IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 25th October 2019
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
KARTARPUR SAHIB CORRIDOR AGREEMENT
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains II–International Relations
In News
- India and Pakistan signed an agreement to operationalise the Kartarpur corridor that will facilitate pilgrims from India to visit the Gurdwara Kartarpur Sahib in Pakistan.
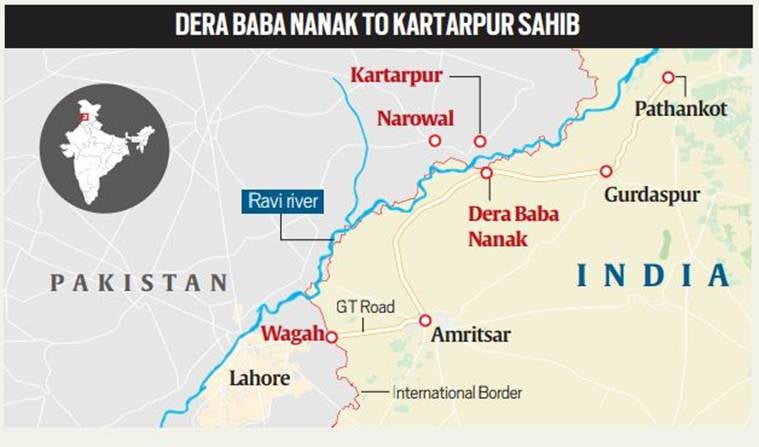
- The corridor is being built to connect Dera Baba Nanak in Gurdaspur with Gurdwara Darbar Sahib in Kartarpur, the final resting place of Sikhism founder Guru Nanak, to commemorate his 550th birth anniversary celebrations on November 12.
- Indian pilgrims of all faiths and persons of Indian origin can use the corridor.
- The travel will be Visa Free; Pilgrims need to carry only a valid passport
- The Pakistan side has assured India to make sufficient provision for ‘Langar’ and distribution of ‘Prasad’. However, there has been no progress on resolving the disagreement over a $20 fee that Pakistan intends to levy on each traveller.
- Pilgrims would be allowed to carry kirpans (dagger), one of the five articles of faith worn by Sikhs.
Pic: https://images.indianexpress.com/2018/11/kartarpur1.jpg
A.P. likely had a flourishing port 2,000 years ago
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains I – Culture
In News
- The first round of excavation at the site near the banks of the Swarnamukhi river in Andhra Pradesh’s Gottiprolu, about 80 km from Tirupati and Nellore,unearthed a huge settlement surrounded by a brick enclosure (fortified settlement)
- A maritime trade centre based out of a fortified settlement may have had a trade guild with its own army to protect its interests around 2,000 years ago, according to Archaeological Survey of India officials involved in the excavation of the site.
- The excavation unearthed brick-built structures in elliptical, circular and rectangular shapes. The size of bricks (43 to 48 cm) can be compared to those in the Satavahana/Ikshvaku period structures in the Krishna valley, according to the ASI. This means the site may date back to 2nd century to 1st century BCE.
- A four-armed 2-metre tall sculpture of Vishnu was unearthed at the site that can be dated back to the Pallava period (8th Century CE), looking at its features like head gear and drapery.
- The excavation also unearthed a series of broken terracotta pipes that fit into each other, pointing towards a form of drainage.
- ASI had excavated about 10% of the site and would start on the second round of excavations in November or December, when more evidence was likely to be unearthed.
Commission for Protection of Child Rights
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains II – Polity
In News
- The Karnataka State Commission for Protection of Child Rights wants the Department of Primary and Secondary Education to ban schools from assigning homework to students in classes I to V.
- This proposal is made on the grounds that the move will ease the pressure on young minds.
- Commissions for Protection of Child Rights Act, 2005 provided for establishment of Commissions for Protection of Child rights both at National level and State level.
About National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR)
- NCPCR is country’s apex child rights body.
- Objective of this commission is to protect, promote and defend the child rights in India including the rights adopted in the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Children, 1989, ratified by India in 1992.
- The Chairperson of NCPCR should be a person of eminence who has done outstanding work on promoting the child rights.
- The Commission’s Mandate is to ensure that all Laws, Policies, Programmes, and Administrative Mechanisms are in consonance with the Child Rights perspective as enshrined in the Constitution of India and also the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child.
Do you know?
- The Child is defined as a person in the 0 to 18 years age group.
DOING BUSINESS REPORT 2020
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains III –Economy
In News
- The World Bank released its latest Doing Business Report (DBR, 2020).
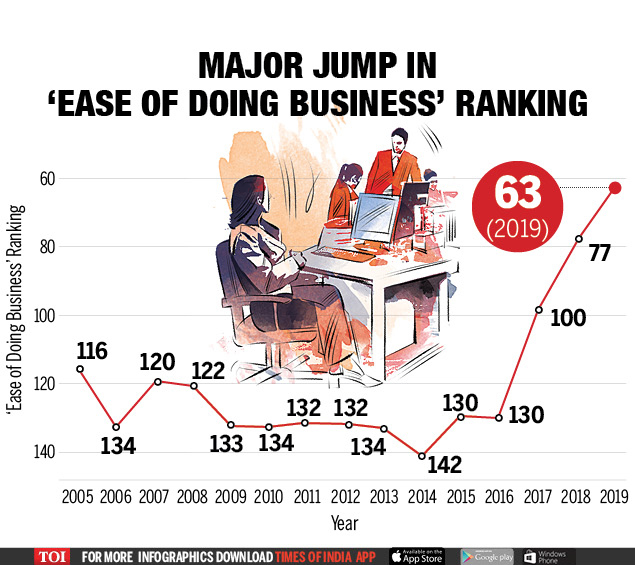
- India ranks at 63rd among 190 countries, moved 14 places from the previous year (77th rank in 2018).
- The DBR ranks countries on the basis of Distance to Frontier (DTF), a score that shows the gap of an economy to the global best practice. This year, India’s DTF score improved to 71.0 from 67.23 in the previous year.
- The report assess improvement in ease of doing business environment in Delhi and Mumbai.
- In the last 5 years, India’s ranking has improved 79 places – to 63 in 2019 from 142 in 2014.
- Significant improvements have been registered in ‘Resolving Insolvency’, ‘Dealing with Construction Permits’, ‘Registering Property’, ‘Trading across Boards’ and ‘Paying Taxes’ indicators
- Recovery rate under resolving insolvency has improved significantly from 26.5% to 71.6%.
- The time taken for resolving insolvency has also come down significantly from 4.3 years to 1.6 years.
- India continues to maintain its first position among South Asian countries. It was 6th in 2014.
Jailed Uighur intellectual wins EU rights award
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains II – Human rights
In News
- The European Parliament has awarded the Sakharov Prize for human rights to Uighur intellectual Ilham Tohti, who has been sentenced to life imprisonment in China for “separatism”.
- The outspoken former Professor of economics at a Beijing university was sentenced in 2014.
- By awarding this prize, European Parliament strongly urge the Chinese government to release Tohti and calls for the respect of minority rights in China
Who are Uighurs?
- The Uighurs are a minority Turkic ethnic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the general region of Central and East Asia.
- The Uighurs have been recognized as native to only one region, the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of the People’s Republic of China
2 out of 3 wild poliovirus strains have been eradicated
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains III – Health
In News
- In an announcement by the World Health Organisation (WHO) on World Polio Day (October 24), an independent commission of experts declared that wild poliovirus type 3 (WPV3) has been eradicated worldwide.
- This follows the eradication of smallpox and wild poliovirus type 2.
- Efforts are being taken to eliminate the wild poliovirus type 1. This virus remains in circulation in just two countries, Afghanistan and Pakistan.
- There are three individual and immunologically distinct wild poliovirus strains: wild poliovirus type 1 (WPV1), wild poliovirus type 2 (WPV2) and wild poliovirus type 3 (WPV3).
- Symptomatically, all three strains are identical, in that they cause irreversible paralysis or even death.
- But there are genetic and virological differences, which make these three strains three separate viruses that must each be eradicated individually.
- There is no cure for polio, it can only be prevented. Polio vaccine, given multiple times, can protect a child for life.
- Two polio vaccines, are used throughout the world to provide immunity to poliovirus. One uses inactivated (dead) poliovirus and the other uses attenuated (weakened) poliovirus.
(MAINS FOCUS)
ECONOMY
TOPIC: General Studies 3:
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources, growth, development and employment
World Bank’s ease of doing business ranking (India 63rd Rank)
Context:
- India hiked 14 places to the 63rd position on the World Bank’s ease of doing business ranking
- India is among the top 10 performers on the list for the third time in a row
- New Zealand, Singapore and Hong Kong topped
- World Bank applauded the reform efforts undertaken by the India in its report
- India is the first country of its type to jump this year by 14 position.
Pic: https://static.toiimg.com/img/71732579/Master.jpg
Journey from 140 to 63:
- In 2014 India was at 140th.
- 100th position in 2018
- 77th position in 2019
- 63rd now
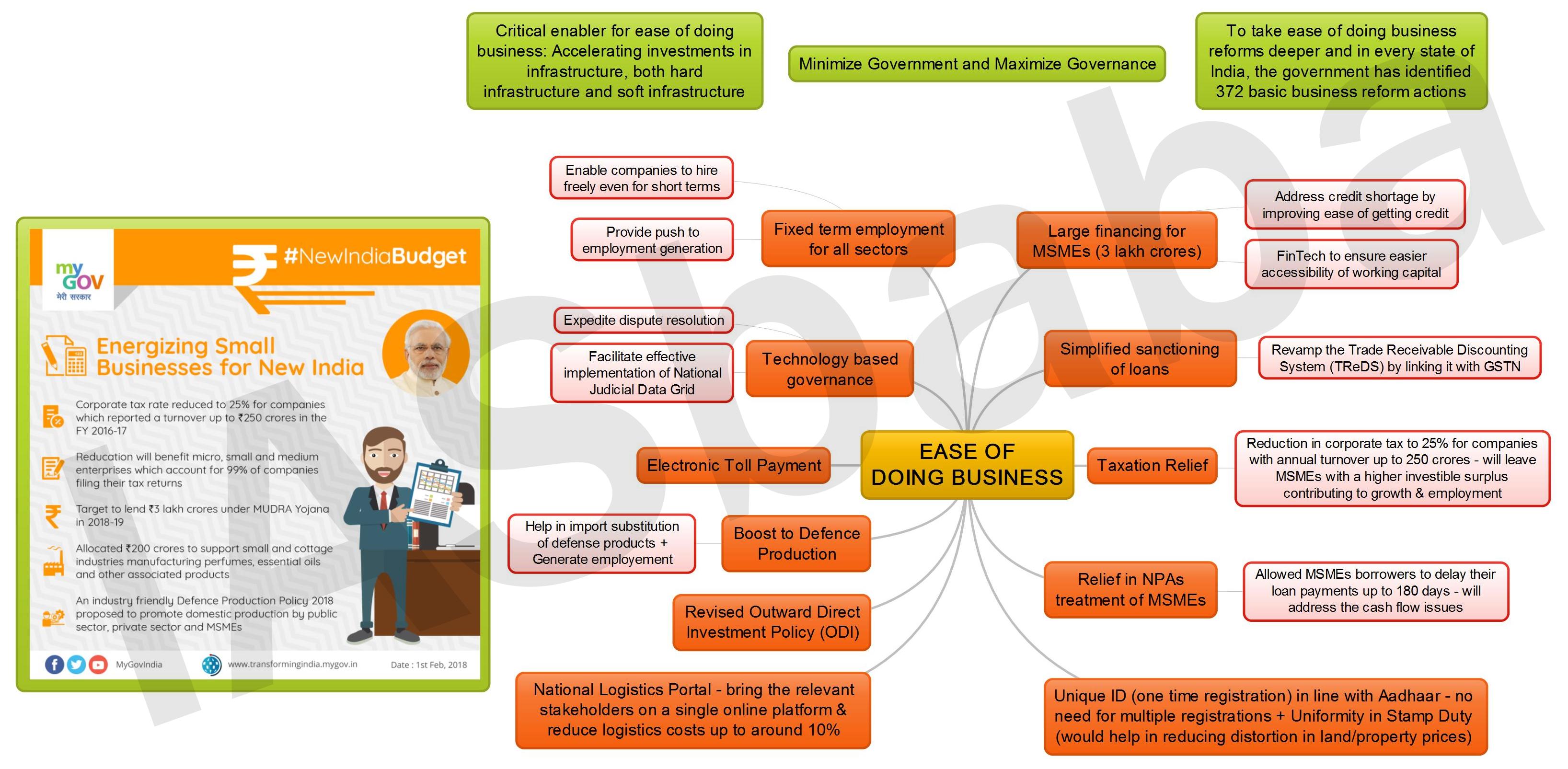
Policies that helped :
- ‘Make in India’ campaign focused on attracting foreign investment, boosting the private sector (manufacturing in particular) and increasing the country’s overall competitiveness
- In 2015, the government’s goal was to join the 50 top Rank in the ease of doing business ranking by 2020.
- successful implementation of the Insolvency And Bankruptcy Code(Before the implementation of the reform, it was very burdensome for secured creditors to seize companies in default of their loans)
- Improvements were registered in starting business(start up India scheme), dealing with construction permits and trading across borders.
- Govt made starting a business easier by abolishing filing fees for the SPICe (Simplified Proforma for Incorporating a Company Electronically) company incorporation form, electronic memorandum of association, and articles of association
- Trading across borders made easier by enabling post clearance audits, integrating trade stakeholders in a single electronic platform, upgrading port infrastructures, and enhancing the electronic submission of documents.
Ease of doing business report:
The report was introduced in 2003 by world bank to provide an assessment of objective measures of business regulations and their enforcement across 190 economies on ten parameters affecting a business through its life cycle
- Starting a business
- Dealing with construction permits
- Getting electricity
- Registering property
- Getting credit
- Protecting investors
- Paying taxes
- Trading across borders
- Enforcing contracts
- Resolving insolvency
Implications:
- First, the Doing Business indicators provide a snapshot of a country’s red tape; they have no pretension of providing a comprehensive picture of the investment climate.
As the World Bank makes clear, the indicators are not designed to comment on macroeconomic indicators or prospects for growth. - Second, there exists a wide divergence between de jure and de facto realities in most economies.
What firms actually encounter “on the ground” is perhaps more important, but there are limitations to our ability to measure and interpret those experiences without bias.
The Way Ahead:
- While we can truly be proud of the extent of India’s macro-policy reforms, it is time we started to focus on the micro-policies of enforcement. Top down macro reforms can only be effective if they are twinned with bottom-up micro reforms. Unless the day-to-day experience of doing business improves, we will continue to under-perform relative to our true potential.
- To secure changes in the remaining areas will require not just new laws and online systems but deepening the ongoing investment in the capacity of states and their institutions to implement change and transform the framework of incentives and regulation facing the private sector. India’s focus on ‘doing business’ at the state level may well be the platform that sustains the country’s reform trajectory for the future
Conclusion:
- The Ease of doing business rankings thus, should not be seen as the ultimate marker of the ruling party’s reform success. Likewise, investors who are considering the prospects for investment in India should recognize what the rankings do and do not tell us.
- While India has made tremendous progress in various categories, it is the depth of these reforms which needs to be worked in the next few years to bring up India into the Top 50 ranking.
Connecting the dots:
- The change in Ease of doing business ranking is fully acknowledged by the growth in Foreign Direct Investment into India. Analyse.
Mind map
Pic: https://iasbaba.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/Ease-of-Doing-Business.jpg
INTERNATIONAL
TOPIC: General Studies 2:
- India and its neighbourhood- relations.
- Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests
- Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests, Indian Diaspora.
Operationalisation of the Kartarpur Corridor
Context
- India and Pakistan signed agreement on Kartarpur corridor.
- The agreement relates to the modalities for operationalisation of the Kartarpur Sahib Corridor at Zero Point, International Boundary, Dera Baba Nanak.
- Indian pilgrims of all faiths and persons of Indian origin can use the corridor and the travel will be Visa Free
- Pilgrims need to carry only a valid passport and the Corridor is open from dawn to dusk
- Pilgrims travelling in the morning will have to return on the same day.

Pic: https://d39gegkjaqduz9.cloudfront.net/TH/2018/11/23/DEL/Delhi/TH/5_01/88722918_2544650_101_mr.jpg
Current status:
- Currently pilgrims from India have to take a bus to Lahore to get to Kartarpur, which is a 125 km journey although people on the Indian side of the border can physically see Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur on the Pakistani side.
- An elevated platform has also been constructed for the same on the Indian side, where people use binoculars to get a good view
Concern:
- Under the agreement, Pakistan will charge a very nominal USD 20 from every Indian Sikh pilgrim for a single trip
- India continues to urge this issue with the Government of Pakistan to reconsider its insistence on levying the fee.
- Indian pilgrims who enter Pakistan through the Kartarpur corridor will not be allowed to visit other gurdwaras in the Punjab province of that country. They would have to go via the normal route, after applying for a visa, and paying the requisite fees.
- Concerns about the pilgrims being exposed to the propaganda of pro-Khalistan elements.

Pic: http://www.samacharnama.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/kartarpur-corridor-map-1.png
Why levy?
- Pakistan has spent about Rs 1,000 crore on the Kartarpur corridor infrastructure. It would be providing langar to the pilgrims who visit Gurdwara Darbar Sahib.
- It would also be providing e-rickshaws to ferry the pilgrims from Dera Baba Nanak on the Indian side.
- The fee has triggered a political controversy within India, and Punjab Chief Minister Capt Amarinder Singh has called the fee a “jazia” tax on pilgrims.
Gurdwara in Kartarpur
- The gurdwara in Kartarpur is located on the bank of river Ravi in Pakistan
- It is about four km from the Dera Baba Nanak shrine, and about 120 km northeast of Lahore
- It was here that Guru Nanak assembled a Sikh community and lived for 18 years until his death in 1539
- The shrine is visible from the Indian side, as Pakistani authorities generally trim the elephant grass that would otherwise obstruct the view
- Indian Sikhs gather in large numbers for darshan from the Indian side, and binoculars are installed at Gurdwara Dera Baba Nanak
- The gurdwara was opened to pilgrims after repairs and restoration in 1999, and Sikh jathas have been visiting the shrine regularly ever since
- Sikh jathas from India travel to Pakistan on four occasions every year- for Baishakhi, the martyrdom day of Guru Arjan Dev, the death anniversary of Maharaja Ranjit Singh, and the birthday of Guru Nanak Dev.
Significance
- First proposed in 1999 by the prime ministers of India and Pakistan, Atal Bihari Vajpayee and Nawaz Sharif, respectively, as part of the Delhi–Lahore Bus diplomacy
- Implemented as an integrated development project with Government of India funding.
- The development comes ahead of the 550th Prakash Purab or 550th birth anniversary of Guru Nanak in 2019.
- Until now, most Indian devotees have had to contend with a darshan using binoculars installed at Dera Baba Nanak Sahib.
- This can be considered a big development since despite the India-Pakistan deadlock in talks, both India and Pakistan have been able to form a consensus on the issue.
Way forward:
- India must work to secure its border from the threat even as it opens the gates for thousands of pilgrims to travel to Pakistan.
- National security must get priority
- there must be an effort by all stakeholders in India — the Centre, the State government and the leadership of the BJP, the Akalis and the Congress — to resist scoring political points against one another.
- Modalities and technical issues, such as on the numbers, eligibility and identity proof required for the trip to Kartarpur Sahib, should be ironed out by both governments.
- India must negotiate with the Government of Pakistan to reconsider its insistence on levying the fee.
Conclusion:
- It will be unfortunate if Pakistan uses the Kartarpur Corridor to fish in troubled waters and cause instability for its political ends
Connecting the dots:
- Security concerns are high-priority, but blocking work on the corridor is not right. Justify.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Featured Comments and comments Up-voted by IASbaba are the “correct answers”.
- IASbaba App users – Team IASbaba will provide correct answers in comment section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1)Uighur problem sometimes seen in the news is predominantly related to which of the following country?
- Afghanistan
- Iran
- Yemen
- China
Q.2)Consider the following statements
- Wild poliovirus type 2 and type 3 has been eliminated world wide
- Wild Polio Virus Type 1 virus remains in circulation in just two countries, Afghanistan and Pakistan.
- There is no cure for polio, it can only be prevented.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.3)Consider the following statements with reference to the National commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR)
- It is a statutory body established under the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act, 2012.
- It defines a Child as a person in the 0 to 18 years age group.
- The commission works under the administrative control of the Ministry of Women & Child Development.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.4)Consider the following statements about Doing Business report (DBR)
- It is released by International Monetary Fund
- The DBR ranks countries on the basis of Distance to Frontier (DTF), a score that shows the gap of an economy to the global best practice.
- The report assess improvement in ease of doing business environment in all Capital cities of States of India.
Which of the statements given above are incorrect?
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
MUST READ
Good report card: On ease of doing business
Two elections and a dent to a jingoistic edifice
Putin takes centre stage in Syria
Legislation against mob lynching must be accompanied by effective policing











