IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 8th July 2019
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Road to agricultural and rural prosperity
Part of Prelims and mains GS III Indian Economy
In news
A truly agriculture and rural development-focussed Budget, it has adequately met the twin objectives of growth and inclusiveness. The crux of the Budget is ‘sustainability’ in every aspect, be it agriculture practices or economic viability.
Farmer producer organisation
- An announcement of formation of 10,000 new FPOs over the next five years is a step towards the same.
- With this, the economies of scale can be harnessed to achieve the goal of doubling farmer’s income by reduction in input costs and assuring better price realisations by the farmers for their output.
Women SHGs
- The incentives proposed for women SHGs will not only lead to livelihood generation and women empowerment, but also nurture first-generation entrepreneurs though the MUDRA loans of ₹1 lakh.
- With the proposed interventions, not only farmers, but also rural entrepreneurship will get the necessary boost.
Fisheries
A new scheme “Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana” will give enough confidence to those who are in fisheries sector, to enhance their income with better fisheries management, infrastructure creation, increasing production and productivity, improved post-harvest management bringing economic viability of the sector.
Artisans and agripreneurs
- The government has shown that every person having potential to bring economic revolution will be given an equal opportunity. SFURTI is an attempt in this direction.
- Rural artisans have received a holding hand from the government in a cluster-based development approach that will upgrade regional and traditional industries, benefiting about 50,000 artisans.
- Enhancing the prospects of agripreneurs, the ASPIRE scheme will create 50,000 skilled rural entrepreneurs, especially in the rural agriculture sector.
Power generation
- To expand the income sources of our farmers, there is a proposal to enable them to take up power generation activities on their field to transform the ‘Annadata’ to an ‘Urjadata’.
Connectivity and marketing
- Now, under Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana, a road network of 1.25 lakh km will bring more villages to rural markets.
- For relieving farmers from uncertain prospects, the States will be forced to implement e-NAM mechanism for better operations under the APMC Act.
Zero budger farming
- The concept of zero-budget farming, which some farmers have exemplarily proved to be viable, will boost the confidence of farmers.
- With conventional means, the farmers will be able to enhance their income levels by keeping the input costs under control.
Jal shakti Abhiyan
- Integration of funds from various Ministries to fund the Jal Shakti Abhiyan may see critical water blocks being regained.
Indo-Afghan trade chokes on U.S. curbs
Part of Prelims and mains GS III Indian Economy, GS II International relations
In news
- The government’s decision to slash its allocation for Iran’s Chabahar port by two-thirds will be a further blow to India-Afghan trade, already hit by Pakistan’s decision to ban airspace rights to most flights to and from India, and U.S. sanctions on Iran.
- The government, which had been allocating ₹150 crore for the port each year for the past few years, has slashed its allocation to just ₹45 crore in the Budget for 2019-20.
Waiver of little help
- Technically, the U.S. has issued India a waiver to develop the Chabahar port, to promote trade with Afghanistan as part of its “South Asia” strategy.
- In practice, however, the cancellation of all waivers for oil and crippling economic sanctions imposed by the Trump administration, have all but frozen deals.
- Afghan banks are hesitant to open credit lines for shipments, and shippers and cargo handlers are staying away from servicing the Iranian port.
- As a result of Pakistan’s airspace ban, Afghan fruit and agricultural products that had made up a bulk of the cargo on flights between Kabul and Delhi are being shipped to other international markets.
Outlay for child welfare sees a meagre increase
Part of Prelims and mains GS II Social justice
In news
- The outlay for children in the Union Budget has shown a marginal increase of 0.05%, going up from 3.24% in the last fiscal to 3.29%.
- The share is less than the low share of 5% that the National Plan of Action for Children, 2016, has recommended.
- A detailed analysis of the budgetary grant carried out by Child Rights and You shows that allocations are insufficient for the ambitious plan for nutritional development.
- The share of education has increased marginally to 68.54% from 68.2%, but has declined by more than 10 percentage points from the 79.02% of 2015-16. These include schemes such as Samagra Shiksha, National Programme of Mid-day Meal in Schools and Navodaya Vidyalaya Samiti.
- Health-related financial allocation as a share of the child health budget has shown a decline of 0.39 percentage point — from 3.9% last fiscal to 3.51%.
- The Anganwadi services and the Poshan Abhiyan (Nutrition Mission) are among the most important government programmes aimed at reducing stunting, anaemia, low weight and low birth weight. Budgetary allocation for both has increased.
- National Child Labour Project Scheme registered a budgetary cut of 16%.
Making a pitch for PPP model in railways
Part of Prelims and mains GS III Indian Economy
In news
Union Finance Minister has proposed a capital expenditure of more than Rs. 1,60,000 crore forthe Railway Ministry for 2019-20. This is the highest ever allocation for Indian Railways.
Railways network will require an investment of Rs. 50 lakh crore till 2030. Thus, to ensure such big investment in modernising Indian railways and its network, the route of public-private partnership (PPP) model has been pitched to achieve faster development.
The money required for Indian Railways will be provided from different sources such as
- Budgetary support
- Nirbhaya Fund
- Internal resources
- Extra budgetary resources
Ways to improve Indian Railways
To modernise and ease congestion of Indian railways, there is a need for constructing new railway lines, gauge conversions (mostly from meter gauge to broad gauge), doubling the present single line, maintain rolling stock and improving signalling and telecommunication along the railway tracks.
There is also need to improve passenger amenities, modernise railway stations and completion of existing dedicated freight corridor projects. Such freight corridor will free up some of the existing railway network for passenger trains. FM highlighted that completing all sanctioned projects will take decades considering its capital nature of investment.
Thus, in such projects PPP model will help in unleashing faster development for completion of work on tracks, rolling stock manufacturing and delivery of passenger freight services.
The government expects that its earnings from Indian Railways will improve primarily from
- Growth in number of passengers
- Growth in freight volume
Suburban Railways: For growth of Indian Railways in suburban India, Finance Minister has encouraged to invest more in Suburban railways through Special Purpose Vehicles (SPV) structures like Rapid Regional Transport System (RRTS) which is presently proposed on Delhi- Meerut Route.
Metro Railways: Enhancement of metro railways initiatives was also proposed by encouraging more PPP initiatives andensuring completion of sanctioned works. While supporting the growth of metro railways network, theminister also supported transit oriented development to ensure commercial activity around such transithubs.
Income inequality among farmers
Part of Prelims and mains GS III Indian Economy: Agriculture
In news
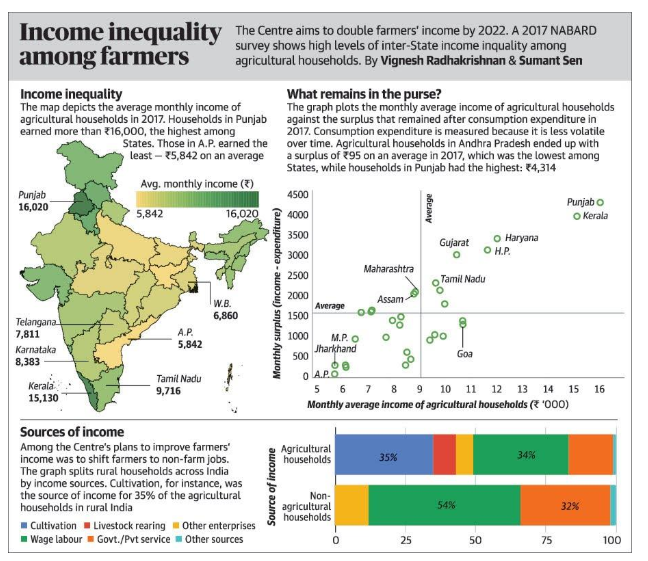
https://epaper.thehindu.com/Home/ShareImage?Pictureid=GRV64CPCV.1
(MAINS FOCUS)
NATIONAL
TOPIC: General studies 3
- Government Budgeting.
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment
Bucks for the banks: Union Budget
Introduction
The 2019-20 budget has many interesting features, but it does not have a defining central theme. There were expectations of a big growth push through either tax cuts or large expenditure programmes even if it meant a rise in the fiscal deficit. But the Finance Minister has chosen to be fiscally conservative, opting to play the long-term game, though it could lead to pain in the short term.
Banking sector and NBFCs
- Budget provided for ₹70,000 crore capital infusion in banks. It is hoped that it will spur lending to growth sectors in the economy.
- It has comprehensively addressed the important issues of liquidity, solvency and poor governance in the NBFC sector.
- A liquidity window of ₹1 lakh crore has been made available to public sector banks through the Reserve Bank of India to buy pooled assets of NBFCs and offered a one-time credit guarantee for first loss of up to 10%.
- To enable better supervision of the sector, housing finance companies will come under the RBI’s regulatory ambit.
- A long-standing demand of NBFCs for equitable treatment with banks in the matter of taxing interest receivable on bad loans has been conceded.
- They will not need to maintain a Debenture Redemption Reserve on public placements that was leading to locking-up of funds, which is their raw material for business.
- The big problem faced by NBFC financing infrastructure is the lack of long-term funding sources to match their lending tenure.
- This pushed them into borrowing short-term funds to lend to long-term projects, leading to asset-liability mismatches.
- The proposal to set up a committee to study the issue, including the experience with development finance institutions, is welcome.
Do you know?
Debenture Redemption Reserve
A debenture redemption reserve (DRR) is a provision stating that any Indian corporation that issues debentures must create a debenture redemption service in an effort to protect investors from the possibility of a company defaulting.
Strategic disinvestment
The government reiterated its commitment to strategic disinvestment and the declared that it is willing to allow its stake to fall below 51% in non-financial PSUs.
Aadhaar and PAN
- The government seems to be moving towards a single identity card for citizens in the form of Aadhaar, which will now be interchangeable with the PAN card.
- Taxpayers who do not have a PAN card can file returns quoting their Aadhaar number, which effectively can be a substitute for PAN in all transactions.
Faceless e-assessment of tax returns
- Another reform measure is the introduction of faceless e-assessment of tax returns taken up for scrutiny.
- This will eliminate the scope for rent-seeking by officers as there will be no interface between assessee and official.
- In fact, the assessee will not even know the identity of the officer scrutinising the return.
- This is an absolutely welcome measure but needs to be closely watched for implementation.
Start-ups and corporate sector
- Start-ups can heave a sigh of relief as the angel tax is practically off the table.
- The corporate sector has got a minor sop with the turnover limit for the 25% tax bracket being raised to ₹400 crore per annum from ₹250 crore.
- The expectation was that this would be extended to all companies irrespective of size.
- It appears that the government wants to wait for the finalisation of the Direct Taxes Code, which is being examined by a committee.
Real estate sector
- Real estate companies may have reason to cheer as the generous tax concession for affordable housing may create demand, especially in the smaller metros.
Nudge theory
The ‘nudge theory’ of economist Richard Thaler, mentioned extensively in the Economic Survey 2018-19, has been put to use to push forward two of this government’s pet themes — increasing digitalisation of money and promoting electric mobility.
Nudging for digitalization
- On the first, there will now be a 2% tax deducted at source when withdrawals from bank accounts exceed ₹1 crore in a year.
- This is a commendable measure, but it could lead to genuine problems for businesses such as construction and real estate that are forced to deal in cash for wage payments.
Nudging towards electric vehicles
- Here those taking loans to buy one will get a tax deduction of up to ₹1.5 lakh on the interest paid by them.
- But the fact is that there are not too many electric vehicles in the market now. And even for those that are there, the waiting period to deliver one is long.
- Besides, there is no ecosystem, such as charging points, even in the major cities. The government’s hope seems to be that this incentive will create a market for e-vehicles that will then lead to the development of the ecosystem.
Fiscal deficit
- The budget documents show that the government has stuck to the glide path for fiscal deficit, which will be at 3.3% this fiscal. This is, however, based on exaggerated growth projections in tax revenues.
- It will be possible with a comfortable buffer if the Bimal Jalan committee that is going into the sharing of RBI’s reserves with the government comes up with favourable recommendations.
- The government also appears to be sliding into a protectionist mode, going by the increase in customs duty on many things.
Connecting the dots:
The Union Budget 2019-20 is hoping to spur the economy by revitalising the financial sector. Analyse.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Featured Comments and comments Up-voted by IASbaba are the “correct answers”.
- IASbaba App users – Team IASbaba will provide correct answers in comment section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1) Consider the following statements,
- SFURTI Scheme launched for making Traditional Industries more productive and competitive by organizing the Traditional Industries and artisans into clusters has been revamped.
- The Scheme for Promotion of Innovation, Rural Industry and Entrepreneurship’ (ASPIRE) has been consolidated for setting up of Livelihood Business Incubators (LBIs) and Technology Business Incubators (TBIs).
Select the correct statements
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements about total fertility rate in India,
- Health-related financial allocation in budget 2019-20 as a share of the child health budget has shown a decline.
- The Anganwadi services and the Poshan Abhiyan (Nutrition Mission) are among the most important government programmes aimed at reducing stunting, anaemia, low weight and low birth weight.
Select the incorrect statements
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
MUST READ
Quota politics: on U.P.’s move to confer SC status on 17 backward castes
Opening a window
Don’t pick and choose











