IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 12th October 2019
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Industrial output shrinks by 1.1% in August 2019
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains III – Economy
In News
- The Index of Industrial Production (IIP) contracted 1.1% from a year earlier, following a growth of 4.3% in July. Industrial output had grown 4.8% in August 2018.
- Industrial production slipped into a contraction in August, driven in large part by poor performances in the mining, manufacturing and capital goods sectors
- Within the Index, the mining sector saw growth decelerating to 0.1%, from a 4.9% expansion in July.
- The manufacturing sector, hampered by poor demand, witnessed a contraction of 1.2%, compared with a growth of 4.2% in July and a 5.2% expansion in the year-earlier period.
About IIP
- IIP is a composite indicator measuring changes in the volume of production of a basket of industrial products over a period of time, with respect to a chosen base period.
- It is compiled and published on a monthly basis by the Central Statistical Office with a time lag of six weeks from the reference month.
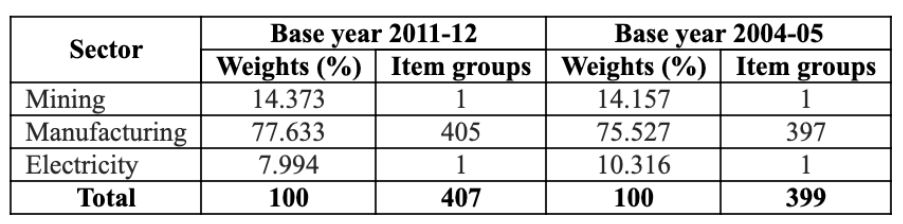
- Coal, Crude Oil, Natural Gas, Refinery Product, Steel, Cement and Electricity are known as Core Industries. The eight Core Industries comprise nearly 37.9 % of the weight of items included in the Index of Industrial Production (IIP).
https://pib.gov.in/newsite/PrintRelease.aspx?relid=161745
NOBEL PEACE PRIZE
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains GS-II – International Affairs
In News
- Ethiopian Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed Ali was awarded the 2019 Nobel Peace Prize for “his important work to promote reconciliation, solidarity and social justice”
- When Abiy became Prime Minister in 2018, Ethiopia had been locked in conflict with Eritrea for 20 years. In July that year, he stepped across the border in Eritrea and in cooperation with Eritrean President Isaias Afwerki, worked out the principles of a peace agreement.
- Ethiopia is landlocked country, while Eritrea has a sea coast which connects the Middle East.
- Through the years of conflict, Ethiopia had depended heavily on Djibouti for access to the Gulf of Aden and onward to the Arabian Sea.
- The peace deal opened up Eritrean ports for Ethiopian use.
- In domestic achievements, he lifted Emergency, granted amnesty to thousands of political prisoners, discontinued media censorship, dismissed leaders suspected of corruption, and increased the influence of women in political and community life.
Do you know?
- Ethiopia is the most populous landlocked country in the world and the second-most populous nation on the African continent.
- Its capital and largest city is Addis Ababa, which serves as the headquarters of the African Union and the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa.
https://cdn.britannica.com/38/183638-050-EEF23553/World-Data-Locator-Map-Ethiopia.jpg
RTI violations go unpunished
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Governance
In News
- As the RTI Act marks its 14th anniversary on Saturday, a report card analysing its performance showed that government officials face hardly any punishment for violating the law by denying applicants the legitimate information sought by them.
- The ‘Report Card on the Performance of Information Commissions in India’ was prepared by the Satark Nagrik Sangathan and the Centre for Equity Studies.
- The State and Central Information Commissions, which are the courts of appeal under the Act, failed to impose penalties in about 97% of the cases where violations took place in 2018-19.
- The State Commissions of Tamil Nadu, Sikkim, Mizoram and Tripura did not impose penalties in any cases at all.
- The report showed that there were 2.18 lakh cases pending with the commissions in March 2019, in comparison with 1.85 lakh pending cases a year earlier.
- Any new appeal would have to wait more than one-and-a-half years for resolution. The backlog is exacerbated by the fact that four out of 11 CIC posts are yet to be filled.
- This destroys the basic framework of incentives and disincentives built into the RTI law, promotes a culture of impunity and exasperates applicants who seek information at a high cost and often against great odds
(MAINS FOCUS)
INDIA’S FOREIGN POLICY
TOPIC: General Studies 2:
- India and its neighbourhood- relations.
- Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
Mamallapuram Summit
Context:
- Chinese President Xi Jinping and Prime Minister Narendra Modi held “productive” talks as part of the second India-China informal summit in the southern coastal town of Mamallapuram in Tamil Nadu
- Modi took Xi to three iconic monuments in the historical coastal city—Arjuna’s Penance, Panch Rathas and the Shore Temple. The monuments date back to the Pallava era (4th-9th century CE). One of the reasons for choosing Mamallapuram was to highlight the contacts between the Pallava kings and China’s Fujian province where Xi served as governor once.
- Talks between Modi and Xi were aimed at building on the relationship reset that began in Wuhan in April last year.
- The broad agenda included their unresolved border dispute, trade and people-to-people contacts besides regional and global issues.
Concerns:
- summit was clouded by a series of irritants including a statement by Xi telling Pakistan’s Prime Minister Imran Khan that he was watching the situation in Kashmir and would support Pakistan on issues related to its core interests
- India has termed it as its internal matter and issued a sharp response to Xi’s comments, that was also notable for its timing—less than 48 hours ahead of Xi’s arrival in India.
- China, on its part, has been reportedly unhappy about Indian military exercises in Arunachal Pradesh, some 100km from the undemarcated border between the two countries. China claims the whole of Arunachal Pradesh as part of its territory.
- The U.S. and China were in a better relationship. Beijing’s focus was entirely on economic development and “peaceful rise”. It was also the beginning of the golden age of globalisation and free trade that softened borders between big trading and investment partners. Now, U.S.-China ties have turned hostile at a time when India is steadily enhancing its strategic partnership with US.
Challenges:
- Relations with Beijing are doubly critical for India as China is both a neighbour and a rising great power.
- There are structural problems in ties — the boundary dispute, the Pakistan factor, and historical mistrust.
- Deepen Tactical engagement further, and for that they should not allow strategic glitches dictate terms for a bilateral partnership.
- U.S wants India to swing to its side and join its Indo-Pacific strategy, the undeclared aim of which is to contain China’s rise. China, obviously, doesn’t want India to swing to the other side.
- The Pakistan factor looms large over ties. With Mr. Modi’s hyper-nationalist government taking an aggressive approach towards Pakistan and cracking down on Kashmir, China’s Pakistan card is now stronger
Trade and border:
- Since 1990, Ind-China have decided to strengthen ties in Economy.
- Economy, as in the early 1990s, India, following China’s footsteps, started liberalising its economy.
- Trade ties between the two countries boomed over the years (it touched $95 billion last year), though it’s largely skewed towards China as the latter was fast emerging as an industrial and technological powerhouse.
- The border has been largely peaceful during this period.
Way forward:
- China must make investments in India, especially in building infrastructure and fifth generation technology architecture.
- India, wants greater market access in China,
- India-China cooperation in projects in third countries.
- India should engage with Pakistan, which will not only calm down its borders but also weaken China’s Pakistan card
- Plan to take economic ties to the next level, addressing mutual concerns.
Example:. In the 1950s and ’60s, the U.S. tried everything it could to weaken and isolate Mao Zedong’s China. But it didn’t stop President Nixon(U.S) from visiting China in 1972 that led to a remarkable turnaround in Sino-American ties.
Conclusion:
- India should turn the focus to its rise and building capacities, not on conflicts and rivalries.
- If it’s driven by such a broader but a realist vision, India could expand the avenues of deep tactical engagement with a powerful China.
Connecting the dots:
- Should India compete with China for dominance of Asia or should it stay focussed on its own rise in which competition with China will be a part? Analyse.
- A nation can pick its friends, but not its neighbours. Elucidate
ECONOMY
TOPIC: General Studies 3:
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources, growth, development and employment.
- Inclusive growth and issues arising from it.
Downturn in India’s economy
Context:
- Gross domestic product (GDP) growth in the first quarter of 2019-20 at 5% was the lowest in six years, even less than the last quarter of 2018-19 at 5.8%, which was the lowest in five years.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has reduced its 2019-20 growth forecast from 6.9% to 6.1%.
Moody’s
- Moody’s Investors Service on slashed its 2019-20 GDP growth forecast for India to 5.8 per cent from 6.2 per cent earlier, saying the economy was experiencing a pronounced slowdown which is partly related to long-lasting factors.
- The projection is lower than 6.1 per cent that the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) had forecast
- Investment-led slowdown that has broadened into consumption, driven by financial stress among rural households and weak job creation.
- private investment has been relatively weak since 2012, consumption — which makes up about 55 per cent of GDP — had remained robust
- Asian Development Bank and the Organisation of Economic Cooperation and Development lowered 2019-20 growth forecast for India by 50 basis points and 1.3 percentage points to 6.5 per cent and 5.9
IMF:
- IMF said global economy now in ‘synchronized slowdown’
- Global growth will fall to its lowest rate in this decade
- Slowdown is emerging markets like India and Brazil to be even more pronounced
- In 2019, IMF expect slower growth in nearly 90 per cent of the world.
- Economic activity is softening in advanced economies, such as the US, Japan and, especially, the eurozone,
- while in other emerging markets, such as India and Brazil, the slowdown is even more pronounced this year.
- China’s accelerated growth is experiencing a gradual decrease
Impacts on India:
- A prolonged period of slower nominal GDP growth constrains the scope for fiscal consolidation
- Keeps the government debt burden higher for longer compared with our previous expectations
- General government deficit, which is likely to remain wide
- Affected the disposable income of households, so that the increase in private consumer expenditure has witnessed a slump, dampening growth further from the demand side.
- The consequences for the automobile sector, which is the driver of manufacturing, and for construction, which is an important source of employment creation, are now being felt.
- Investment rates as a percentage of GDP are progressively lower. So are savings rates. The stagnation in the dollar value of exports continues.
Criticisms:
- The government has been in denial mode about the slowdown.
- The Union budget presented in early July, was a missed opportunity, did little,
- Since then, as a consequence of significant changes introduced in the budget, stock markets have plummeted and business sentiment has floundered.
- Theory and experience both suggest that tax cuts work with a time lag and do not ever lead to an equivalent increase in investment. (Because Higher profits emanating from lower taxes could be used by firms to restructure debt and clean up their balance sheets, increase dividends paid to shareholders)
- Tax cut increase the fiscal deficit by 0.7% of GDP, compared with budget estimates for 2019-20.
Measures taken by govt:
- Measures to boost the economy,
- Correcting for mistakes on taxation,
- Decriminalizing defaults on corporate social responsibility obligations,
- Simplifying laws related to labour, companies and the environment,
- Streamlining government procedures,
- Facilitating capital flows in financial markets
- The government slashed corporate income tax rates. The effective rate, including the surcharge, was reduced from 35% to 25%.
Connecting the dots:
- Economic downturns do have political consequences. Analyse
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Featured Comments and comments Up-voted by IASbaba are the “correct answers”.
- IASbaba App users – Team IASbaba will provide correct answers in comment section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1) Consider the following statements Right to Information Act, 2005
- Non-Resident Indians can also file RTI applications under the Act to seek governance-related information from Central government
- The State and Central Information Commissions act as the courts of appeal under the Act
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements about Index of Industrial Production (IIP)
- It is released on monthly basis by Central Statistical Office
- The revised 2011-12 series of IIP has increased the weightage of electricity in comparison to 2004-05 series of IIP
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3) Horn of Africa is home to which of the following countries?
- Djibouti
- Eritrea
- Kenya
- Ethiopia
- Rwanda
- Somalia
Select the correct answer from the codes given below
- 2, 4, 5 and 6
- 1, 2, 4 and 6
- 1, 3, 4 and 5
- 1, 2, 3 and 5
MUST READ
Towards an Asian Century
Warm up to the Valley: On Kashmir lockdown
The policy way out
Unworthy Nations
Abiy Ahmed Ali, Laureate, for Peace in Horn of Africa: What was his role?











