IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs (Prelims + Mains Focus)- 6th June 2018
Archives
(PRELIMS+MAINS FOCUS)
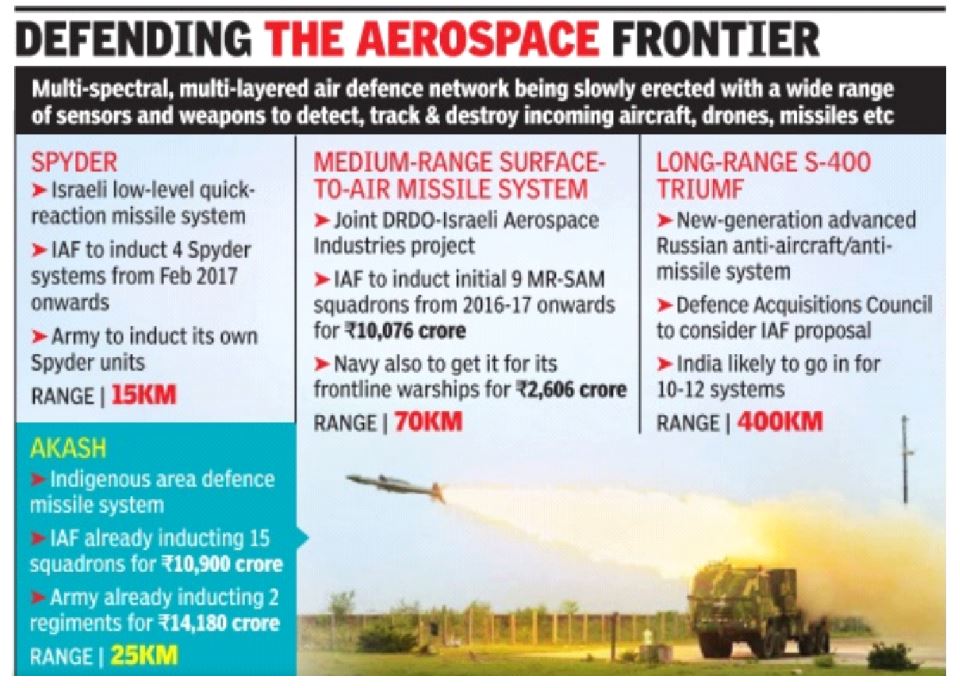
Long-Range S-400 Triumf
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains III – Defence and Security
Key Pointers:
- India has decided to purchase S-400 Triumf long-range air defence system from Russia.
- Defence Minister Nirmala Sitharaman indicated that India would go ahead with the deal.
Value Additions:
- S-400 ‘Triumf’ long-range air defence missile system is one of the most advanced long-range defence systems in the world.
- It can destroy incoming hostile aircraft, stealth fighters, missiles and drones at ranges of up to 400-km.
- It is referred to as SA-21 Growler by NATO.
- India will be the second export customer, after China to purchase this most advance defence system.
Do you know?
Article link: Army will abide by govt. peace plan, says Nirmala Sitharaman
Controversy over Article 35A
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains II – Indian polity; Indian Constitution
In news:
- Article 35A is often in news.
- The Article, which was unknown to the public domain till recent times, has raked up an intense debate in the country when a Kashmiri woman, Charu Wali Khan filed a petition to change the constitutional provision as she wanted succession rights in the state though she is settled outside the state.
- An NGO, ‘We the Citizens’ had also filed a writ petition to strike down Article 35A.
- The NDA Government wants to have a larger debate over the Article 35A challenging the constitutional validity of the clause.
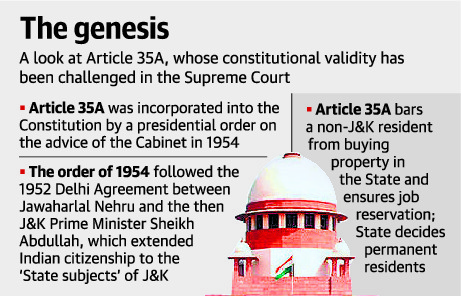
What is Article 35A?
Article 35A of the Indian Constitution is an article that empowers the Jammu and Kashmir state’s legislature to define “permanent residents” of the state and confer on them special rights and privileges in public sector jobs, acquisition of property in the State, scholarships and other public aid and welfare.
The provision mandates that no act of the legislature coming under it can be challenged for violating the Constitution or any other law of the land.
It was added to the constitution through a presidential order of 1954 with the then J&K government’s concurrence.
Article 35A does not allow people from outside the state of Jammu & Kashmir to work, settle or own property in the state.
(For time being, let us remember only this. Analysis part will be dealt in future once we come across any editorials or op-eds)
Pic link: https://d39gegkjaqduz9.cloudfront.net/TH/2018/06/06/DEL/Delhi/TH/5_01/ec87954a_2152744_101_mr.jpg
Article link: Centre not to file counter-affidavit on Article 35A
World Environment Day: Outcomes
Part of: Prelims and Mains GS Paper III – Environment and Ecology; Pollution
In news:
- Yesterday we read about Green Skill Development Programme (GSDP); theme for the World Environment Day 2018 – “Beat Plastic Pollution”.
- India is committed to reducing the use of plastic and would join the Clean Seas programme — a Sweden-led initiative to reduce littering of marine ecosystems.
- Delegation of the European Union (EU) and embassies of the member states adopted a ‘Green Pledge’, under which the 28 EU member-states made a commitment to green their embassies.
Miscellaneous points:
- Animal Discoveries, 2017 – publication released by Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) lists 300 newly discovered species of fauna.
- Plant Discoveries, 2017 – publication released by Botanical Survey of India (BSI) lists 239 newly found flora species.
- Among the States, Kerala recorded the highest number of discoveries — 66 species, sub-species and varieties of plants and 52 species of animals.
Article link: Environment Day bouquet: 539 species discovered in India in 2017 …
Classical Music: Jugalbandi
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains I – Indian Culture; Music
Do you know?
- Jugalbandi is a performance in Indian classical music, especially in Hindustani classical music, that features a duet of two solo musicians.
- The word jugalbandi means, literally, “entwined twins.” The duet can be either vocal or instrumental.
- What defines jugalbandi is that the two soloists be on an equal footing.
Nitrogen: largest PM2.5
Part of: Prelims and Mains GS Paper III – Environment and Ecology; Pollution
What is PM2.5?
PM2.5 refers to atmospheric particulate matter (PM) that have a diameter of less than 2.5 micrometers, which is about 3% the diameter of a human hair.
Fine particles can come from various sources. They include power plants, motor vehicles, airplanes, residential wood burning, forest fires, agricultural burning, volcanic eruptions and dust storms.
Key Pointers:
- Nitrogen particles make up the largest fraction of PM2.5
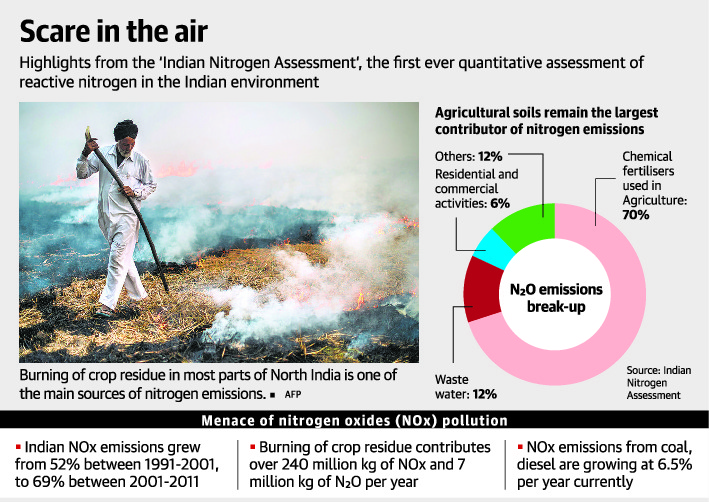
- While the burning of crop residue is said to be a key contributor to winter smog in many parts of North India, it contributes over 240 million kg of nitrogen oxides.
- Though agriculture remains the largest contributor to nitrogen emissions, the non-agricultural emissions of nitrogen oxides and nitrous oxide are growing rapidly, with sewage and fossil-fuel burning — for power, transport and industry — leading the trend.
- As fertilizer, nitrogen is one of the main inputs for agriculture.
- Agricultural soils contributed to over 70% of N2O emissions from India in 2010, followed by waste water (12%) and residential and commercial activities (6%). Since 2002, N2O has replaced methane as the second largest Greenhouse Gas (GHG) from Indian agriculture.
- Chemical fertilizers (over 82% of it is urea) account for over 77% of all agricultural N2O emissions in India, while manure, compost and so on make up the rest.
Pic link: https://d39gegkjaqduz9.cloudfront.net/TH/2018/06/06/DEL/Delhi/TH/5_11/b3c0ed88_2152794_101_mr.jpg
Do you know?
- Cattle account for 80% of the ammonia production, though their annual growth rate is 1%, due to a stable population.
- India is globally the biggest source of ammonia emission, nearly double that of NOx emissions.
- But at the current rate of growth, NOx emissions will exceed ammonia emissions and touch 8.8 tonnes by 2055, studies highlight.
- Nutrient recovery/recycling from waste water for agriculture could cut down N2O emissions from sewage and waste water by up to 40%.
Article link: Nitrogen emissions going up: study – NATIONAL – The Hindu
(MAINS FOCUS)
SOCIAL ISSUES
TOPIC:General Studies 2:
- Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections of the population by the Centre and States and the performance of these schemes
- Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources.
- Issues relating to Poverty and hunger
Preventing the next health crisis: Over-nutrition and Obesity
Introduction:
Government had announced that it would release an annual “state of nutrition” report, detailing India’s level of stunting, malnutrition and feature best practices for States to scale up nutrition interventions.
Concerns:
- 26 million children in India suffer from wasting (a low weight-for-height ratio) – more than in any other country.
- Country has the second highest number of obese children in the world — 15.3 million in China and 14.4 million in India.
- Between 1980 and 2015, obesity doubled for children and tripled for adults; an additional 2.6 million children will be obese in India by 2025, a trend that will not reverse without action.
- Research shows that Indians have higher levels of body fat and lower levels of lean muscle when compared to many other populations.
The rise in obesity is deeply concerning because just as growing up underweight gives that person a lifetime of health problems so does a childhood of being overweight.
Over-nutrition: Becoming an emergency
What is ironic is that over-nutrition is emerging as an emergency in India.
- As per the recent findings of the National Family Health Survey-4 (2015-16), the Body Mass Index (BMI) of 15.5% of urban women was found to be less than 18.5 kg/m2, whereas 31.3% of urban women were in the category of overweight or obese (BMI of or more than 25.0 kg/m2).
- Around 15% of urban men were underweight, while 26.3% belonged to the category of overweight and obese.
Reason– Dramatic changes in lifestyle and dietary patterns in recent decades have contributed to an increasing prevalence of non-communicable diseases.
The potent combination of Indian children eating more junk food while becoming increasingly sedentary puts them at an even greater risk. Research has shown that early warning signs for fatty liver disease can be found in children as young as eight.
Fallout– If this double burden of undernutrition and growing percentage of obesity and associated non-communicable diseases is not controlled, it can have serious implications for the economy.
Way forward:
While tackling under-nutrition through assurance of adequate nutrition (usually interpreted as dietary calories), policy makers should also ensure appropriate nutrition (the right balance of nutrients).
- India must step up its efforts to fight overweight and obesity just as it has been doing with wasting and stunting.
- To ensure food and nutrition security, there is a growing need for a multi-sectoral approach.
- The policies and programmes of various ministries should be converged for better results.
- Apart from transforming India’s agricultural practices, we also need to spread awareness about nutritious food among key target groups, including tribals, women and children.
- Policy responses should include agricultural systems that promote crop diversity (to enable dietary diversity) as well as regulatory and fiscal measures (to decrease the availability, affordability and promotion of unhealthy foods, while making healthy foods more accessible).
- India should ban the sale of junk food in and around schools. Legislators should also put into practice the results of a recent Lancet study on India. It showed that higher taxes on junk food can actually lead those on lower incomes to live healthier lives.
- We need to focus on the role of micronutrients. Deficiencies of micronutrients such as zinc, folic acid, magnesium, selenium and vitamin D needs to be given adequate attention.
The Sustainable Development Goal-2, which aims to “end hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture”, is a priority area for India. India should link obesity and undernutrition and treat them as twinned challenges to be jointly addressed under the universal health coverage umbrella.
By tackling obesity through prevention and early care, financially debilitating NCDs can be avoided.
Connecting the dots:
- The double burden of undernutrition and growing percentage of obesity and associated non-communicable diseases can have serious implications for the economy. Discuss.
- A multi-sectoral approach is required to ensure food and nutrition security. Analyze.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Q.1) Consider the following pairs and choose the correctly matched pair/s from below options:
Missile deal : : Associated country
- SPIKE anti-tank guided missile : : India-US
- S-400 Triumf long-range surface-to-air missile systems : : India-Russia
- SPYDER Surface-to-Air Missile System : : India-Israel
Choose appropriate code from options below:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
Q.2) Consider the following statements:
- Article 35A of the Indian Constitution empowers the Jammu and Kashmir state’s legislature to define “permanent residents” of its state.
- Article 35A does not allow people from outside the state of Jammu and Kashmir to work, settle or own property in the state.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3) Clean Seas Campaign is –
- a global UN Environment initiative
- a Green Pledge taken by 28 EU member-states
- Both a and b
- None of the above
Q.4) Which among the following is the largest contributor to nitrogen emissions from India?
- Waste water
- Fertilizers used in Agriculture
- Residential and commercial activities
- Automobile
Q.5) Which among the following is the largest contributor to ammonia production in India?
- Fertilizers used in Agriculture
- Residential and commercial activities
- Automobile
- Cattle
MUST READ
Life in plastic
A tale of two countries
Who is a citizen — in Assam, India?
The West Asia Stalemate
The Shangri-La moment











