youth to reduce educated unemployment due to mismatch between educational qualification and industrial requirement.
It also helps in skill development of youth to reduce educated unemployment due to mismatch between educational qualification and industrial requirement.
A unique feature of the understanding reached between Abe and Modi is that Japanese money would be used to create manufacturing facilities in India. On similar lines committing $12 billion of Japanese funds for creating such projects in India would be a big boost to investments in an economy that is desperately looking for a pick-up in its investment rate. More importantly, it will go a long way in implementing the Indian government’s ‘Make in India’ programme.
The China factor: Two things made Japan wake up to the India opportunity.
- First, the fact that countries like South Korea began to overtake Japan in the Indian market.
- Second, the emergence of China as the world’s second-biggest economy, overtaking Japan.
However, more than the change in the business environment in India, it is the growing challenge posed by China’s rise that has finally forced Japan to invest in India’s rise.
India-Japan Vision 2025: statement of long-term bilateral engagement defined by shared interests and values.
- First, the agreement on peaceful uses of nuclear energy ends years of painstaking negotiations, delayed both by the Fukushima nuclear tragedy in Japan and India’s own confused legislation of a nuclear liability law.
- Second, India’s decision to agree to “tied aid”, enabling Japanese funds to finance Japanese investment, especially in infrastructure and high-speed railway projects.
- Third, India’s willingness to promote Japanese industrial townships aimed at making India a more hospitable destination for Japanese business.
Shared strategic concerns:
- Japan is a member of the U.S.-led Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) and India is not, both countries are engaged in creating a Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) and Japan has agreed to support India’s case for membership of Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC), even as the U.S. continues to drag its feet over this.
- There are several interesting new initiatives that Mr. Abe and Mr. Modi have signed on for. One of them is an agreement for Japanese funding of India’s own “belt-and-road” connectivity projects across Asia.
- While committing itself to investing in infrastructure within India to improve road and rail connectivity, Japan has also agreed to promote India’s “Act East” policy by developing and strengthening “reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructures that augment connectivity within India and between India and other countries in the region” aimed at advancing Asian industrial networks and regional value chains with open, fair and transparent business environment in the region.
- Japan and India can build road and rail connectivity across the Eurasian landmass, running parallel to China’s own “One Belt, One Road” project.
Connecting the dots:
- Critically examine the need of the Nuke deal between India and Japan and bring out the positive outcomes of the deal which would address Energy security with best of safety standards based on the recent mishaps?
- New found interest of Japan to Invest in India encouraging ‘Make in India’ initiative will it be a new zeal in old friendship between India and Land of Rising sun? Comment.
MUST READ
Today many articles related to ‘Climate Change’ were published in various National Dailies. We had covered this issue comprehensively. Click on the below link to get the detailed analysis of the ‘Climate Change: Paris Summit’
http://iasbaba.com/2015/12/iasbabas-daily-current-affairs-14th-december-2015/
A postscript on the NJAC
For detailed analysis of NJAC, refer the below link
http://iasbaba.com/2015/10/iasbabas-daily-current-affairs-19th-october-2015/
http://iasbaba.com/2015/10/iasbabas-daily-current-affairs-20th-october-2015/
India wants WTO to discuss farm subsidies of the rich
Since the meet at Nairobi has just begin today (15th December, 2015), this issue will be covered comprehensively in the upcoming days.
Get smart on diesel cars
The renewable energy revolution- The relatively rapid transition away from fossil fuels in China and India is driven by the economic benefits renewable energy sources are perceived as conveying
MIND MAPS
1. India- Japan
2. Commodity Meltdown
3. Panchayat Gender Imbalance