IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 19th November 2019
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Bharatiya Poshan Krishi Kosh
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Agriculture
In News
- Ministry of Women and Child Development has launched Bharatiya PoshanKrishiKosh
- It is a repository of diverse crops across 128 agro-climatic zones to help enable better nutritional outcomes
- It aims to promote and reinforce healthy dietary practices both at the individual and community level and tackle malnutrition in a sustainable manner.
- The kosh helps in reducing malnutrition through a multi-sectoral results-based framework, including agriculture, among women and children across the country.
- Harvard Chan School of Public Health and the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation will be a part of this initiative.
- They will document and evaluate promising regional dietary practices and the messaging around them and develop a food atlas on regional agro-food systems.
Winter-grade diesel
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III- Energy, Security
In News
- State-run Indian Oil Corporation Ltd (IOC) launched a special winter-grade diesel that remains unfrozen up to minus 33 degree Celsius.
- Motorists in high-altitude sectors like Ladakh, Kargil, Kaza and Keylong face the problem of freezing of diesel in their vehicles when winter temperatures drop to as low as -30o Celsius.
- Regular diesel fuel contains paraffin wax which is added for improving viscosity and lubrication. At low temperatures, the paraffin wax thickens or “gels” and hinders the flow of the fuel in the car engine.
- Indian Oil has come up with an innovative solution to this problem by introducing a special winter-grade diesel with a low pour-point of -33o Celsius, which does not lose its fluidity function even in extreme winter conditions
- In general, it is achieved by treatment with additives that change the low temperature characteristics of the fuel.
- The fuel would help provide year-round access to snow-capped border regions, and is part of India’s efforts to speed up strategic road connectivity
Starlink network
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains III – Science & Technology (Space)
In News
- SpaceX, the world’s leading private company in space technology, fired a spray of 60 satellites into low earth orbit, the first operational batch of what is intended to eventually evolve into a constellation of nearly 12,000 satellites aimed at providing low-cost and reliable space-based Internet services to the world.
- Internet has now become a part of humanity’s basic infrastructure and an important means of delivering a wide variety of public services to the world’s peoples
- Currently, about 4 billion people, more than half the world’s population, do not have access to reliable Internet networks.
- And that is because the traditional ways to deliver the Internet — fibre-optic cables or wireless networks — cannot take it everywhere on Earth.In many remote areas, or places with difficult terrain, it is not feasible or viable to set up cables or mobile towers.
- Signals from satellites in space can overcome this obstacle easily.
- In space-based networks, data requests travel from the user to the satellite, and are then directed to data centres on the ground
- Criticism to the project:
- Increased space debris
- Increased risk of collisions and
- The concern of astronomers that these constellations of space Internet satellites will make it difficult to observe other space objects, and to detect their signals.
Do You Know?
- There are fewer than 2,000 operational satellites at present, and fewer than 9,000 satellites have been launched into space since the beginning of the Space Age in 1957. Most of the operational satellites are located in the lower orbits.
- On September 2019, the European Space Agency (ESA) had to perform, for the first time ever, a “collision avoidance manoeuvre” to protect one of its live satellites from colliding with a “mega constellation”
India-Bhutan
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains II –India and Neighbourhood
In News
- Bhutan plans to levy charges on tourists from regional countries, including India, Bangladesh and the Maldives, who atpresent are exempted from any charges.
- The sharp increase in the number of tourists from the region was cited for the move to start imposing levy on tourists from India, Bangladesh & Maldives
- In contrast to other international tourists, who pay $250 (Approx. INR. 18,000) as a minimum charge per day per person, tourists from India, Bangladesh and the Maldives had so far paid no fees, and were able to cross over without visas.
- The objective of “tourism tax” is to combat over-tourism and get visitors to pay for the upkeep and maintenance of the public spaces they are visiting
- Tourist levy will put Bhutan out of the league of budget destination but the counter argument is that without such charges Bhutan would not be able to preserve its local heritage and culture.
- In 2018, of the 2,74,000 tourists visiting Bhutan, the council estimated that about 2,00,000 were from the region, of which about 1,80,000 were from India.
Maternity scheme performance
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains II – Health
In News
- Pradhan MantriMatruVandanaYojana (PMMVY)scheme benefitted just 31% eligible mothers, say researchers who extrapolated data obtained under RTI
- PMMVY is a vital programme to support lactating mothers and pregnant women by compensating them for loss of wages during their pregnancy.
- The PMMVY is targeted only at women delivering their first child. A cash amount of ₹6,000 is transferred to the bank account of the beneficiary in three instalments upon meeting certain conditions including early registration of pregnancy, having at least one ante-natal check-up and registration of child birth.
- Given the stipulated conditions, the scheme brings under its ambit 23% of all births and pays full benefits to a mere 14% of all births, which was at 270.5 lakh for 2017
- Several factors impeded proper implementation of the programme that aims to fight malnutrition among children. These include an application form of about 23 pages, a slew of documents such as mother-child protection card, Aadhaar card, husband’s Aadhaar card and bank passbook aside from linking their bank accounts with Aadhaar.
Gram Sabha to have power to ban liquor
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains II – Panchayat Raj Institutions
In News
- The Haryana Cabinet took an in-principle decision to bring an amendment in Section 31 of the Haryana Panchayati Raj Act, 1994, allowing devolution of powers to the Gram Sabha to ban liquor within the local area of a Gram Panchayat
- The quorum of the Gram Sabha meeting for passing such a resolution shall be one-tenth of its members
- No liquor vends will be allowed in Haryana villages from the next financial year without its panchayat’s approval.
- Article 47 state that “The State shall endeavour to bring about prohibition of the consumption except for medicinal purposes of intoxicating drinks and of drugs which are injurious to health”.
Cartosat-3
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains III – Science & Technology (Space)
In News
- ISRO is set for launch of Cartosat-3
- Cartosat-3, an advanced earth imaging and mapping satellite, will be flown on the PSLV-C47 vehicle
- The 1,560 kg satellite will have 13 small U.S. customer satellites riding as secondary passengers. They will be placed in a polar orbit.
- Cartosat-3, with an ISRO-best resolution of 25 cm, will be the first of a series of high resolution, third generation satellites planned for observing the Earth.
- The satellite will be able to pick up objects of that size (25 cm) from its orbital perch about 509 km away. This will make Cartosat-3 among the few sharpest, if not the best, civil earth imagers worldwide.
(MAINS FOCUS)
ECONOMY
TOPIC:General Studies 3:
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources, growth, development and employment
SC’s judgment in Essar Steel insolvency case
Context:
- Essar Steel owes Rs 54,547 crore to its creditors — financial creditors and operational creditors combined.
- The company had been put on the block under IBC to recover the unpaid dues.
- The Ahmedabad-bench of National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) had on March 8 okayed the bid submitted by ArcelorMittal, led by steel tycoon Lakshmi Mittal, for the takeover of Essar Steel.
- The operational creditors had opposed the bid on the basis that they were getting notional payment, while 92.5 per cent of the financial creditors’ dues were being paid.
- This case being one of India’s most high-profile insolvency cases, any order on Essar Steel is likely to have ramifications for similar resolution schemes.
SC judgement:
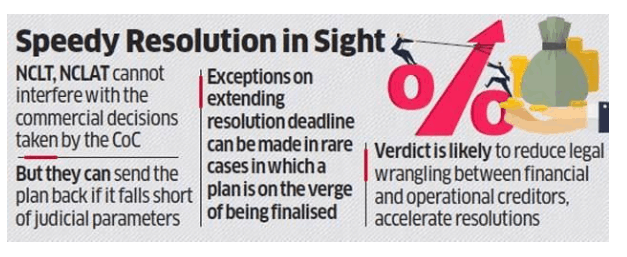
- The committee of creditors (CoC) will have a final say in the resolution plans under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC).
- The National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) and National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT) cannot interfere with the commercial decisions taken by the CoC.
“The law talks of “equitable” and not “equal” treatment of operational creditors. Fair and equitable dealing of operational creditors’ rights involves the resolution plan stating as to how it has dealt with the interests of operational creditors, which is not the same thing as saying that they must be paid the same amount of their debt proportionately” SC

Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 19th November 2019
Do you know?
Financial creditors are those who provide long-term capital in the form of loans.
Operational creditors are usually the suppliers of raw materials, etc.
NCLT order:
- The NCLAT, in its order, said financial creditors would get 60.7 per cent of their admitted claims of Rs 49,473 crore, about the same as operational creditors.
- The operational creditors with admitted claim amount of less than Rs 1 crore would get 100 per cent, while above Rs 1 crore would get 60.26 per cent and workmen and employees would get 100 per cent.
- The tribunal had said that the CoC will have no role in the distribution of Rs 42,000 crore and allowed claims of the operational creditors.
Crux:
- A consortium of banks led by the SBI had moved the Supreme Court against a National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT) order in the case.
- The NCLAT had held that Essar Steel’s operational creditors be treated on par with financial creditors when settling the claims.
- Essar Steel’s Committee of Creditors (CoC) had sought the quashing of NCLAT’s July 4 order that approved the Rs 42,000-crore bid for the debt-laden firm by ArcelorMittal.
- This was to be divided between the financial creditors who are owed Rs 30,030 crore and the operational creditors who are owed Rs 11,969 crore.
Advantages for Bank :
- Banks are expected to recover 90 per cent of their exposure to the Essar Steel account.
- Compares with only 60 per cent they would have recovered earlier as per the order of the National Company Law Appellate Tribunal
Conclusion:
- The Court order and government move on financial service providers — bode well for the banks battling high NPAs.
- While banks will recover money resolution process in large accounts, likely stress from NBFC and telecom accounts will remain a drag.
Connecting the dots:
- The Supreme Court’s order is being seen as bringing the rigour and momentum back into the IBC as an effective tool to deal with stressed assets in the economy. Analyse
ECONOMY
TOPIC: General Studies 3:
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources, growth, development and employment.
- Inclusive growth and issues arising from it.
Wage Code Bill
- The government introduced the labour codes on wages and on occupational safety, health and working conditions in the Lok Sabha.
- The Code Of Wages, 2019 is applicable to employees in organised sector and unorganised sector, while the central government will continue to make wage related decisions for railways, mines, oil fields, and central public sector undertakings.
- It subsumes The Payment of Wages Act, 1936;The Minimum Wages Act, 1948;The Payment of Bonus Act, 1965; and The Equal Renumeration Act,1976.
Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 19th November 2019
Need for Wage code:
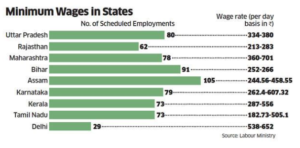
- 62% of the workforce is made up of casual workers who need the right to minimum wages
- Present minimum wages act is complicated
- 33% of the workers are underpaid than the indicative minimum wages in 2009-10
Features:
- Consolidate India’s 44 labour laws into four codes in order to rationalize labour laws and improve ease of doing business.
- Benefit two fifths of its population, or 50 crore workers
- End a complicated wage system and bring down the number of wage rates from 2,000-plus to around 300
- This will ensure that process of registration and filing of returns will get standardised and streamlined. With various labour related definitions getting standardised, it is expected that there shall be less dispute
- Now 60% of workers are not covered under the Minimum Wages Act. The new law will give the right to minimum wages to the entire 50 crore workforce
- Ensures timely payment of wages.
- The floor wage will be fixed by the Centre on the basis of recommendations of a central advisory board, which would be represented by members of trade unions, employers’ association, state government and independent experts
- This will lead to transparency, accountability, better enforcement of labour laws and better utilisation of available workforce
Occupation identification:
- There are four skill levels — unskilled, semiskilled, skilled and highly skilled — while geography can be plains, hilly and undulated, coastal, urban and rural, among others.
- The occupation category is done away with. The states have an ‘and/or’ option while considering skills and geography to decide on a minimum wage rate.
- A state may well decide to have one wage rate if it goes for one geographical parameter
Concerns:
- Applies only to people earning less than `24,000 a month in scheduled employments, leaving out a large number of workers
- There will still be no single national minimum wage rate.
- the floor wage might be worse than the market wage rate in which case the entire purpose of having minimum wages and improving standard of living collapses
- The Equal Remuneration Act, 1976, prohibits gende rbased discrimination in terms of wages, recruitment and conditions of service. The Code has omitted this act
- It will be tough for the government now to ensure implementation and redress even if there is a 10% lapse in compliance – or 5 crore complaints – for the 50 crore workers the law aims to cover.
- The removal of essential powers of labour inspectors
MNREGA
- MNREGA workers will not come under code wage bill
- MNREGA payout is not exactly a wage.
- It is a scheme, which does not have a strict employer-employee relation.
- Its wages will continue to be fixed by the Rural Development Ministry.
Connecting the dots:
- A ‘national minimum wage’ is a good idea, but its computation is cause for concern. Analyse
- The proxy economic exercise on gauging the gap between actual average wage of casual workers and the national floor level minimum wages (NFLMW) hides more than it reveals. Comment
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1) Article 47 deals with which of the following provisions?
- Education for all children below 6 years
- Uniform Civil Code
- Duty of the State to raise the level of nutrition and the standard of living and to improve public health
- None of the above
Q.2) Consider the following statements about Starlink network
- It is launched by Coalition of Space agencies and Private organisation led by NASA and International Telecommunication Union (ITU)
- It is aimed at providing low-cost and reliable space-based Internet services to the world.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3) Consider the following statements about Cartosat-3
- Cartosat-3, with an ISRO-best resolution of 25 cm, will be the first of a series of high resolution, third generation satellites planned for observing the Earth
- It will be launched by GSLV MK-III
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.4) Consider the following statements about Pradhan Mantri Matru VandanaYojana (PMMVY)
- The aim of the scheme is to support lactating mothers and pregnant women by compensating them for loss of wages during their pregnancy.
- The PMMVY is targeted only at women delivering their first child where a cash amount of ₹6,000 is transferred to the bank account of the beneficiary
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.5) Consider the following statements about Bharatiya Poshan Krishi Kosh
- It is a repository of diverse crops across 128 agro-climatic zones to help enable better nutritional outcomes
- United Nations Food & Agricultural organisation (FAO) will be a part of this initiative, who will document and evaluate promising regional dietary practices
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 18 Nov 2019 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | A |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | C |
| 4 | A |
| 5 | A |
MUST READ
When longevity is the biggest achievement: on Shinzo Abe
An elusive reconciliation in Sri Lanka
BRICS on the ball?
Rajapaksa challenge for Delhi in Lanka
Government data always come with limitations, but now they have a political dimension
SC has always upheld and strengthened secularism, but its Ayodhya ruling is problematic on that score











