IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs (Prelims + Mains Focus)- 21st June 2018
Archives
(PRELIMS+MAINS FOCUS)
June 21: International Day of Yoga
Part of: GS Prelims
Key pointers:
- The International Day of Yoga is marked on June 21.
- The theme for the 2018 celebration, organized by the Permanent Mission of India to the United Nations, is ‘Yoga for Peace.’
- The International Day of Yoga aims to raise awareness worldwide of the many benefits of practicing yoga.
Governor Rule in Jammu and Kashmir
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains II – Indian Polity; Special provisions to Jammu and Kashmir
In News:
- Governor N.N. Vohra took charge in J&K
- Vohra issued the proclamation to impose Governor’s rule under Section 92 of the Constitution of J&K, immediately after getting the President’s approval.
- It is important to understand difference between President’s Rule and Governor’s rule.
Do you know?
- In all states of India, the government’s failure results in President’s rule. However, the process is slightly different in Jammu and Kashmir where not the President’s but governor’s rule is imposed.
- The President’s rule in other states of India is imposed under Article 356 of the Constitution of India.
Important Value Additions
- Under the provision of Section 92 of the Jammu and Kashmir constitution, governor’s rule is imposed for six months, but only after the consent of the President of India.
- Under the governor’s rule, the state assembly is either kept in suspended animation or dissolved.
- If it is not possible to restore the Constitutional machinery before the expiry of this six month period, the provision of Article 356 of the Constitution is extended and the President’s rule is imposed in the State.
- Article 370 of the Constitution of India states that Parliament of India and the Union government jurisdiction extends over limited matters with respect to state of Jammu and Kashmir, and in all other matters not specifically vested in federal governments, actions have to be supported by state legislature.
- The government of India can declare emergency in Jammu and Kashmir and impose governor’s rule under certain conditions. Matters related to defence, foreign relations, communication and finance of Jammu and Kashmir are under jurisdiction of the Constitution of India.
Crux:
- Governor’s rule is imposed on Jammu and Kashmir only, while the President rule on the rest of India. Both these rules are imposed if the constitutional machinery fails in the state i.e. the government of state fails to run the state constitutionally.
- Governor’s rule is imposed for 6 months (in Jammu and Kashmir). If constitutional machinery is not restored within this period, then President rule is extended to this state too. (Therefore, even President Rule can be extended to Jammu and Kashmir)
Article link: Vohra takes charge in J&K, reviews security situation
Person in news: Chief Economic Adviser Arvind Subramanian resigns
Part of: GS Prelims
In news:
- Chief Economic Adviser Arvind Subramanian resigns
About CEA
- The Chief Economic Adviser (CEA) is the economic advisor to the Government of India.
- The CEA is the ex-officio cadre controlling authority of the Indian Economic Service.
- The CEA is under the direct charge of the Minister of Finance.
- CEA enjoys rank and pay equivalent to that of a Secretary to Government of India.
- The CEA heads the Economic Division under the Department of Economic Affairs (DEA).
Article link: CEA resigns, cites personal reasons – Today’s Paper – The Hindu
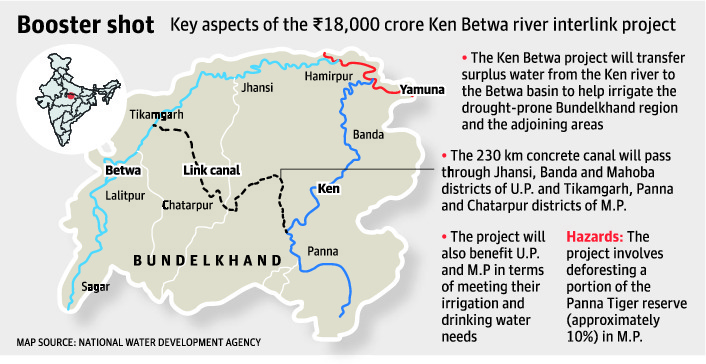
India’s first river interlinking project: Ken-Betwa project
Key Pointers:
- Ken-Betwa interlinking Project aims to transfer surplus water from the Ken River to the Betwa basin through concrete canal to irrigate India’s worst drought-prone Bundelkhand region.
- On completion, the multipurpose project will benefit Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh in terms of meeting irrigation, drinking water and electricity needs of people across 6 districts in the two states.
Pic link: https://d39gegkjaqduz9.cloudfront.net/TH/2018/06/21/DEL/Delhi/TH/5_07/6301c8c7_2187648_101_mr.jpg
Do you know?
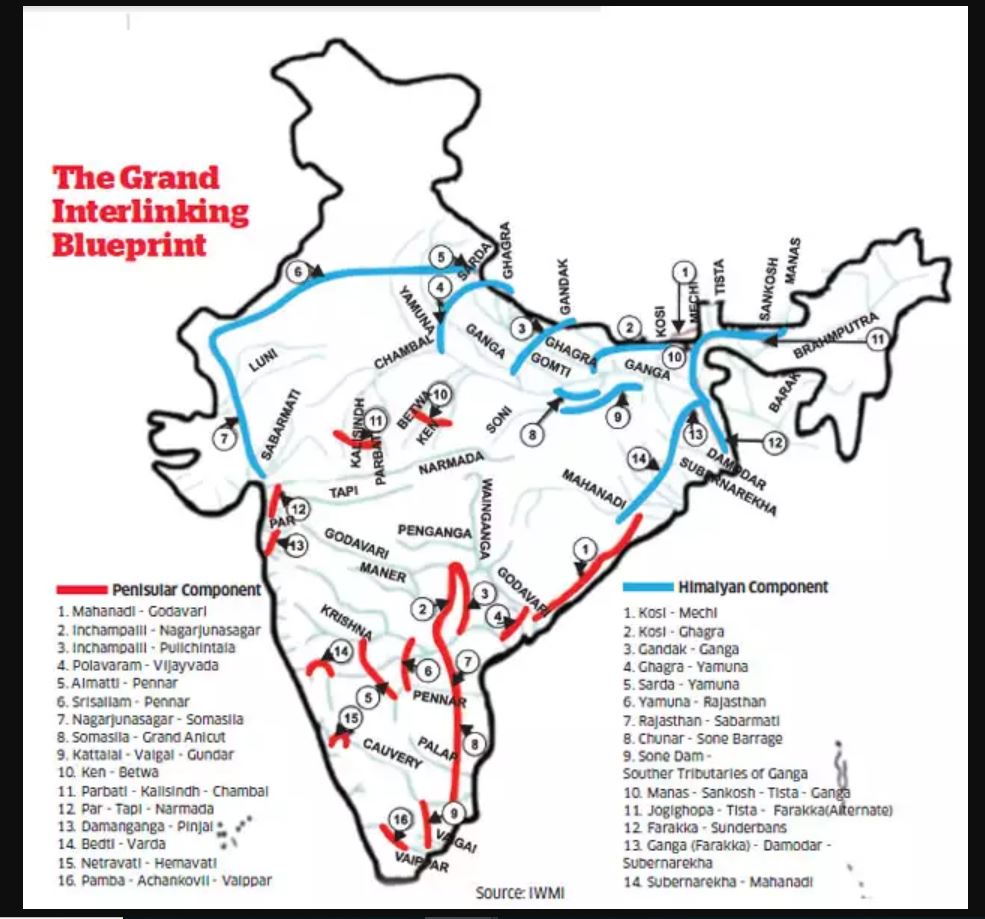
- It is India’s first inter-State river interlinking project (among the 30 linkages proposed by the water resources ministry under its national water plan).
- Observe fig below – for 30 river linking projects
![]()
Pic link: https://img.etimg.com/photo/49209064/interlink.jpg
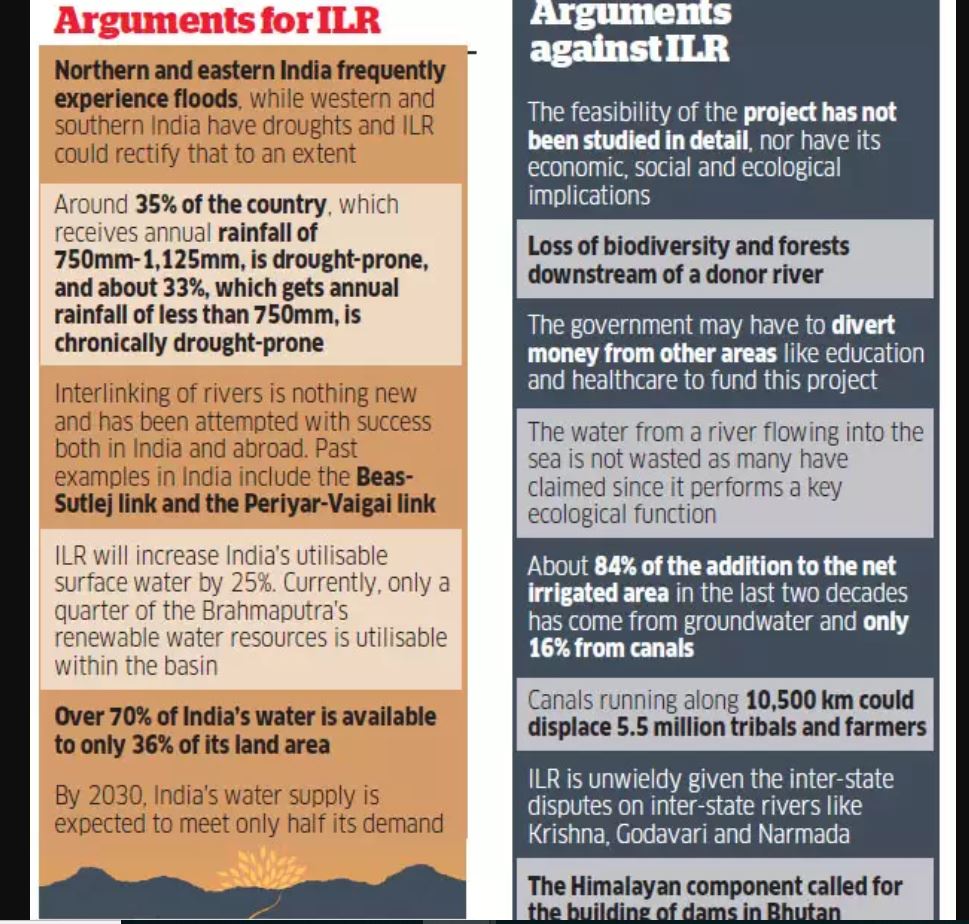
Concerns:
- Environmental, financial and feasibility impediments
- Ken-Betwa interlinking Project will be located within tiger reserve. It will submerge about 10% of the Panna Tiger Reserve in Madhya Pradesh which has been feted as a model tiger-conservation reserve.
- Land acquisition, water sharing issues impede Ken-Betwa project
Pic credits: https://img.etimg.com/photo/49209347/first-table.jpg
Artile link: India’s first river interlinking project caught in U.P.-M.P. tussle
U.S. quits UN human rights body
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains II – International Affairs; International institutions and fora
In news:
- United States announced its withdrawal from the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC) terming it “hypocritical and self-serving.”
- Under Trump’s presidency, the U.S. has withdrawn from the U.N. climate treaty and the UNESCO.
About UNHRC
- UNHRC is a United Nations body whose mission is to promote and protect human rights around the world.
- It is an inter-governmental body within the United Nations system
- It meets at the UN Office at Geneva. The headquarters of UNHRC is in Geneva, Switzerland.
- UNHRC was established by the UN General Assembly in 2006. Then President George W. Bush was dismissive of the body. Under President Barack Obama, the U.S. joined it in 2009.
Caution: Don’t get confused between UNHRC and UNCHR
- The United Nations Commission on Human Rights (UNCHR) was a functional commission within the overall framework of the United Nations from 1946 until it was replaced by the United Nations Human Rights Council in 2006.
- On 15 March 2006, the UN General Assembly voted overwhelmingly to replace UNCHR with the UN Human Rights Council.
- Since the Council’s inception in 2006, Human Rights Watch has been involved in strengthening its capacity to promote and protect human rights worldwide and be more responsive to the needs of victims of rights violations.
Article link: US quits UN human rights body – Today’s Paper
Toothpastes contribute to antibiotic resistance
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains II – Health; Science and Technology
Do you know?
- According to a study, common ingredient found in toothpastes and hand washes could be contributing to the rise of antibiotic resistant bacteria.
- Triclosan, a compound which is used in more than 2,000 personal care products can induce multi-drug resistance.
- Overuse and misuse of antibiotics could create ‘superbugs’.
- Triclosan is an antibacterial and antifungal agent found in your soap, handwash, talcum powder and even in the wall paint.
- In a world obsessed with cleanliness, antimicrobial agents like triclosan have been touted as the panacea for a disease-free world.
- But their use remains controversial: experts say indiscriminate usage of antimicrobial agents like triclosan over the years has led to bacteria developing resistance to them, leading to the need for stronger chemicals.
Article link: Toothpaste contribute to antibiotic resistance – The Hindu
(MAINS FOCUS)
NATIONAL
TOPIC
General studies 2:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector or Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources.
General studies 3:
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources, growth, development and employment.
- Inclusive growth and issues arising from it.
Indian startup ecosystem: Changing landscape
Background:
A slew of policies has been rolled out under the “Start Up India” scheme, launched in 2016. It is an effort to address the challenge of unemployment amongst educated youth, by encouraging them to become job creators — not job seekers.
Changing landscape:
The global start-up landscape is still dominated by the West, though a discernible shift is underway. As per the Global Start-up Eco System Report 2018, the US remains the leader with a 41 per cent share of start-ups but China is closing the gap with a 35 per cent share of the market.
A Grant Thornton-Assocham report estimates that there are nearly 10,000 start- ups in India, of which 43 per cent are tech-based ventures. Annually, close to 800 start-ups are taking root in the country. Bengaluru is one of the emerging global hubs.
Flipkart, Ola, PayTm are some of the start-ups that have made it big. Start-ups are now occupying the social development space as well.
Key ingredients for a successful start-up ecosystem:
The USP of Silicon Valley, spread around San Francisco, is that-
- It is home to some of the major technology companies — Apple, Facebook, Oracle, Visa, Intel, Cisco. These companies have served as anchors for new companies, a large number of which are founded by ex-employees. The anchor companies end up financing start-ups, given the lower costs of research or product development, and provide access to global markets.
- The area is also home to two world class universities: Stanford and the University of California at Berkeley.
- There is also no dearth of capital with venture capitalists (VCs) providing flexible financing options.
The three key ingredients for a successful start-up ecosystem are: A thriving city, availability of talent and capital and the presence of large companies.
Indian start-up ecosystem:
No dearth of talent in the technology space:
According to the NITI Aayog, India has 2.6 million STEM graduates ( Science, Technology, Engineering and Math), next only to China.
The Department of Science and Technology and the Ministry of Human Resource Development have approved the establishment of 13 start-up centres, 16 technology business incubators and six research parks in technical institutions across the country.
Access to easy low-cost finance:
- Under the Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana, nearly 6.5 million loans of up to Rs 10 lakh have been sanctioned this year, with disbursement of nearly Rs 30,000 crore.
- Bank lending for larger start-ups remains a challenge because banks are averse to taking risks and charge high interest rates.
VC finance offers a good alternative. The SEBI has recently liberalised the regulatory framework for VC. - SIDBI has established a “Fund of Funds for Start Ups” with an initial corpus of Rs 10,000 crore to finance alternate investment funds.
- Government of India has also allowed exemptions from income tax and capital gains tax up to three years for investment in start-ups.
- Philanthropic organisations like the Tata Trust have also stepped in to finance incubation labs.
What else can be done?
- Identifying start-up hubs and priority sectors– Twenty Tier 2 and 3 cities, with flourishing technology ecosystems, could be declared “National Start Up Hubs” for targeted investments to build linkages between industry, academia and finance.
- Pioneers of the Indian IT revolution could be roped in to create a pool of start-up mentors. Technologists and entrepreneurs of the Indian diaspora in the Bay area and other parts of the world could be one of the finest resources of this movement.
- A platform could be created to channelise NRI investment in technology-based startups.
Conclusion:
A “soft touch” and responsive regulatory framework will be required to support the rapidly changing technology landscape. The policies being implemented along with the suggestions made above will be right for catalysing an Indian Start Up Revolution, which could turn India’s demography to its advantage.
Connecting the dots:
- Discuss the potential and the challenges for the Indian startup ecosystem.
- The landscape of Indian startup ecosystem is rapidly changing. Critically comment.
NATIONAL
TOPIC
General Studies 3:
- Issues related to direct and indirect farm subsidies and minimum support prices
- Inclusive growth and issues arising from it.
General Studies 2:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Zero Budget Natural Farming: A model for the future
In news:
In early June, Andhra Pradesh government has recently announced that the State would fully embrace Zero Budget Natural Farming (ZBNF), a chemical-free method that would cover all farmers by 2024.
With successful pilot programmes that were initiated in 2015 and partners who brought experience in different aspects needed to carry out such a transformation, Andhra Pradesh has become the first State to implement a ZBNF policy.
Natural farming:
Subhash Palekar, an Indian agriculturist who practiced and wrote many books about Zero Budget Natural Farming, developed the ZBNF after his own efforts at chemical farming failed.
He identified four aspects that are now integral to his process:
- Seeds treated with cow dung and urine.
- Soil rejuvenated with cow dung.
- Cow urine and other local materials to increase microbes.
- Cover crops, straw and other organic matter to retain soil moisture and build humus.
- Soil aeration for favourable soil conditions.
These methods are combined with natural insect management methods when required.
How is ZBNF beneficial?
- In ZBNF, yields of various cash and food crops have been found to be significantly higher when compared with chemical farming.
- Input costs are near zero as no fertilizers and pesticides are used.
- Profits in most areas under ZBNF were from higher yield and lower inputs.
- Model ZBNF farms were able to withstand drought and flooding, which are big concerns with regard to climate change.
- The planting of multiple crops and border crops on the same field has provided varied income and nutrient sources.
- As a result of these changes, there is reduced use of water and electricity, improved health of farmers, flourishing of local ecosystems and biodiversity and no toxic chemical residues in the environment.
The programme can have a positive effect on many of the sustainable development goals through improvements in soil, biodiversity, livelihoods, water, reduction in chemicals, climate resilience, health, women’s empowerment and nutrition.
Different from organic farming:
In early 2016, Sikkim was declared India’s first fully organic State. But organic agriculture often involves addition of large amounts of manure, vermicompost and other materials that are required in bulk and need to be purchased. These turn out to be expensive for most small farm holders.
Model for other States:
- Over the years, Andhra Pradesh has supported and learned from its many effective civil society organisations such as the Watershed Support Services and Activities Network, Centre for Sustainable Agriculture and the Deccan Development Society.
- Farmer-to-farmer connections as vital to its success. Farmer’s collectives such as Farmer Producer Organisations need to be established and these would be critical to sustaining the programme.
- A step-by-step increase in the area covered. The scaling up relies primarily on farmers and local groups — all in all, very much a bottom-up process.
- The approach taken to monitor the improvements is vital to understanding the outcomes of large-scale changes that are under way; this is critical to expanding the ZBNF to other States.
With its combination of delta regions, arid and hilly tribal areas, districts in Andhra Pradesh are similar to those in other parts of the country and could therefore serve as a model for replication.
Conclusion:
The world is at critical junctures on many planetary boundaries and establishing a system that shows promise in improving them while supporting people sustainably is surely one worth pursuing.
Connecting the dots:
- What do you understand by ‘zero budgent natural farming’ (ZBNF)? Discuss its benefits over conventional form of agriculture.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Q.1) Consider the following statements:
- United Nations proclaimed 21 June as the International Day of Yoga.
- The theme for the 2018 celebration is Yoga for Peace.
Choose the correct code from below:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements:
- Governor’s rule is imposed on Jammu and Kashmir only, while the President rule on the rest of India.
- President Rule is not extended to Jammu And Kashmir State as Governor’s rule is imposed if the constitutional machinery fails in the state.
Choose the correct code from below:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3) Consider the following statements regarding the features Jammu and Kashmir Constitution
- It declares the State of J&K to be an integral part of India
- It provides for Governor’s rule as appointed by President of India
- It clarifies that the permanent residents of the state are entitled to all rights guaranteed under the Constitution of India
Select the correct statements
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 1 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.4) Which of the following organization is responsible for the preparation of economic survey in India?
- Department of revenue
- Department of economic affairs
- Department of revenue
- Department of financial services
Q.5) Consider the following statements:
- Ken-Betwa river inter-linking project is the first river link project by the Central government.
- Dhaudhan dam is built as part of the project.
- Surplus water in the Bundelkhand region is transferred to other areas.
Select the correct answer from the following codes
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.6) Which among the following are tributaries of River Yamuna?
- Betwa
- Chambal
- Son
- Ken
Choose the appropriate code:
- 1, 2 and 3
- 2, 3 and 4
- 1, 2 and 4
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q.7) Ken-Betwa river linking project has received the final environmental clearance. A major chunck of one of the tiger reserve/national park will get submerged. Which is the tiger reserve that we are referring to?
- Panna
- Pench
- Kanha
- Bandhavgarh
Q.8) Which of the following properties is true for a tooth paste?
- It is acidic
- It is neutral
- It is basic
- It is made up of Calcium phosphate, the material of tooth enamel
MUST READ
Neither new nor undesirable
Beating plastic pollution
The state is taking healthcare
River, state and Centre
Going beyond lateral entry in civil services











