IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis, IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Oct 2016, International, UPSC
Archives
IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs – 17th October, 2016
INTERNATIONAL
TOPIC: General Studies 2
- India and its neighborhood- relations.
- Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
- Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests, Indian diaspora.
- Important International institutions, agencies and fora- their structure, mandate.
8th BRICS SUMMIT — GOA DECLARATION
In News:
- The 8th BRICS summit was held in Goa. The summit concluded with adaptation of Goa Declaration.
- The theme for the summit was “Building Responsive, Inclusive and Collective Solutions”.
- BRICS — Five-nation powerful grouping — Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa
- BRICS brings together five major emerging economies, comprising 43% of the world population, having 30% of the world GDP and 17% share in the world trade.
- The ninth BRICS Summit will be hosted by China in 2017.

Eight BRICS Summits have taken place so far. The 8th BRICS Summit was hosted by India during its Chairmanship in 2016. The earlier Summits were held as under :
- 7th BRICS Summit – 8-9 July 2015 in Russia (Ufa)
- 6th BRICS Summit – 14–16 July 2014 in Brazil (Fortaleza)
- 5th BRICS Summit – 26–27 March 2013 in South Africa (Durban)
- 4th BRICS Summit – 29 March 2012 in India (New Delhi)
- 3rd BRICS Summit – 14 April 2011 in China (Sanya)
- 2nd BRIC Summit – 16 April 2010 in Brazil (Brasilia)
- 1st BRIC Summit – 16 June 2009 in Russia (Yekaterinburg)
Starting essentially with economic issues of mutual interest, the agenda of BRICS meetings has considerably widened over the years to encompass topical global issues.
BRICS cooperation has two pillars – consultation on issues of mutual interest through meetings of Leaders as well as of Ministers of Finance, Trade, Health, S&T, Education, Agriculture, Communication, Labour, etc. and practical cooperation in a number of areas through meetings of Working Groups/Senior Officials.
Regular annual Summits as well as meetings of Leaders on the margins of G20 Summits are held.
During India’s BRICS Chairmanship, we will adopt five-pronged approach:
- Institution building to further deepen, sustain and institutionalise BRICS cooperation;
- Implementation of the decisions from previous Summits;
- Integrating the existing cooperation mechanisms;
- Innovation, i.e., new cooperation mechanisms; and
- Continuity, i.e., continuation of mutually agreed existing BRICS cooperation mechanisms.
In short, the Indian approach towards its BRICS Chairmanship could be captured by ‘IIIIC or I4C’.
Outcome of the summit:
- BRICS called for tackling terrorism, early adoption of CCIT
- Goa Declaration condemned terrorism in all its forms and stressed that there can be no justification for such acts.
- It called upon all nations to adopt a comprehensive approach in combating terrorism, violent extremism, radicalisation, recruitment, movement of terrorists including foreign terrorists and blocking sources of financing terrorism.
- BRICS called upon all nations to work together to expedite the adoption of the Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism (CCIT) in the UN General Assembly without any further delay.
- Reaffirmed commitment to the FATF (Financial Action Task Force)
- The BRICS said sources of terror funding like organised crime by means of money-laundering, drug trafficking, criminal activities, dismantling terrorist bases, and countering misuse of the internet including through social media by terror entities should be focus areas.
- BRICS said it reaffirmed commitment to the FATF (Financial Action Task Force) international standards on combating money laundering and the Financing of Terrorism and Proliferation.
- The FATF is an intergovernmental organization founded in 1989 on the initiative of the G7 to develop policies to combat money laundering. In 2001 the purpose expanded to act on terrorism financing.
- It also called for swift, effective and universal implementation of FATF on combating terrorist financing, including effective implementation of its operational plan.
- UN Reforms
- India is among the many countries that are worried about the weakening of international institutions and the tendency to impose unilateral preferences over others.
- For instance, American military action (2003) to remove President Saddam Hussein from power in Iraq à an action the United States launched unilaterally in violation of the UN Charter.
- To guard against this kind of unhelpful trends, the wings of the United Nations must be suitably strengthened.
- With only China as a permanent member presently, Asia is grossly underrepresented, whereas Africa and Latin America do not have any representation in the inner circle of this important organ.
- BRICS called for urgent need to reforms of the United Nations, including UN Security Council, to increase representation of developing countries.
Other highlights:
- Resolution of civil war in Syria, in accordance with the “legitimate aspirations of the people of Syria” and action against U.N.-designated terrorist groups like IS and Jabhat al-Nusra.
- Appreciated progress in implementation of Strategy for BRICS Economic Partnership and emphasise importance of BRICS Roadmap for Trade, Economic and Investment Cooperation until 2020.
- Welcomed adoption of 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and its Sustainable Development Goals.
- BRICS also welcomed the Paris Climate Agreement and its imminent entry into force on 4 November.
- Reiterated determination to use all policy tools to achieve the goal of sustainable and inclusive growth.
Connecting the dots:
- India and China share multiple concerns when it comes to security and trade engagements. Multilateral and regional summits provide a platform to discuss these issues. Critically analyse.
- Is BRICS an effective Multilateral Forum in a Multi-polar International Order? Substantiate your views.
- BRICS countries must extend the synergy being witnessed in economic and strategic areas to the fight against terrorism? Discuss.
ECONOMY
TOPIC: General Studies 3
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources, growth, development and employment.
Inflation assessment: India needs to explore more
India has multiple inflation indicators.
- There are four consumer price indices (CPIs) — Countrywide CPI, CPI for agricultural labourers, rural labourers and industrial workers.
- These sector-specific CPIs are used for fixation of agricultural wages, rural wages and the inflation compensation or dearness allowances for employees in the government.
- In addition to CPI, there is a wholesale price index (WPI). Until recently, it was the preferred inflation anchor because of its wider coverage, a short time lag and weekly (it became a monthly index from 2011) availability.
CPI is the new inflation indicator
- Now, the new series of CPI with its all-India coverage, updated base (2012) and availability with similar time lag has become the new inflation anchor and also basis for monetary policy changes.
- The shift in focus and use of CPI has been in line with many other countries which formally or informally having an inflation target approach.
- It has also been consistent with the objective of minimizing the impact of rising prices on people.
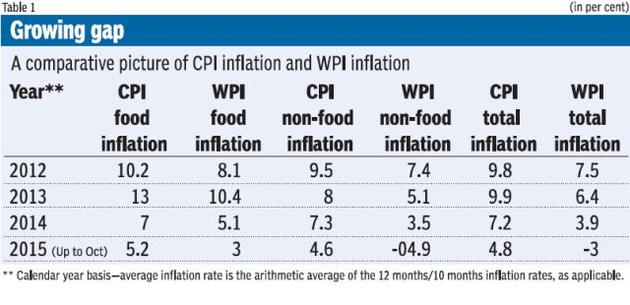
Difference between WPI and CPI
| WPI | CPI | |
| By | Compiled and published by Office of the Economic Advisor on a monthly basis. | Compiled and published by the Labour Bureau on a monthly basis. |
| Stage | Measures inflation at each stage of production. | Measures inflation only at final stage of production. |
| What | Middle point of the sum of all the goods bought by the traders. | Middle point of the sum of all the goods bought by consumers. |
| Basis | Based on the price prevailing in the wholesale markets or the price at which bulk transactions are made. | Based on the final prices of goods at the retail level. |
| Groups | Manufacturing, agriculture, quarrying, mining, and in the export/import industry. | Education, apparel, foods and beverages, communication, transportation, recreation, housing and medical care. |
Only CPI apt as an inflation indicator?
A former Chairman of the Prime Minister’s Economic Advisory Council, C. Rangarajan had mentioned that if WPI is behaving same as CPI, there is no additional information. But, if there is a difference, it is not affordable to ignore the behaviour of WPI as it does not reflect only international commodity prices but also domestic conditions.
- CPI looks at inflation purely from the perspective of a consumer and ignores the prices that a producer faces.
- The CPIs completely ignore the inflation for investment and capital goods.
- A diverging trend between WPI (which is more akin to a producers’ price index) and CPIs is observed because two sets of prices now confront producers and consumers.
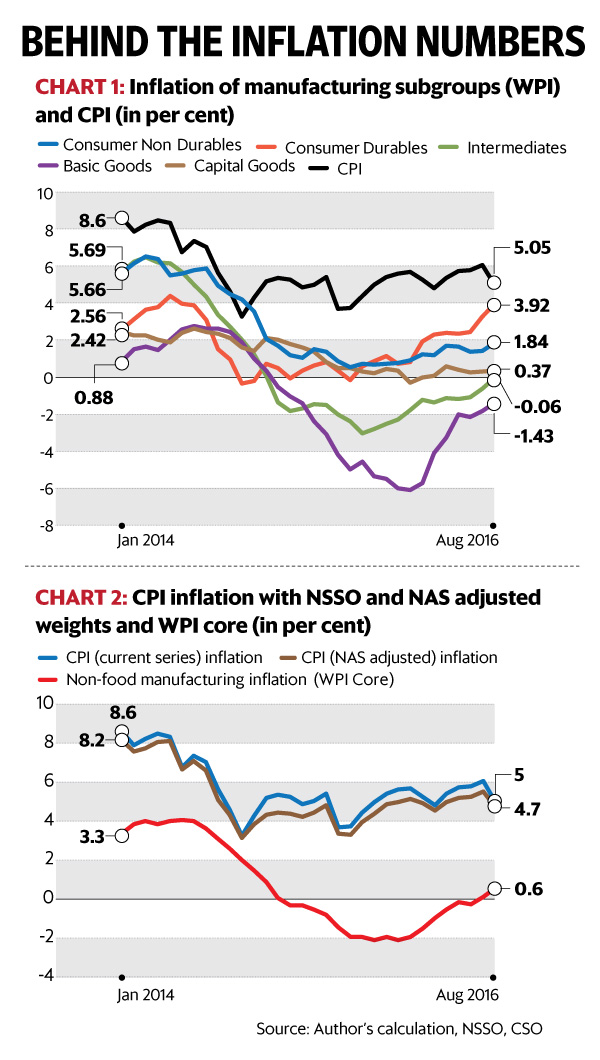
- There has been average inflation for manufactured products which are further sub-divided into consumer non-durables, consumer durables, intermediates, basic goods and capital goods.
- The inflation of these has been averaging between 2.8%, 1.8%, 0.7%, (-) 1.3% and 1.2% during the 32 month period of January 2014 to August 2016. Whereas, the CPI has averaged 5.7%.
Picture Credit: http://www.livemint.com/r/LiveMint/Period2/2016/10/17/Photos/Processed/g_oped_new_web.jpg
Picture Credit: http://www.thehindubusinessline.com/multimedia/dynamic/02637/bl27_CPI_table1_2637039g.jpg
Use of weights
- CPI uses the consumption proportions as derived from the NSSO consumer expenditure surveys for inter-commodity weights.
- But there are huge differences between NSSO consumption expenditure and the expenditure as derived from the National Accounts Statistics (NAS) — at aggregate level and commodity groups level.
- The NSA weighs used for CPI show that there is a moderation in inflation by nearly 60 basis points during the aforementioned 32-month period
- The CPI adjusted for NAS weights has always been lower than the CPI with NSSO weights
- Thus, there is a need for adjustment in current CPI as it is based on data on consumption and not the complete data.
- The adjusted CPI inflation will not only be below the maximum threshold level of inflation but there can also be a possibility of moderating inflation because of improved availability of food products. This may lead to an indication of possible moderation in policy rates in the near future by the Reserve Bank of India.
Conclusion
- Management of inflation has always been a tricky issue because the interest rate, which is used as the key policy instrument, is double-edged.
- While containing inflationary expectations, it also affects adversely the investor perception and investment costs.
- The use of a single inflation anchor in a situation of divergent inflation perceptions for consumers and producers may often amount to ignoring the structural realities of the economy.
- However, the current official mandate is for the use of CPI in targeting inflation, but scope exists for using CPI with commodity weights being derived through NAS rather than NSSO.
- The monetary authorities can also consider other indicators like WPI in situations where CPI is at odds with WPI.
Connecting the dots:
- Is using CPI as the sole indicator for measuring inflation adequate? Examine
Related articles:
Diverging CPI, WPI: The inflation conundrum
MUST READ
Climate change- An onerous task ahead
Kairana and the politics of exclusion
The End TB strategy
Health spending: How States splurge on salaries
Unprepared for bad days
No one asks the farmer
Uniform Civil Code debate is not new, divided Constituent Assembly as well
Missing stock is harming our food security
Taking stock of India’s reforms
Rs70,000 crore budget, and not even 70,000 connected?
Clearing up the bad debt mess