IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 19th September 2019
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Astra missile
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Security
In News
- India has successfully flight-tested air-to-air missile Astra indigenously designed and developed by DRDO as part of the Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP).
- The state-of-the-art missile was launched from Sukhoi-30 MKI off the coast of Odisha as part of user trials by the Indian Air Force(IAF)
- Modifications of the Sukhoi-30 MKI jets to accommodate Astra missiles has been carried out by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited.
- The Astra missile is a beyond visual range missile. It is capable of engaging different targets at different altitudes.
- The missile has a strike range of 70km.
- The missile has a 15-kg high-explosive pre-fragmented warhead.
- It is smoke free, having two way data link and provides very less chances to enemy to be alert about it.
Tejas
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains GS-III- Security
In News
- Rajnath Singh became the first defence minister to fly on the Tejas.
- The Tejas is an indigenous light weight, multi role supersonic aircraft developed in both fighter and trainer versions.
- Conceived as a MiG-21 replacement, the aircraft has been designed and developed by Aeronautical Development Agency (arm of DRDO) and produced by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL)
- The Tejas is designed to carry a veritable plethora of air-to-air, air-to- surface, precision guided and standoff weaponry.
- A batch of the Tejas aircraft has been already been inducted into the Indian Air Force.
- The naval version is in the development stage and a critical test was conducted successfully in September first week through “arrested landing”, an ability to land on board an aircraft carrier.
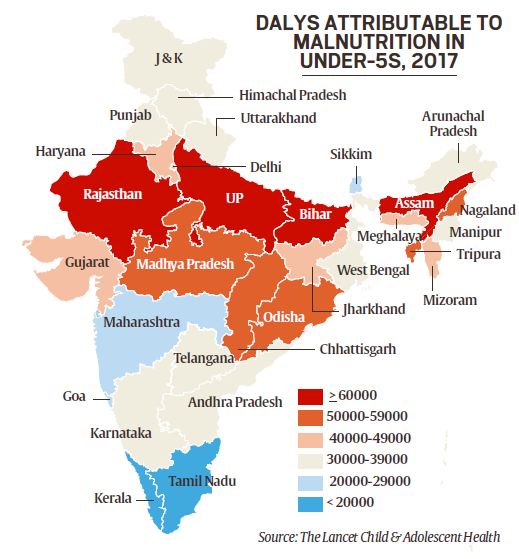
Malnutrition
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains GS-II – Health
In News
- Two-thirds of the 1.04 million deaths in children under five years in India are still attributable to malnutrition,
- This was revealed in the state-wide data on malnutrition presented by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), Public Health Foundation of India (PHFI) and National Institute of Nutrition (NIN).
- The Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALY) rate attributable to malnutrition in childrenvaries 7-fold among the states — a gap between a high of 74,782 in Uttar Pradesh and a low of 11,002 in Kerala.
- Other findings of the report were:
- low birthweight was 21.4 % ranging from 9 % in Mizoram to 24 % in UP.
- child stunting (low height-for-age) 39.3 % ranging from 21 % in Goa to 49 % in UP
- child wasting (low weight for height) 15.7 %
- child underweight7 % ranging from 16% in Manipur to 42 % in Jharkhand.
- anaemia in children 59.7 % ranging from 21 % in Mizoram to 74 % in Haryana
- anaemia in women 15–49 years of age 54.4 %
- exclusive breastfeeding 53.3 % and
- overweight child5 %
- Schemes to tackle malnutrition in India are: Integrated Child Development Scheme launched in 1975, the National Nutrition Policy 1993, the Mid Day Meal Scheme for school children 1995, and the National Food Security Act 2013, POSHAN Abhiyan
- In order to reduce malnutrition, focus will be needed on major determinants like provision of clean drinking water, reducing rates of open defecation, improving women’s educational status, and food and nutrition security for the most vulnerable families.
Pic: https://images.indianexpress.com/2019/09/malnutrition-1.jpg
Indian Diaspora
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains GS-II – Indian Diaspora
In News
- At 17.5 million, Indian diaspora largest in the world says the UN report.
- Report: The International Migrant Stock 2019, a dataset released by the Population Division of the UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs (DESA)
- It provides the latest estimates of the number of international migrants by age, sex and origin for all countries and areas of the world.
- In 2019, the number of migrants globallyreached an estimated 272 million.
- Migrants from Mexico constituted the second largest diaspora with 11.8 million people followed by China (10.7 million), Russia (10.5 million) and Syria (8.2 million).
- Regionally, Europe hosted the largest number of international migrants (82 million),followed by Northern America (59 million) and Northern Africa and Western Asia (49 million).
- At the country level, United States of America hosting the largest number of international migrants (51 million),with Germany and Saudi Arabia hosting the second and third largest numbers of migrants (13 million each).
- India hosted 5.1 million international migrants in 2019. The highest number of international migrants came from Bangladesh, Pakistan and Nepal.
- The global number of refugees and asylum seekersincreased by 13 million between 2010 and 2017. Northern Africa and Western Asia hosted around 46% of the global number of refugees and asylum seekers.
- The share of women and girls in the global number of international migrantsfell slightly, from 49% in 2000 to 48% in 2019.
(MAINS FOCUS)
ECONOMY
TOPIC: General Studies 3:
- Effects of liberalization on the economy, changes in industrial policy and their effects on industrial growth.
- Infrastructure: Energy, Ports, Roads, Airports, Railways etc.
- Investment models.
Trade tensions between the US and China
Context:
- The unending escalation of trade tensions between the US and China has led to a disruption of long established supply chains between the two countries
- Firms exporting from China, both domestic and foreign, have begun to move to other countries in Asia.
Origin of the US-China dispute
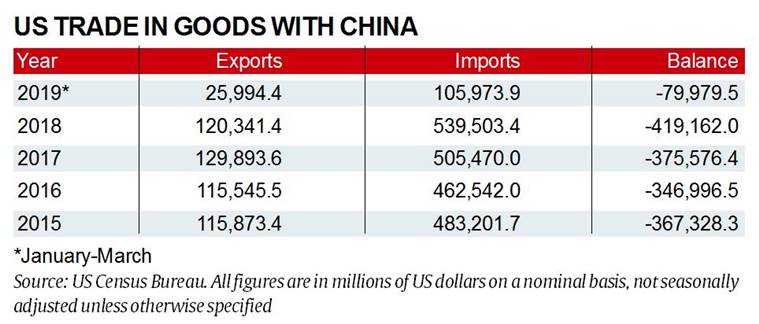
- The US and China have been slugging it out since Trump slapped heavy tariffs on imported steel and aluminium items from China last year, and China responded by imposing tit-for-tat tariffs on billions of dollars worth of American imports.
- The dispute escalated after Washington demanded that China reduce its $375 billion trade deficit with the US, and introduce “verifiable measures” for protection of Intellectual Property Rights, technology transfer, and more access to American goods in Chinese markets.
Pic: https://images.indianexpress.com/2019/05/box-1.jpg
What is there in for India?
- opportunity for India to expand trade with the US and China—by filling in supply gaps.
- India might attract firms exiting China to use India as an exporting base, thereby improving India’s manufacturing base, creating jobs and further expanding its trade—especially with the US.
- the scale of Chinese exports (roughly ten times India’s exports) implies that even small changes to some of China’s less significant exports may create opportunities of significant scale for countries such as India.
For instance,
- Chinese textiles account for nearly 20% of US textile imports while Indian exports account for only a little over 5%.
- Chinese global machinery exports amount to nearly $1.2 trillion, while India exports are a paltry $27 billion.
- Indian machinery exports would increase by over 40%, were India to take over a mere 1% of Chinese machinery exports.
Challenges in India
- India the acquisition of land to set up large manufacturing operations remains hugely problematic and where infrastructure support remains less than ideal
- competitive labour costs, a tax and regulatory environment hospitable to business, and easy and hassle-free access to all of the factors of production—land, labour, capital and other inputs, such as raw materials and intermediate inputs.(need to be checked)
- an inadequate road, rail, and seaport network,
- increasing costs of getting goods to market
- the investments that are likely to flow to India, exiting China, will be characterized by low fixed costs and relative capital non-intensity—that is, relatively “footloose” investments.
- The danger with footloose capital, is that it may leave just as easily as it had arrived with even a small change in incentives either in India or abroad.
Footloose industry
- Footloose industry is a general term for an industry that can be placed and located at any location without effect from factors of production such as resources, land, labour, and capital.
- These industries often have spatially fixed costs, which means that the costs of the products do not change despite where the product is assembled. Diamonds, computer chips, and mobile manufacturing are some examples of footloose industries.
Do you know?
- Vietnam, have been far more successful than India in attracting firms exiting China. Indeed, Vietnam’s exports to the US last year have risen by more than 40%
Conclusion
- India has enjoyed an improvement in its “investment climate” and the “ease of doing business” rankings over the years, and while it has implemented significant liberalization of its foreign domestic investment (FDI) rules, setting up manufacturing operations in India remains a daunting challenge for many would-be investors.
- Major capital-intensive manufacturing activities move to India permanently, requires a very substantial improvement in the basic factors that drive FDI.
- Now is not the time for tinkering at the margins but for bold moves to make India a serious player in global value chains.
Connecting the dots:
- Govt’s recent announcements offering improved trade facilitation—especially in dealing with paperwork relating to taxes, trade credits and so forth—are welcome improvements . Justify?
ECONOMY/ENVIRONMENT
TOPIC: General Studies 3:
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources, growth, development and employment (especially in Environment and Renewable energy sector).
- Environment and Ecology, Bio diversity – Conservation, environmental degradation, environmental impact assessment, Environment versus Development
Green bonus- Integrating mountains with the mainstream
Context:
- In the last week of July 2019, 11 Himalayan States of India met in Dehradun demanding a “green bonus”.
- Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) promised inits general election manifesto to provide a financial package to address the special developmental needs of the Himalayan States
What is Green bonus:
11 Himalayan states gathered together and made the following demands to the centre
- A separate Union ministry to deal with problems endemic to them
- The States asked to develop hydropower resources, subsidies for their environmental protection measures which deny them normal ‘development models’, and recognition of their efforts to meet human development parameters.
- Bring political, social, or ecological-economical terms with the specificity of the Himalayan region.
- A green bonus in recognition of their contribution to environment conservation.
Rationale behind such demands
- Most of the country’s rivers originate in the Himalayan states and thus they have to play significant role in water conservation efforts
- Also large part of their land fell into eco-sensitive zones where developmental activities are severely restricted
- A green bonus is thus needed to compensation for their disadvantages
Scenarios in integrating mountain regions with the national mainstream:
- The mountain zone starts from Balochistan, through Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, J&K, Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Nepal, Sikkim and Gorkhaland, to Arunachal Pradesh, Meghalaya, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram and the Chittagong Hill Tracts.
- They have difficulty in integrating these hilly regions with these national states which are primarily anchored in the plains.
- Authors/writers have also opinioned about the structural, social, and economical differences of the mountain states from the rest of India in their writings:
- Integration problem’ is not just a South Asian phenomenon — China is struggling to integrate its mountain people and their homelands with its national mainstream, as are Myanmar, Thailand, and other countries.
Colonial era:
- The establishment of Pax Britannica’s border lines along India’s northern mountain which was anchored in the society and political economy of the plains could for the first time could reach so deep into the Himalayas and control them which were historically unprecedented.
- In brief, the Himalayas successfully provided a barrier to Russian colonial expansion but were unsuccessful in providing a trade route into China.
- Keeping the mountains politically quiet and socially peaceful was both a desirable aim and a hopeful description by the end of the 19th century.
- The independent nation states of Asia like India, Pakistan, China or Myanmar have all imagined themselves to be the inheritors, in the high Himalayas, of the geopolitical stakes of their colonial predecessors.
- The happiness of the ‘hill station’ or the war-like strategies towards the northern tribesmen was both creations of this colonial policy.
Norms of an Indian village:
- The norms of an ‘Indian village’ depends on how its society is structured, how its economy is backward or in what ways does its political life work make no reference to the specificities of the mountain regions.
- This is not only a social-psychological feature but has direct practical consequences as policies and programmes are devised with the ‘national norm’ in mind, which almost always have unintended consequences on the hilly regions.
Conclusion:
- There is a direct, yet short, link between the demands of the Himalayan States seeking a special “green bonus” — which the BJP supports.
- The massive expansion of the national economy over the past three decades now allows for commodification of mountain resources (forests, water, labour, tourism, horticulture and even agriculture).
- It has led to changes in the class structure and the emergence of a new middle class with national aspirations that find the geographical specificity of the Himalayas.
Connecting the dots:
- How the secessionist movements in J&K and Nagaland and integrationist movements in Himachal Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh and Manipur help the people to come to the national mainstream?
- What are the main reasons for the low focus on the Himalayan states with respect to social, economical and political measures?
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Featured Comments and comments Up-voted by IASbaba are the “correct answers”.
- IASbaba App users – Team IASbaba will provide correct answers in comment section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1) Consider the following statements about Tejas aircraft
- The aircraft has been indigenously designed and developed by Aeronautical Development Agency (arm of DRDO) and produced by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL)
- The Tejas is designed to carry air-to-air, air-to- surface, precision guided and standoff weaponry.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements about Astra missile
- It is indigenously designed and developed by DRDO as part of the Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP).
- It is a surface-to-air missile having a range of 300 kms.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3) Consider the following statements
- At 17.5 million, Indian diaspora largest in the world followed by Mexico (11.8 million), China (10.7 million) and Russia (10.5 million)
- The highest number of international migrants into India came from Africa and ASEAN countries.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
MUST READ
Obama was right about Iran
A self-inflicted economic slowdown
The multitudes dispossessed by the ‘Gujarat model’
Changing times: The musclemen of new India are crushing old values
India’s actions over the status of J&K provide an opportunity to revisit four-point plan for Kashmir
Focusing on health, education of women











