IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 11th October 2019
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
SURAKSHIT MATRITVA AASHWASAN (SUMAN)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains II – Health
In News
- Union Minister for Health along with several State Health Ministers launched SUMAN initiative for Zero Preventable Maternal and Newborn Deaths.
- The initiative aims at assuring dignified, respectful and quality health care at no cost and zero tolerance for denial of services for every woman and newborn visiting the public health facility in order to end all preventable maternal and newborn deaths.
- Under it, pregnant women, mothers up to 6 months after delivery, and all sick newborns will be able to avail free healthcare benefits.
- The government will also provide free transport from home to health institutions.
- The pregnant women will have a zero expense delivery and C-section facility in case of complications at public health facilities.
DHRUV Programme
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains GS-II – Education
In News
- Pradhan Mantri Innovation Learning Programme – DHRUV is a 14-day learning programme launched by Ministry of HRD in ISRO HQ in Bengaluru.
- It aims to further sharpen innovative imagination, skills and knowledge of the students to bringsolutions to socio-economic, political and environmental issues in the country.
- 60 brightest and talented students from Science, Mathematics and Performing Arts have been chosen for the programme through rigorous selection process
- Every student to be called ‘DHRUV TARA’ will be mentored by renowned experts.
Invasive weeds threatening tiger habitats in Adilabad, Telangana
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III- Environment
In News
- Invasive weeds affect population of herbivores which are prey to the big cats
- As a result, there is increase in influx of tigers from forests across the border in Maharashtra.
- It was way back in 1992 at the Rio de Janeiro Convention on Biodiversity that biological invasion of alien species of plants was recognised as the second worst threat to the environment after habitat destruction.
About Invasive Species
- Those species whose introduction into an ecosystem successfully out-compete native organisms and harms ecosystems. Common characteristics are:
-
- Rapid reproduction and growth,
- High dispersal ability,
- Phenotypic plasticity (ability to adapt physiologically to new conditions)
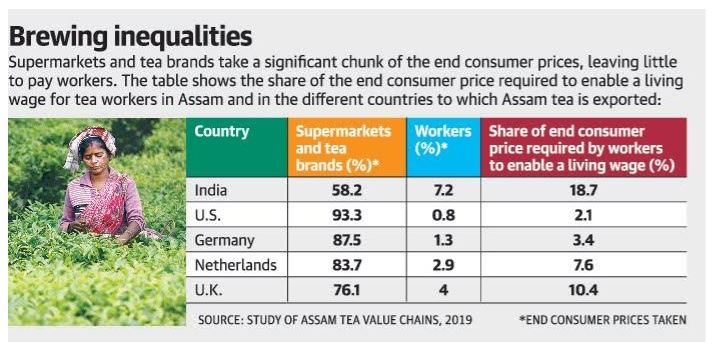
Assam tea estates violating labour laws
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III- Economy
In News
- A report by Oxfam, a confederation of independent charitable organisations focussing on the alleviation of global poverty, has flagged violation of labour rights in the tea estates of Assam.
- The report noted that the Assam government’s commitment to increasing the minimum wages of tea plantation workers to ₹351 met with hurdles of financial viability in the sector.
- The researchers found that despite working for over 13 hours a day, workers earn between Rs 137-167
- Tea brands and supermarkets “typically capture over two-thirds of the price paid by consumers for Assam tea in India — with just 7% remaining for workers on tea estates”
- Oxfam asked consumers, supermarkets and brands to support the Assam government’s move to provide living wages to workers and to ensuring more of the price paid by the consumers trickle down to them.
- State government is trying to increase the wages of tea plantation workers through the upcoming Occupational Health and Safety Bill.
Miscellaneous
NOBEL PRIZE IN LITERATURE
- Austria’s Peter Handke won the 2019 Nobel Prize for Literature, and the postponed 2018 award went to Polish author Olga Tokarczuk.
- Austria’s Peter Handke won the 2019 prize for “for an influential work that with linguistic ingenuity has explored the periphery and the specificity of human experience”.
- Polish author Olga Tokarczuk won the 2018 prize – delayed by one year after a sexual assault scandal rocked the award-giving Academy – for “a narrative imagination that with encyclopaedic passion represents the crossing of boundaries as a form of life.”
- Olga Tokarczuk, the 15th woman to win the Nobel Literature Prize, also won the International Booker Prize in 2018.
- The Nobel Prize in Literature is a Swedish literature prize that is awarded annually, since 1901.
- It is awarded to an author from any country who has produced “in the field of literature the most outstanding work in an ideal direction”.
(MAINS FOCUS)
LAW
TOPIC: General Studies 2:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation
Motor Vehicles bill 2019
Context:
- The Motor Vehicles Bill 2019 seeks to amend the Motor Vehicles Act, 1988 to provide for road safety.
- The Act provides for grant of licenses and permits related to motor vehicles, standards for motor vehicles, and penalties for violation of these provisions.
- The bill suggests a new National Transportation Policy, which may replace the existing National Urban Transport Policy, 2014.
Background:
- The past two decades have witnessed a huge rise in road accidents, fatalities and other safety concerns in India.
- A government committee estimated that road accidents rose by about 50% between 2005 and 2015.
- 2014 that the National Urban Transport Policy (NUTP) committee proposed a new legislation, incorporating all modes of transportation, multi-modal integration, road safety, etc. Following that, the Road Transport and Safety Bill was drafted in 2014.
Amendment:
The amendments in the Bill mainly focus on issues relating to improving road safety, citizens’ facilitation while dealing with the transport department, strengthening rural transport, last mile connectivity and public transport, automation and computerization and enabling online services.
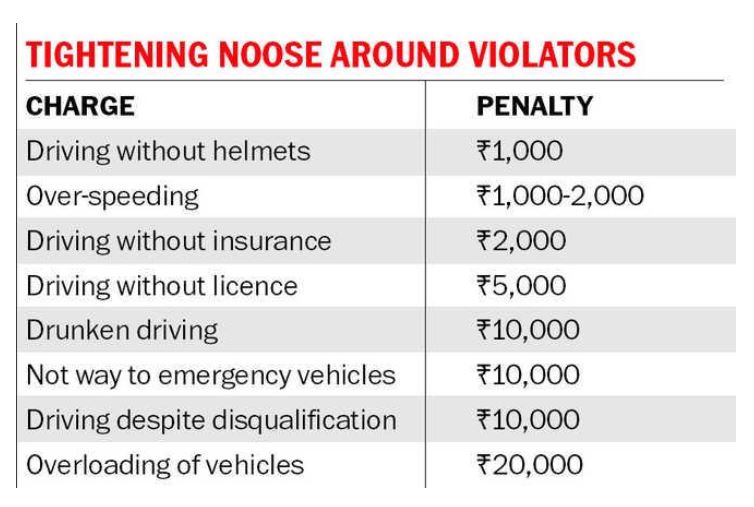
Road Safety: In the area of road safety, the Bill proposes to increase penalties to act as deterrent against traffic violations. Stricter provisions are being proposed in respect of offences like juvenile driving, drunken driving, driving without licence, dangerous driving, over-speeding, overloading etc.
Vehicle Fitness: The Bill mandates automated fitness testing for vehicles. This would reduce corruption in the transport department while improving the road worthiness of the vehicle. Penalty has been provided for deliberate violation of safety/environmental regulations as well as body builders and spare part suppliers. The Bill also provides for compulsory recall of defective vehicles and power to examine irregularities of vehicle companies.
Recall of Vehicles: The Bill allows the central government to order for recall of motor vehicles if a defect in the vehicle may cause damage to the environment, or the driver, or other road users.
Road Safety Board : The Bill provides for a National Road Safety Board. The Board will advise the central and state governments on all aspects of road safety and traffic management
Protection of Good Samaritan: To help road accident victims, Good Samaritan guidelines have been incorporated in the Bill. The Bill defines a Good Samaritan as a person who renders emergency medical or non-medical assistance to a victim at the scene of an accident, and provides rules to prevent harassment of such a person.
Cashless Treatment during Golden Hour: The Bill provides for a scheme for cashless treatment of road accident victims during golden hour.
Third Party Insurance : The Bill has included the driver’s attendant in 3rd Party insurance. re will be no cap on liability of insurers. There will be a 10 time increase in insurance compensation, from Rs 50, 000 to Rs 5 lakh.
Motor Vehicle Accident Fund: The Bill requires the central government to constitute a Motor Vehicle Accident Fund, to provide compulsory insurance cover to all road users in India.
Improving Services using e-Governance: Provision for online driving licenses, Process of Vehicle Registration, Drivers Training
Taxi aggregators: The Bill defines aggregators as digital intermediaries or market places which can be used by passengers to connect with a driver for transportation purposes (taxi services). The Bill provides guidelines for Aggregators.
Aftermath:
- All these amendments are intended to reduce traffic crashes by at least 50% by 2030 (a target set by the United Nations).
- Out of the many amendments proposed in the Act, the increased penalties have been implemented in many States from September 1, 2019; at the same time, many States have decided to “dilute” the suggested increase in penalties.
Criticisms:
- The idea of higher fines as a deterrent to traffic crashes is based on the assumption that a driver is careless and that the fear of a higher penalty will encourage “careful” behaviour while on the road. This goes against current scientific understanding in reducing traffic crashes that promotes the design of a system which can forgive mistakes made by road users.
- Road safety experts suggest that road designs such as lane width, shoulder presence, number of lanes and median design influence driving behaviour such as operating speeds, lane changing, etc.
- In the past two decades, there have been major investments in expanding the national highway system in India. Yet, fatalities have continued to grow.
- The MVA amendments do not address the reliability of crash estimates, which form the basis of designing preventive strategies
Data:
- A Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) report of 2018 has listed 1,51,430 fatalities. However, for the same year, the World Health Organisation estimates nearly 300,000 deaths.
- A government of India study by the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India (‘The Million Death’ study) also reports at least a 50% under-reporting of traffic fatalities
Way forward:
- ‘Roads themselves play an important role in road safety, and improved geometry design and infrastructure could in turn help to improve road safety.
- Stricter penalties and intensive driver training cannot reduce the risk of driver fatigue. However, road engineers can change the road design to reduce boredom and monotony.
- Recognition of human frailty, acceptance of human error, and creation of a forgiving environment and appropriate crash energy management.
Conclusion:
- If there is to be a reduction in India in traffic crashes, it requires establishing a system or institutional structure which enables the generation of new knowledge-new road standards thereby ensuring safe highways and urban roads.
Connecting the dots:
- In spite of the ambitious provisions in the amended Motor Vehicles law, safe road behaviour is still miles away. Analyse.
CITIZENSHIP
TOPIC: General Studies 2:
- Indian Constitution- historical underpinnings, evolution, features, amendments, significant provisions and basic structure.
Countrywide National Register of Citizens (NRC)
Context:
- After rolling out the National Register of Citizens in Assam, the BJP-led government at the Centre has said it will conduct a similar exercise in the rest of the country.
About:
- It is the register containing names of Indian Citizens. It was prepared first in 1951 after the conduct of the Census of 1951.
- It is used to identify who is a bona fide Indian citizen and those who fail to enlist in the register will be deemed illegal migrants.
Updates in the National Register of Citizens (NRC) of Assam: To compile a list of the names of genuine Indian citizens residing in Assam and, in the process, detect foreigners (read Bangladeshis) who may have illegally entered the state after March 24, 1971.
Background
Pre-independence: Assam’s demographic changes date back to the introduction of the plantation economy by the colonial state in the 19th century. The colonial state brought in tribal labourers from Chota Nagpur and Bihar to work the plantations and encouraged the migration of Muslim farmers from Bengal.
Post-independence: Migrations continued after Independence even as Partition solidified national identities. The ethnic, cultural and religious dimensions of the situation demanded sensitive and imaginative solutions from the political class.
- In 1970s, All Assam Students’ Union spearheaded a massive drive, popularly known as the Assam Agitation calling for the detection, deletion and deportation of illegal Bangladeshi migrants.
- In 2013, the Supreme Court finally ordered to complete the exercise by December 31, 2017, leading to the present updating of NRC in Assam.
Significance of updated NRC:
The publication of the updated NRC is a positive step in so far as-
- It is an important milestone in dealing with the influx of illegal migrants from Bangladesh into that state.
- It puts to rest wild speculations about the extent of the illegal migrant population in Assam and the resulting polarization that political parties have been exploiting to make electoral gains.
Concerns highlighted in the process
- Process of adding person to NRC list is too complex and confusing – riddled with legal inconsistencies and errors.
- Instances of arbitrary rejection of the gram panchayat certificates.
- Robust non-transparent “family tree verification” process resulted in numerous instances of parents being on the draft list but children being left out. Each person who is left out will now have to prove not only his or her linkages afresh, but also the documents themselves before the appropriate forum.
- Faults on part of the Supreme Court
- Lack of proper monitoring process
- Failed to ensure legal clarity over the manner in which the claims of citizenship could be decided
- Failed to understand the implications of the results, and after effects as well as recourse that should be made available for people who have failed to be recognized as citizens of the State
- Inability to comprehend the further political and policy actions in case of loss of citizenship
Criticisms:
- Without legal aid being provided to the people. Any adjudication process without legal aid for the poor is a null and void adjudication. And any adjudication on a tribunal without a judicially trained person there is a null and void adjudication. It is a terrible legal failure of the entire system in which the judiciary itself has played a very negative role, to put it mildly.
- The aspect of incarceration of people. That you can incarcerate stateless people is unheard of. That’s another travesty of human rights taking place.
- Why is it that only Assam has NRC? Indian citizenship law is such that Assam is the only place where there’s an exception. The idea that you can do an NRC on an all-India scale is bizarre.
- The Supreme Court saying you need it because you have an enemy invasion into Assam! It is a Supreme Court-created problem.
- 1.9 million people are there. And you can’t push them back at gunpoint across the border with Bangladesh.
- The mass insecurity and social crisis stalking the 1.9 lakh people of Assam.
- Many people are in stake who lives in strategic and sensitive border state. Their documents are being ambiguous.
- Assam has a peculiar problem of villages getting ravaged, or disappearing, due to annual floods unleashed by the fiery Brahamaputra. Documents get destroyed, geographies shift, addresses change.
- Several cases of transparent injustice whereby families have been divided – some declared Doubtful Voters and foreigners, others as bonafide citizens.
- Widespread perception that specifically linguistic and religious minorities are being targeted – namely, Bengali speaking Muslims and Hindus.
Connecting the dots:
- The NRC process has an Assam-specific history. Extending it to the rest of the country is bizarre. Analyse.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Featured Comments and comments Up-voted by IASbaba are the “correct answers”.
- IASbaba App users – Team IASbaba will provide correct answers in comment section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1) Consider the following statements
Assertion (A):Invasive weeds are threatening tiger populations leading to increased man-animal conflict
Reason (R): Biological invasion of alien species of plants is recognised as the second worst threat to the environment after habitat destruction
Select the correct answer from codes given below
- Both A and R are correct, and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are correct, and R is not correct explanation of A
- A is correct while R is incorrect
- A is incorrect while R is correct
Q.2) SUMAN scheme often seen in the news is being implemented by which Ministry?
- Ministry of Women and Child Development
- Ministry of Minority Affairs
- Ministry of Health
- None of the above
Q.3) Consider the following statements about Dhruv Scheme
- It is intended to increase the spread awareness about space and astronomy among the school children.
- It is being implemented by Ministry of Women and Child Development
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
MUST READ
Going down together: On IMF’s slowdown warning
Do we need a countrywide National Register of Citizens?
In Mamallapuram, seeking the true north in ties
RCEP: Opportunity, fears in regional trade deal
Let’s use cognitive science insights for better learning
The efficiency promise of the Bankruptcy Code











