IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 29th March 2019
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Humans can detect the earth’s magnetic fields
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains I and III – Geography; Science and Technology
In news:
- Scientists have long known that turtles, birds, honeybees and even bacteria can sense the earth’s magnetic field and use them for navigation.
- But this magneto-reception has hardly been tested in humans and many studies have been inconclusive.
- However, a team of scientists has found that the human brain is capable of detecting the Earth’s magnetic field, challenging previous studies. But they are yet to decode what our brains may be using this information for.
- The discovery shows humans have not entirely lost the mechanism of orienting themselves using the magnetic field.
Do you know what causes the Earth’s magnetic field?
- Our planet’s magnetic field is believed to be generated deep down in the Earth’s core.
- Right at the heart of the Earth is a solid inner core, two thirds of the size of the Moon and composed primarily of iron. At a hellish 5,700°C, this iron is as hot as the Sun’s surface, but the crushing pressure caused by gravity prevents it from becoming liquid.
- Surrounding this is the outer core, a 2,000 km thick layer of iron, nickel, and small quantities of other metals. Lower pressure than the inner core means the metal here is fluid.
- Differences in temperature, pressure and composition within the outer core cause convection currents in the molten metal as cool, dense matter sinks whilst warm, less dense matter rises. The Coriolis force, resulting from the Earth’s spin, also causes swirling whirlpools.
- This flow of liquid iron generates electric currents, which in turn produce magnetic fields. Charged metals passing through these fields go on to create electric currents of their own, and so the cycle continues. This self-sustaining loop is known as the geodynamo.
- The spiralling caused by the Coriolis force means that separate magnetic fields created are roughly aligned in the same direction, their combined effect adding up to produce one vast magnetic field engulfing the planet.
Why Earth’s magnetic field is important?
- Without Earth’s magnetic field, solar winds — streams of electrically charged particles that flow from the sun — would strip away the planet’s atmosphere and oceans.
- As such, Earth’s magnetic field helped to make life on the planet possible, researchers have said.

pic: http://www.livescience.com/images/i/000/077/565/original/earth-magnetic-shield.jpeg
(MAINS FOCUS)
ECONOMY/WELFARE ISSUE
TOPIC: General studies 2 and 3
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation
- Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections of the population by the Centre and States and the performance of these schemes; mechanisms, laws, institutions and bodies constituted for the protection and betterment of these vulnerable sections
- Issues related to unemployment and economy
- Inclusive growth and issues arising from it
The shape of an urban employment guarantee
Key pointers:
- We had read that the unemployment rate has reached a 45-year high (6.1%) in 2017-18, as per leaked data from NSSO’s Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) report.
According to the PLFS report –
- Unemployment problem is especially aggravated in India’s cities and towns
- India is in the midst of a massive jobs crisis
- Aside from unemployment, low wages and precarity continue to be widespread.
- Majority of the population work in the informal sector.
- Hence, India cannot ignore the crisis of urban employment.
To handle the Urban Employment, Government Policy Framework should –
- Focus on skills: Both State and Central governments tend to treat towns as “engines of growth” for the economy but ignore the people who toil to make a living. Urban wage employment can be increased by properly skilling and implementing skill development schemes effectively.
- Focus on small and medium towns: India’s small and medium towns are particularly ignored in the State’s urban imagination. National-level urban programmes such as the Smart Cities Mission and the Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) only benefit a fraction of them.
- Focus on Funds, Functions and Functionaries: Most ULBs are struggling to carry out basic functions because of a lack of financial and human capacity.
- Focus on ecology: There are many challenges associated with degradation of urban ecological commons due to untrammelled urbanization.
- Focus on Sustainable Employment: Government policy framework should focus on strengthening towns through sustainable employment.
Solution: Employment guarantee programme (EGP)
In the context of the present employment crises, it is worthwhile considering introducing an employment guarantee programme (EGP) in urban areas.
- EGP will help to address the concerns of underemployment and unemployment, as it can bring in much-needed public investment in towns to improve the quality of urban infrastructure and services, restoring urban commons, skilling urban youth and increasing the capacity of ULBs.
- EGP would give urban residents a statutory right to work and thereby ensure the right to life guaranteed under Article 21 of the Constitution.
- Given the State’s relative neglect of small and medium towns and to avoid migration to big cities, EGP can cover all ULBs with a population less than 1 million.
- Urban informal workers with limited formal education would benefit from EGP as they can undertake standard public works such as building and maintenance of roads, footpaths and bridges for a guaranteed 100 days in a year, at ₹500 a day.
- Including “green jobs” under EGP would help to create, restore, rejuvenate and maintain urban commons such as green spaces and parks, forested or woody areas, degraded or waste land, and water bodies.
- EGP will benefit educated youth as it can focus on creation of skilling and apprenticeship programme for unemployed youth with higher education who can sign up for a contiguous period of 150 days (five months), at ₹13,000 a month for five months to assist with administrative functions in municipal offices, government schools, or public health centres, and for the monitoring, measurement, or evaluation of environmental parameters.
Conclusion:
- An urban employment guarantee programme not only improves incomes of workers but also has multiplier effects on the economy.
- It will boost local demand in small towns, improve public infrastructure and services, spur entrepreneurship, build skills of workers and create a shared sense of public goods.
- Hence, the time is ripe for an employment guarantee programme in urban India.
Connecting the dots:
- Discuss the merits and challenges associated with urban employment guarantee programme.
- Do you think introducing urban employment guarantee programme can solve India’s massive jobs crisis? Critically analyse.
SCIENCE AND TECH/DEFENCE
TOPIC: General studies 3
- Achievements of Indians in science & technology; indigenization of technology and developing new technology.
- Defence and Security issues
Mission Shakti: India prepare to take the enemy in space
Introduction:
- India became the fourth country (after Russia, the United States, and China) to have the capability in taking down an enemy in space.
- India shot down a low-orbit satellite through an Indian anti-satellite weapon A-SAT, in an operation called ‘Mission Shakti’
About Mission Shakti
- It was an anti-satellite missile test, from the Dr A P J Abdul Kalam Island launch complex.
- This was a technological mission carried out by DRDO.
- The ASAT comprised a Ballistic Missile Defence (BMD) Interceptor developed by the DRDO.
- The significance of the test is that India has tested and successfully demonstrated its capability to interdict and intercept a satellite in outer space based on complete indigenous technology.
- India’s space programme is a critical backbone of India’s security, economic and social infrastructure.
- The test was done to verify that India has the capability to safeguard our space assets.
- It is the Government of India’s responsibility to defend the country’s interests in outer space.
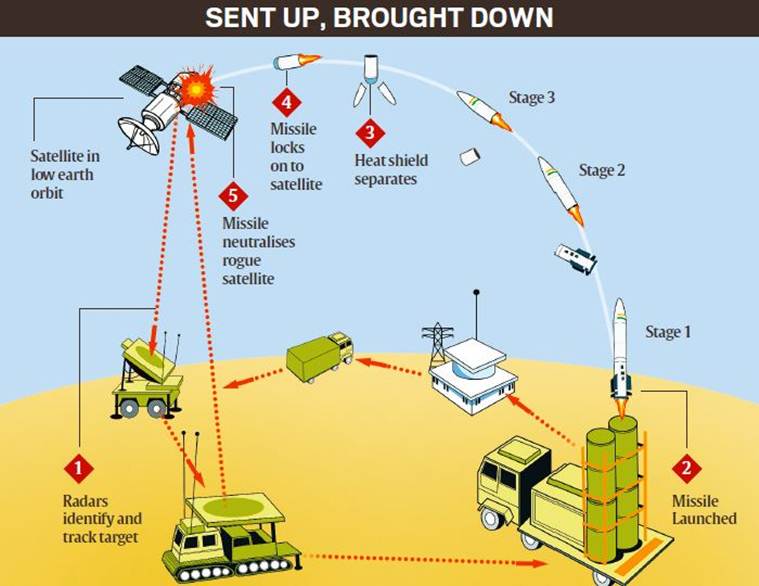
Pic: https://images.indianexpress.com/2019/03/capture-29.jpg
Is India entering into an arms race in outer space?
- PM reiterated that the mission focus is to strengthen its defence and not to wage war.
- PM also said that India has always been against the presence of weapons in the space and this development will not change our stand.
- India has always maintained that space must be used only for peaceful purposes. India is against the weaponization of Outer Space and support international efforts to reinforce the safety and security of space based assets.
- India believes that Outer space is the common heritage of humankind and it is the responsibility of all space-faring nations to preserve and promote the benefits flowing from advances made in space technology and its applications for all.
Do you know?
- India is a party to all the major international treaties relating to Outer Space.
- India already implements a number of Transparency and Confidence Building Measures(TCBMs) – including registering space objects with the UN register, pre-launch notifications, measures in harmony with the UN Space Mitigation Guidelines, participation in Inter Agency Space Debris Coordination (IADC) activities with regard to space debris management, undertaking SOPA (Space Object Proximity Awareness and COLA (Collision Avoidance) Analysis and numerous international cooperation activities, including hosting the UN affiliated Centre for Space and Science Technology Education in Asia and Pacific.
- India has been participating in all sessions of the UN Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space.
- India supported UNGA resolution 69/32 on No First Placement of Weapons on Outer Space.
- India’s sees the No First Placement of weapons in outer space as only an interim step and not a substitute for concluding substantive legal measures to ensure the prevention of an arms race in outer space, which should continue to be a priority for the international community.
- India supports the substantive consideration of the issue of Prevention of an Arms Race in Outer Space (PAROS) in the Conference on Disarmament where it has been on the agenda since 1982.
What is the international law on weapons in outer space?
- The principal international Treaty on space is the 1967 Outer Space Treaty.
- India is a signatory to this treaty, and ratified it in 1982.
- The Outer Space Treaty prohibits only weapons of mass destruction in outer space, not ordinary weapons.
- India expects to play a role in the future in the drafting of international law on prevention of an arms race in outer space including inter alia on the prevention of the placement of weapons in outer space in its capacity as a major space faring nation with proven space technology.
- India is not in violation of any international law or Treaty to which it is a Party or any national obligation.
MUST READ
Dangerous precedent: on U.S. endorsing Israel’s Golan sovereignty
What the world thinks
There’s a deep asymmetry of power in our society
Their rights to the cities
Why the prosecution fails
A weapon that could change the game if India plays tough
The fading boundary between humans and machines
The world must avert an arms race in space












