IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs (Prelims + Mains Focus)- 8th May 2018
Archives
(PRELIMS+MAINS FOCUS)
Food Safety: New norms for labelling food
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains GS Paper II- Government interventions in key sectors
In News:
Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has drafted following regulations –
- All packaged food with at least 5% content from genetically engineered sources need to be labelled so.
- Foods that exceed norms of sugar and fat will need to carry ‘red’ and ‘green’ labels specifying the extent to which they do so.
Do you know?
- Current laws, however, prohibit any GM food — unless cleared by the Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee, a Union Environment Ministry body — from being sold in India.
- Through a 2007 notification, the Environment Ministry had exempted processed foods from this requirement. This has been stayed by the courts.
- There was also dispute between the FSSAI, a Union Health Ministry body, and the Environment Ministry on who checks if a particular food had a GE provenance.
Important Value Additions:
- FSSAI was already in news.
- FSSAI launched ‘Project Dhoop’ in April 2018 – an initiative aimed at shifting the school assembly time to noon to ensure maximum absorption of Vitamin D in students through natural sunlight.

About FSSAI
- FSSAI is established under FSS Act, 2006
- It is a statutory body for laying down science based standards for articles of food and regulating manufacturing, processing, distribution, sale and import of food so as to ensure safe and wholesome food for human consumption.
- Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India is the Administrative Ministry for the implementation of FSSAI.
Article link: New norms for labelling food planned
India gets $200 million loan for nutrition mission
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains GS Paper II- Government interventions in key sectors; Social issue and Welfare Schemes
In News:
- India and World Bank signs agreement for a $200 million loan for implementing National Nutrition Mission.
Key pointers:
About National Nutrition Mission
- Targeted mission – NNM targets to reduce stunting, under- nutrition, anemia (among young children, women and adolescent girls) and reduce low birth weight by 2%, 2%, 3% and 2% per annum respectively.
- It also strives to reduce the prevalence of stunting from the current level of 38.4% (as per the National Family Health Survey 4) to 25% by 2022.
- Aims at reaching 10 crore beneficiaries.
- Beneficiaries are mainly children up to the age of six years, pregnant women and lactating mothers and adolescent girls.
- Will be implemented in three phases between 2017 and 2020 across all districts of the country.
Important Value Additions:
- POSHAN Abhiyaan (National Nutrition Mission) is a flagship programme of the Ministry of Women and Child Development (MWCD)
- The National Nutrition Mission (NNM) has been set up with a three year budget of Rs.9046.17 crore commencing from 2017-18.
Article link: India inks $200 mn. WB loan for nutrition mission – The Hindu
India and Serbia celebrating their 70th year of cooperation
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains Paper II – India and the world, International Relations
In news:
- India and Serbia are celebrating their 70th year of cooperation.
- India and Serbia should revive ties from the non-alignment era, as their relations are not as well developed as in the past.
Important Value Additions:
- India and Serbia (Successor State of former Yugoslavia) have traditionally enjoyed deep friendship as co-founders of the Non-Aligned Movement.
India and Serbia:
- Serbia has abolished visa requirements for Indians, unilaterally (along with visas for China, Turkey, Iran, Indonesia and other countries we have historical ties with).
- India-Serbia trade is very low at about $160 million.
- Serbia is a bridge between the east and the west, is on the road to joining the European Union.
- Serbia supports India in multilateral for a including India’s membership of NSG, permanent and non-permanent membership of UNSC and Indian candidatures to various international organizations.
- Serbian leadership has expressed solidarity with India in the fight against terrorism.
Map work:
Observe figure/map below and try to locate the following –
- Serbia is a landlocked country.
- Capital – Belgrade
- Situated in Europe but not part of EU
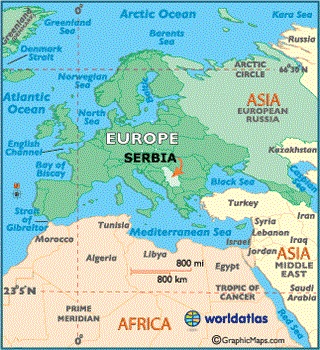
Article link: NAM needs new cause, says Ivica Dacic, Serbian Deputy … – The Hindu
Putin sworn in for fourth term
In News:
- Vladimir Putin was sworn in as Russia’s President for a fourth term
- The 65-year-old, in power since 1999, is on course to become the longest-serving Russian leader since Joseph Stalin.
Important Value Additions:
Russian Constitution says –
- The President of Russia is directly elected for a term of six years.
- Any citizen of the Russian Federation not younger than 35 years of age and with a permanent residence record in the Russian Federation of not less than 10 years may be elected President of the Russian Federation.
- One and the same person may not be elected President of the Russian Federation for more than two terms running.
Now you may think – Article says 4th term, but in Russia, President may not be elected for more than two terms running.
Answer: It is his second consecutive—and fourth overall—term as president.
Article link: Putin becomes President for 4th time, says improving economy will be priority in new six-year term
Australia pledges $34 million to help save koala population
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains Paper III – Environment and Conservation of Biodiversity
In News:
- The Australian Koala Foundation estimates that there may be as few as 43,000 koalas left in the wild.
- Habitat loss, dog attacks, climate change & diseases have taken their toll on the animals.
Important Value Additions:

About Koalas
- IUCN Status: Vulnerable
- Endemic to Australia. Koalas are found in the eucalyptus forests of eastern Australia.
- It is an arboreal herbivorous marsupial native to Australia.
- Koalas typically inhabit open eucalypt woodlands, and the leaves of these trees make up most of their diet. Because this eucalypt diet has limited nutritional and caloric content, koalas are largely sedentary and sleep up to 20 hours a day.
- Koalas get almost all their moisture from the leaves they eat, and rarely drink water.
- Eucalyptus leaves are super tough and poisonous! Luckily for koalas, they have a long digestive organ called a cecum which allows them to break down the leaves unharmed.
Article link: Australia pledges US$34-million to help save the koala
(MAINS FOCUS)
NATIONAL/WELFARE
TOPIC:
General Studies 2:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections of the population by the Centre and States and the performance of these schemes; mechanisms, laws, institutions and Bodies constituted for the protection and betterment of these vulnerable sections.
General Studies 3:
- Infrastructure: Energy, Ports, Roads, Airports, Railways etc
- Disaster and disaster management.
Rail Accidents: Need for amendments in Railways Act
In news:
The recent deaths of schoolchildren at an unmanned rail crossing highlight why the Railways Act must be amended.
Flaw in compensation or claims procedure
- In relation to claims for railway accidents, the Railways Act provides for fixed compensation on predetermined scales.
- It also provides a forum for passengers to make claims in the form of Railway Claims Tribunals situated in different parts of India. But there is a limitation.
- Only a passenger on a train can make a claim before the Tribunal.
Concern: Passengers of a bus or motor vehicle who may have been harmed after a collision with a train can only approach the Motor Accidents Claims Tribunal.
Important case:
- In Donoghue v. Stevenson (1932) case, SC held that – the duty of care for the Railways extends not only to those who use the Railways’ services but also to people who are “neighbours” — namely, users of vehicles on roads that intersect with tracks.
- In other words, there is a common law liability for the railway administration for an accident at an unmanned crossing, even in the absence of specific provisions in the Railways Act.
- An action at common law can be filed against Railways because the Railways was involved in what are recognised as dangerous operations and hence is bound to take care of road users.
- Railways should take all precautions that will reduce danger to the minimum.
What does the Railways Act say?
The Railways Act 1989 (through Section 124) provides compensation on strict liability basis. This means that “when an accident occurs in the course of working a railway” (a collision between trains, or when one is a train carrying passengers, or derailment, or any other accident with a train or any part of a train carrying passengers), then whether or not there has been any wrongful act, neglect or default on the part of the railway administration, an injured passenger or one who has suffered a loss can lawfully maintain an action and recover damages.
Way ahead:
It is time the government amends the Railways Act to provide for compensation on a proactive basis without driving victims or their families to file applications in Tribunals or Courts.
It is also essential to include within Section 124 of the Railways Act a provision for a claim from a “neighbour to a passenger” in the manner that the Supreme Court recognises, namely, a road user of a motor vehicle.
Connecting the dots:
- Safety standards and associated institutional framework in the railways need immediate attention. Comment.
- Railways is considered to be the lifeline of our country but the frequency of fatal accidents have only increased in the recent past. What does it tell about Indian Railway’s ecosystem? Critically analyse.
NATIONAL
TOPIC:General Studies 2:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections of the population by the Centre and States and the performance of these schemes
Land administration in India and boosting farmers’ income
Background:
Recently, over 30,000 farmers marched nearly 200 km to Mumbai to share their grievances with the Maharashtra government. Only weeks ago, thousands of more farmers led a comparable demonstration in Shimla. While loan waivers and better MSP (Minimum Support Price) were part of these agendas, land remains the common agenda.
The agricultural sector dialogue focuses on supply chain efficiency or improving the quality of inputs like seeds and fertilisers. Land is one key issue that often remains unfocussed.
Land and agriculture:
- The land market in India inhibits agricultural productivity.
According to the 2010-11 Report on Agriculture Census, 85 per cent of India’s total operational land holdings are less than 2 hectares in area. The yield from such small plots is barely enough to feed the farmer’s family, leaving very little produce to sell in the market.
Consolidation of land holdings can drive higher efficiency and yields, but this requires a land market that allows people to buy or lease land.
- Existing laws constrain formal land leasing. A 2013 NSSO report estimates 13 per cent of household lease land, but other reports by NGOs suggest this could well be 50 per cent due to informal tenancy arrangements.
Non-existence of accurate land records:
Issue:
It makes difficult for farmers to access critical welfare schemes.
The government spends close to one per cent of GDP on fertiliser subsidies every year, while other huge subsidies exist for seeds, pesticides, crop insurance, and farm loans. But, if underlying land records don’t reflect the true names of owners, lessors, and cultivators or the correct size of the plots, the benefits won’t reach the targeted beneficiaries.
The reasons behind absence of accurate records are varied, ranging from unregistered sale, inheritance, and tenancy, to decades-old official maps no longer reflecting ground reality.
Way out:
We need to elevate the importance of efficient government systems for land administration to the forefront of the agriculture sector conversation; however, it’s a complex subject.
Its systemic issues cannot be fixed with public policy alone and will require new thinking and collaboration among multiple stakeholders, including governments, philanthropic institutions, entrepreneurs, and civil society.
Integrating land records:
- Philanthropic institutions and state governments should take a holistic view of the role of land and land records. These large-scale programmes need to allocate part of the resources to help their target farmer population obtain accurate land records.
Role of tech:
- The availability of geospatial and mobile technology is revolutionising the way we update land records, offering new and cheap ways to capture household and plot level information. Odisha is already setting the example as the first State to use drones to capture information on about thousands of slum households to provide title documents.
Entrepreneurial solutions:
- Given the scale of the problem, there is a huge opportunity for millions of innovators and entrepreneurs to step in and solve it.
Conclusion:
These above suggested solutions can create a more dynamic, proactive approach to land administration. This is important as improving the system of land administration in the country will help boost farmers’ income.
Connecting the dots:
- Poor land administration in India is one of the key issue affecting agricultural productivity as well as farmers’ income. Discuss.
MUST READ
Where the law needs to change track
Stop this jobs charade
The problems with a DNA registry
New Indo-Pacific axis
Preparing for India’s next telecom revolution
Time to focus on Indo-US bilateral trade
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Q.1) Consider the following statements with respect to Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI)
- It is established under the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006
- Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution is administrative ministry for the implementation of FSSAI
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None of the above
Q.2) Which of the following statements about National Nutrition Mission is/are true?
- The programme through the targets will strive to reduce the level of stunting, under-nutrition, anemia and low birth weight babies.
- It aims at reaching 10 crore beneficiaries in three phases between 2017 and 2020 across all districts of the country.
- Beneficiaries of the programme include children upto the age of 12 years, pregnant women and lactating mothers.
Choose the appropriate answer:
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.3) Which organization recently signed an agreement with India to provide a $200 million loan for implementing National Nutrition Mission?
- World Bank
- World Health Organization
- International Monetary Fund
- Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation
Q.4) Which among the following countries does not border the Mediterranean sea?
- France
- Italy
- Serbia
- Syria
Q.5) Consider the below statements with reference to Koalas:
- Koala bears are carnivoran mammals of the family Ursidae.
- They are found on the continents of North America, Europe, and Australia.
- They are considered to be vulnerable according to IUCN.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only



![IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs [Prelims + Mains Focus] – 8th May 2018 IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs [Prelims + Mains Focus] – 8th May 2018](https://iasbaba.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/0-1-e1525858866474.jpg)








