IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 18th December 2019
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
First Global Refugee Forum (GRF)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains II- International Affairs
In News
- The first Global Refugee Forum (GRF), a two-day gathering of United Nations member states, began in Geneva, Switzerland, on December 17th
- The Forum, jointly hosted by the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) and the government of Switzerland,
- Aims to debate and discuss the response of the world’s countries to the global refugee situation.
- The first GRF has been organised around six areas of focus: burden- and responsibility-sharing, education, jobs and livelihoods, energy and infrastructure, solutions, and protection capacity.
- The number of refugees has risen to over 25 million people worldwide
- The GRF will be held every four years at the Ministerial level.
- It is intended to present an opportunity for UN member states and other stakeholders to announce action plans and pledges towards meeting objectives such as easing the burden on the host country, enhancing refugee self-reliance, expanding access to third-country solutions, and supporting conditions in countries of origin for return in safety and dignity.
Indian Culture Portal
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-I- Culture
In News
- Culture Minister unveiled a portal on Indian culture which brings together all the cultural resources of the country on one platform i.e. www.indianculture.gov.in
- The Indian Culture Portal is a part of the National Virtual Library of India project, funded by the Ministry of Culture, Government of India.
- The portal has been created and developed by the Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay.
- Data has been provided by organisations of the Ministry of Culture (such as the National Archives of India, Gandhi Smriti and DarshanSmriti, Archaeological Survey of India and Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts) and curated by Indira Gandhi National Open University.
- The portal currently has details on 90 lakh items, including manuscripts, archives, research papers, audio books and folk tales with some of them dating back to 4000 years
National Broadband Mission
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economic Development
In News
- The government announced a new ‘mission’ aimed at providing broadband access in all villages in the country by 2022,
- Under the mission, the government plans to lay incremental 30 lakh route km of Optical Fiber Cable, while also increasing tower density from 0.42 to 1 tower per thousand of population by 2024.
- The mission envisages stakeholder investment of $100 billion (Rs7 lakh crore), including Rs70,000 crore from Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF) in coming years
- The vision of the national broadband mission is to fast-track growth of digital communications infrastructure, bridge the digital divide, facilitate digital empowerment and inclusion, and provide affordable and universal access of broadband for all
- Additionally, a Broadband Readiness Index will be developed to measure the availability of digital communications infrastructure within a State/UT.
Unique Identification Authority of India(UIDAI) drops Monitoring agency plan
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II- Governance
In News
- UIDAI was seeking to hire a social media agency that will employ ‘social listening’ tools to monitor and influence conversations on Aadhaar on Facebook and Twitter.
- However, it has informed the Supreme Court -which is hearing a plea objecting such a proposal – that it has decided to withdraw hiring Social media monitoring agency
About UIDAI
- UIDAI was created with the objective to issue Unique Identification numbers (UID), named as “Aadhaar”, to all residents of India that is (a) robust enough to eliminate duplicate and fake identities, and (b) can be verified and authenticated in an easy, cost-effective way.
- UIDAI is a statutory authority established under the provisions of the Aadhaar (Targeted Delivery of Financial and Other Subsidies, Benefits and Services) Act, 2016.
- Prior to its establishment as a statutory authority, UIDAI was functioning as an attached office of the then Planning Commission (now NITI Aayog)
- Under the Aadhaar Act 2016, UIDAI is responsible for
- Aadhaar enrolment and authentication, including operation and management of all stages of Aadhaar life cycle,
- Developing the policy, procedure and system for issuing Aadhaar numbers to individuals and
- Perform authentication and
- To ensure the security of identity information and authentication records of individuals.
- It comes under the Electronics & IT ministry.
No State-wise minority classification
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Polity
In News
- The petition asked the Supreme Court to frame guidelines to “identify and define” religious minorities in every State, especially where Hindus are in a minority (in eight states) so as to protect their culture and interests.
- Articles 29 (protection of the interests of minorities) and Article30 (the right of minorities to administer educational institutions) of the Constitution deals with special provisions for minorities.
- However, the Supreme Court dismissed a petition stating that the States have been carved language-wise. But religion is beyond all borders, especially political borders. Religion has to be taken on a pan-India basis
(MAINS FOCUS)
SOCIETY
TOPIC: General Studies 1:
- Role of women and women’s organization, population and associated issues, poverty and developmental issues, urbanization, their problems and their remedies
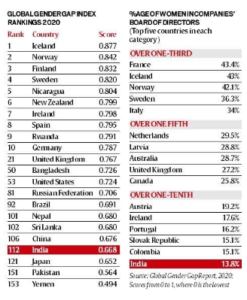
Global Gender Gap Index, 2020(India has ranked 112th among 153)

Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 18th December 2019
Context:
- India has ranked 112th among 153 countries in the annual Global Gender Gap Index for 2020,
- The Report was published by the World Economic Forum (WEF) recently.
- Iceland, Norway, and Finland occupy the top three spots in the Report.
The Global Gender Gap Index
- The Report benchmarks countries on their progress towards gender parity in four dimensions.
- The dimensions are: Economic Participation and Opportunity, Educational Attainment, Health and Survival and Political Empowerment.
- The Report aims to serve as a compass to track progress on relative gaps between women and men on health, education, economy and politics.
- It measures women’s disadvantage compared to men, and is not a measure of equality of the gender gap.
- Through this annual yardstick, stakeholders within each country are able to set priorities relevant in each specific economic, political and cultural context.
Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 18th December 2019
Global Gender Gap Index for 2020: Key findings
- Globally, the average (population-weighted) distance completed to gender parity is at 68.6%, which is an improvement since last edition.
- The largest gender disparity is in political empowerment.
- Projecting current trends into the future, the overall global gender gap will close in 99.5 years, on average.
- There is a sharp deterioration in the economic opportunity gap, especially in women’s under-representation in emerging roles, such as cloud computing, engineering and data and artificial intelligence.
India’s Status
- India has slipped four places in the report to 112, behind neighbours China, Sri Lanka, Nepal and Bangladesh,
- It is due to due to rising disparity in terms of women’s health and participation in the economy.
- The country ranked 98th in WEF’s first report in 2006. Since then, it has fallen due to poor performance in three out of four indicators.
- India is also ranked in the bottom-five in terms of women’s health and survival and economic participation.
- The report showed that economic opportunities for women are extremely limited in India (35.4 per cent).
- India also ranked among countries with very low women representation on company boards.
- The report highlighted abnormally low sex ratios at birth in India (91 girls for every 100 boys).
- On health and survival, four large countries — Pakistan, India, Vietnam and China — fare badly with millions of women not getting the same access to health as men.
- India is the only country among the 153 countries studied where the economic gender gap is larger than the political one.
- On a positive note, India has closed two-thirds of its overall gender gap.
Way forward
- The Indian government needs to make sure that maternal and women’s healthcare is a top priority.
- It needs to increase efforts to skill more women in technology-based fields.
- Else, the potential of a large chunk of the population will remain unrealised.
Conclusion:
- Supporting gender parity is critical to ensuring strong, cohesive and resilient societies around the world.
- Diversity forms an essential element in the global economy too.
Connecting the dots:
- Do you agree that India badly needs to focus on improving women’s access to healthcare?
- What ways would you suggest to improve gender parity?
ECONOMY
TOPIC: General Studies 3:
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources, growth, development and employment.
Indian economy is losing its growth momentum (Part 1)

Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 18th December 2019
Context:
- In April, the IMF had that predicted India will grow at a rate of 7.2 per cent in FY20, but recent data indicates a falling GDP growth (4.5 per cent).
- The IMF particularly spoke of the “slow growth in rural incomes, domestic demand (as reflected in a sharp drop in sales of automobiles) and credit from non-banking financial companies (NBFCs)” as plausible causes.
- According to the World Inequality Report 2018, the top 10 per cent of India’s population got 54 per cent of all income while the bottom 50 per cent shared only 15 per cent.
- Low wages and income inequality have led to a fall in demand.
Fundamental equation in macroeconomics:
GDP = C + G + I + (NX)
In other words, four drivers determine a country’s GDP.
These are:
C – the total expenditure (demand) by private individuals
G – the total expenditure (demand) by the Government
I – the total expenditure (demand) on investments made businesses in the country
NX – the net effect of imports and exports
Current status of Indian Economy:
- Indian economy is facing both structural (that is, more long-term issues related to the overall framework of the economy such as the flexibility or inflexibility of labour laws etc.) and cyclical (that is, more short-term issues such as a bad monsoon that disrupts production of food articles etc.) challenges.
- Since the causes are both structural and cyclical, Experts say, arresting this economic slowdown is proving to be so difficult.
Two balance sheets- TBS:
- The two balance sheets are referred to the Indian banks (especially public sector banks or the government-owned banks) and the corporate sector, respectively.
- The balance sheets of Indian banks were burdened by a high proportion of non-performing loans and the balance sheet of corporate were clogged because they had over-borrowed and were unable to pay.
Economic boom 2005-09:
- The origins of India’s TBS is credited to the economic boom that happened between 2005 and 2009.
- This was a period when economic prospects were rosy and the economy was growing at near double-digit growth rates.
- Companies borrowed heavily in the hope of making profits in the future.
- The banks, especially the government-owned ones, too, ignored prudential norms and lent a lot of money to companies in the hope that this would help boost economic growth.
- As it happened, economic prospects collapsed quite sharply after the Global Financial Crisis (GFC) and companies found that their projects were no longer viable.
- The end result was that the companies were left with huge loans they could not pay back in time and the banks were left with huge loans that had turned to NPA.
- This meant that neither the Indian companies were in position to invest nor were the Indian banks in a position to lend.
Economic growth 2010-12:
- Economy continue to grow faster between 2010 and 2012 9% to 10% in the succeeding years (2010 and 2011).
- Between 2009 and 2013, companies were in no position to invest. So the “I” (total expenditure (demand) on investments made businesses in the country )component became weak.
- During this period There was a hit to India’s exports because of a decline in global demand. So “NX” component also weakened.
- But unlike in the developed world, where such companies would have been declared bankrupt and liquidated, in India, both the companies and the banks survived.
- Why? Because most of the struggling banks were owned by the government and so there was no risk associated with them because it was always believed that the government would bail them out.
- Most companies survived because banks took a call that giving these companies more time will help the companies repay and many banks lent new loans to such companies so that these companies stayed afloat.
- Another reason why India continued to grow fast in the immediate aftermath of the GFC. That had to do with the robust demand from the other two components – C the total expenditure (demand) by private individuals and G– the total expenditure (demand) by the Government . In particular, private consumer demand — which is quite weak these days
Economy going from 2014 to 2018
- Even though the TBS problem remained unsolved – in other words, the bank NPAs continued to climb and share of debt-ridden companies unable to pay interest payments continued to rise – yet, due to sharp fall in crude oil prices, Indians experienced an income boost.
- During 2015 and 2016, international crude oil prices fell to a third of what they were in 2014. This essentially meant that Indians could spend more and the “C” component of the equation boosted the GDP. Experts claim this gave a 1 to 1.5 percentage point boost to the GDP.
- 2017 and 2018 saw an uptick in world demand and a real depreciation of the rupee, resulted non-oil export growth rose from -8.6 percent in 2015-16 to 8.9 percent in 2017-18”.the “NX” component helped bump up the GDP growth.
- Increased government spending increased the “G” component
- India’s growth was boosted by a lending spree provided by non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) like IL&FS and DHFL.
- NBFCs took over the leading role of lending to the economy because banks were still struggling with NPAs and were largely unwilling to lend directly to businesses. T
- he credit provided by NBFCs fuelled both private consumption (C) and business investment (I), and through this route fuelled GDP growth.
Connecting the dots:
- Do you think govt shouldn’t bail out Public sector banks during distress?
- Do you think NPA problems of the Banks can be resolved ?
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1) Consider the following statements about the First Global Refugee Forum
- The Forum is jointly hosted by the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) and the government of Switzerland.
- It aims to debate and discuss the response of the world’s countries to the global refugee situation
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements about Indian Culture Portal
- It is a part of the National Virtual Library of India project, funded by the Ministry of Culture
- It is being created and developed by NITI Aayog in collaboration with Indira Gandhi National Open University.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3) Consider the following statements about Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF)
- Money for this fund would be raised through a prescribed percentage of the revenue earned by the telecom licensees.
- The Indian Telegraph (Amendment) Act, 2003 gives statutory status to the fund which is to be utilized exclusively for meeting the Universal Service Obligation.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.4) Global Gender Gap Index is released by which body/organisation?
- World Bank
- International Council of Women
- United Nations Development Programme
- World Economic Forum
Q.5) Consider the following statements about Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI)
- It is a statutory body established under the provisions of the Aadhar Act, 2016
- It functions under the overall guidance of Ministry of Home Affairs
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 17 DEC 2019 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | C |
| 3 | A |
| 4 | C |
MUST READ
Justice for the Rohingya
Time to defend India’s secularism
Bearing the brunt of slack laws
Rationalise, not raise, rates of GST
Protest is legitimate but violence is not
Unfree speech
The cost of food











