IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 3rd December 2019
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
NHRC seeks report on assault cases
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Polity
In News
- Expressing concern over the recent sexual assault cases, NHRC issued notices to the Centre, States and Union Territories seeking reports on the standard operating procedure (SOP) for dealing with such cases and the use of the Nirbhaya Fund.
- The Commission’s action comes in the wake of the gang-rape and murder of a doctor in Hyderabad that has spurred a debate on the condition of women’s security in the country once again
- Taking suomotu cognisance of media reports, the NHRC observed that there was a “dire need for all stakeholders to work jointly to get rid of this evil.”
About National Human Rights Commission (NHRC)
- It is a statutory organization established under the Protection of Human Rights Act (PHRA), 1993.
- It is in conformity with the Paris Principles, adopted at the first international workshop on national institutions for the protection of human rights held in Paris in 1991
- The purpose of the NHRC is, suo moto or through the petition of a person, to investigate the violation of human rights or the failures of the state or other to prevent a human rights violation.
- The commissions may also take on research about human rights, create awareness campaigns through various mediums, and encourage the work of NGOs.
About Nirbhaya Fund
- It was established in 2013 for implementation of initiatives aimed at enhancing the safety and security for women in the country.
- It is a non-lapsable corpus fund, established by Union Finance Ministry
Bill banning e-cigarettes passed
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Health
In News
- A Bill banning the manufacture and sale of electronic cigarettes, but not their possession and use, was passed by Parliament
- The Rajya Sabha passed the Prohibition of Electronic Cigarettes (Production, Manufacture, Import, Export, Transport, Sale, Distribution, Storage and Advertisement) Bill, 2019 by voice vote after four hours of discussion.
- The Bill, which was passed by the Lok Sabha on November 27, will replace an ordinance brought by the government on September 18.
- Opposition MPs, however, alleged that the ban was enacted to benefit tobacco companies.
Do You Know?
- Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) had in June 2019 recommended a complete ban on Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems (ENDS) including e-cigarettes, saying their use can initiate nicotine addiction among non-smokers.
- ENDS, which includes e-cigarettes, Vape and E-Hookah, are devices that heat a solution to create an aerosol, which also frequently contains flavours, usually dissolved into propylene glycol and glycerin
- E-cigarettes adversely affects the cardiovascular system, impairs respiratory immune cell function and airways in a way similar to cigarette smoking and is responsible for severe respiratory disease.
Panel finalises role of Chief of Defence Staff
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains III- Security
In News
- An implementation committee constituted to finalise the responsibilities of the post of Chief of the Defence Staff (yet to be created) has submitted its report
- The government said the post would come within the ambit of the RTI Act
- In his 2019 Independence Day address, Prime Minister Modi announced the creation of the post of Chief of Defence Staff to provide “effective leadership at the top level” to the three wings of the armed forces, and to help improve coordination among them
- The CDS will act as the single-point military adviser to the government on military and strategic issues and oversee procurement, training and logistics
- CDS offers seamless tri-service views and single-point advice to the Executive on long-term defence planning and management, including manpower, equipment and strategy, and above all, “jointsmanship” in operations.
Existing scenario in India:
- India has had a feeble equivalent known as the Chairman, Chiefs of Staff Committee (CoSC); but this is a toothless office, given the manner in which it is structured.
- The senior-most among the three Service Chiefs is appointed to head the CoSC, an office that lapses with the incumbent’s retirement.
Power of Siberia
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains II- International Affairs
In News
- Chinese President Xi Jinping and his Russian counterpart Vladimir Putin remotely inaugurated the “Power of Siberia” gas pipeline
- Russia has been a primary gas supplier to Europe, but the Power of Siberia is the first cross-border gas pipeline between Russia and China, adding a prominent eastern dimension to Moscow’s energy blueprint.
- Under the contract, Russia will deliver 1 trillion cubic meters of natural gas to China over the next 30 years.
- From Siberia to China’s Yangtze River delta in Shanghai, the massive pipeline will cover 8,000 km, with 5,111 km inside China, passing through nine provinces and municipalities.
- A massive cross-border undertaking not only central to China’s energy security but also for bolstering special ties between Beijing and Moscow.
- The 30-year project is anchored by a $400 billion gas deal.
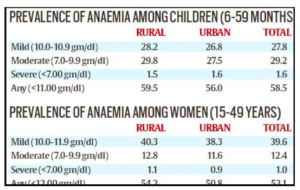
Anaemia: Nearly 3 out of 5 babies and children in India are anaemic
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains II –Health
In News
- As many as 58.5% of children between the ages of 6 months and 59 months, and 53.1% of women between the ages of 15 and 49 years, are anaemic in the country.
- Anaemia means that either the level of red blood cells or the level of haemoglobin is lower than normal.
- When a person has anaemia, their heart has to work harder to pump the quantity of blood needed to get enough oxygen around their body.
- The data, based on the findings of the National Family Health Survey (NFHS) IV (2015-16), divide the incidence of anaemia into ‘Mild’, ‘Moderate’ and ‘Severe’ kinds for both rural and urban India.
- Government had launched in 2018 Anaemia Mukt Bharat (AMB) Strategy under POSHAN Abhiyaan with the aim to reduce anaemia prevalence by three percentage points every year till 2022
- AMB is a 6x6x6 strategy that is targeting six age groups, with six interventions and six institutional mechanisms.
- The six age groups include pre-school children (6-59 months), children (5-9 years), adolescent girls (10-19 years), adolescent boys (10-19 years), women of reproductive age group (15-49), and pregnant women and lactating mothers
Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 3rd December 2019
GANGETIC DOLPHINS
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains III – Environment Conservation
In News
- According to data provided in Rajya Sabha by Ministry of Environment, At last count, the rivers of Assam and Uttar Pradesh respectively had 962 and 1,275 Gangetic dolphins (or Platanistagangetica).
- The International Union for Conservation of Nature has listed the Gangetic dolphin as an endangered species in India.
- According to the WWF, the main threat to the Gangetic dolphin is the creation of dams and irrigation projects.
- In addition to the species being India’s national aquatic animal, the Gangetic dolphin has been notified by the Assam government as the state aquatic animal, too.
- Silting and sand lifting from rivers in Assam has been stopped to maintain its population.
Miscellaneous
China’s facial recognition roll out
- China put into effect new regulations that require Chinese telecom carriers to scan the faces of users registering new mobile phone services.
- This move the government says is aimed at cracking down on fraud.
- China is home to some of the world’s leaders in facial recognition software, including Megvii and SenseTime.
- Supermarkets, subway systems and airports already use facial recognition technology. Alibaba gives customers the option to pay using their face at its Hema supermarket chain.
- Reception by people:Surveillance technologies have encountered little public opposition within China, but there has been some mostly anonymous debate on social media platforms like Weibo
- Some users argue that it is a needed to combat fraud, like scam calls, but others have voiced concerns about its implications for personal data, privacy and ethics.
- Revenue Potential:Countries from Myanmar to Argentina have purchased surveillance technology from the likes of China’s ZTE Corp and Huawei Technologies as part of plans to create “smart cities”
(MAINS FOCUS)
POLITY
TOPIC: General Studies II
- Indian Constitution- historical underpinnings, evolution, features, amendments, significant provisions and basic structure
National Register of Indian Citizens
Context:
- On November 20, 2019 the Union Home Minister, Mr. Amit Shah, answered a starred question in the Rajya Sabha thus: “Preparation of National Register of Indian Citizens (NRIC) is governed by the provisions of Section 14A of The Citizenship Act, 1955 and The Citizenship (Registration of Citizens and Issue of National Identity Cards) Rules 2003. Section 14A of the Citizenship Act, 1955 provides for compulsory registration of every citizen of India and maintenance of NRIC. The procedure to prepare and maintain NRIC is specified in The Citizenship (Registration of Citizens and Issue of National Identity Cards) Rules, 2003.”
Rules that authorise an NRIC
- Rule 11 states that the “Registrar General of Citizen Registration shall cause to maintain the National Register of Indian Citizen in electronic or some other form which shall entail its continuous updating on the basis of extracts from various registers specified under the Registration of Births and Deaths Act, 1969 and the [Citizenship] Act [1955].”
- Rule 4 places the responsibility to carry out a census-like exercise on the Central government and not on citizens. This deals with the “Preparation of the National Register of Indian Citizens” which provides that the Central Government shall carry out a “house-to-house enumeration for collection for particulars related to each family and Individual including the citizenship status”.
- Rule 6 provides that every individual must get himself/herself registered with the Local Registrar of Citizen Registrations during the period of initialisation (the period specified as the start date of the NRIC). Note that this does not begin with a non-obstante clause or words that give it overriding effect over all other clauses. What this means is that this rule is circumscribed by the other clauses in the Act.
Do you know?
NRC :The National Register of Citizens (NRC) is a register maintained by the Government of India containing names & certain relevant information for identification of Indian citizens First started in Assam state of India.
Who are illegal migrants?
- Migration of people into a country in violation of the immigration laws of that country, or the continued residence of people without the legal right to live in that country.
What is the Passport Act?
- The Passport (Entry into India) Act, 1920, was one of the early set of rules made against illegal migrants,
- It empowered the government to make rules requiring persons entering India to be in possession of passports.
- It also granted the government the power to remove from India any person who entered without a passport.
- The concept of “burden of proof” was introduced in Foreigners Act, 1940.
- Section 7 of the Act provided that whenever a question arose with regard to the nationality of a person, the onus of proving that he was not a foreigner lay upon the person.
When was the Foreigners Act made more stringent?
- The legislature enacted the Foreigners Act, 1946, by repealing the 1940 Act.
- It conferred wide powers to deal with all foreigners.
- It empowered the government to make provisions for prohibiting, regulating or restricting the entry of foreigners into India.
- It also restricted the rights enjoyed by foreigners in terms of their stay in the country if any such orders are passed by the authority.
- The 1946 Act empowered the government to take such steps as are necessary, including the use of force for securing compliance with such directions.
- The ‘burden of proof’ lies with the person, and not with the authoritiesis still applicable in all States and Union Territories.
- This has been upheld by a Constitution Bench of the Supreme Court.
What about the Foreigners (Tribunals) Order?
- In 1964 the Foreigners (Tribunals) Order was brought in.
- The tribunal has the authority to decide whether a person is a foreigner within the ambit of the Foreigners Act, 1946.
- The tribunal has powers similar to those of a civil court.
- It gives reasonable opportunity to the person alleged to be a foreigner to produce evidence in support of his case, before passing its order.
- In June this year, the Home Ministry made certain amendments in the Foreigners (Tribunals) Order, 1964.
- It was to empower district magistrates in all States and Union Territories to set up tribunals to decide whether a person staying illegally in India is a foreigner or not.
Why did the IMDT Act fail?
- The Illegal Migrants (Determination by Tribunals) Act, 1983, was also referred to as the IMDT Act.
- It was introduced for the detection and deportation of illegal migrants who had entered India on or after March 25, 1971.
- It was unsuccessful.
- One factor for its failure was that it did not contain any provision on ‘burden of proof’ similar to the Foreigners Act, 1946.
- This put a very heavy burden upon the authorities to establish whether a person is an illegal migrant.
- The result of the IMDT Act was that a number of non-Indians who may have entered Assam after March 25, 1971 without possession of valid documents, continue to reside in Assam.
- Iin the Supreme Court landmark verdict on a petition by Sarbananda Sonowal (now the Chief Minister of Assam), challenging the IMDT Act in 2005 the top court quashed the IMDT Act.
- The verdict also closed all tribunals in Assam functioning under the Act.
- It transferred all pending cases at the IMDT tribunals to the Foreigners Tribunals constituted under the Foreigners (Tribunals) Order, 1964.
- Any person excluded from the National Register of Citizens (NRC) recently concluded in Assam can approach The Foreigners Tribunals, established only in Assam, within 120 days of receiving a certified copy of rejection.
- In other States, a person suspected to be a foreigner is produced before a local court under the Passport Act, 1920, or the Foreigners Act, 1946.
Connecting the dots:
- The NRC mess in Assam should serve as a cautionary tale for a nationwide exercise. Comment.
ECONOMY
TOPIC:General Studies III
- Infrastructure: Energy, Ports, Roads, Airports, Railways etc.
Telecom sector changes (PART 1)
Context:
- The telecommunications sector has grown at a rapid pace with growing demand and increasing competition that has pushed down prices to levels not seen anywhere else in the world.
- The sector is in trouble
- Due to the fast-paced growth in the past and regulation that increased tele-density by pushing down average revenue per user(ARPU) which lead the businesses to work with a single mind focus on consumer acquisition as the base of users increased
- SC ruling on revenue-sharing agreement
- India is faced with the prospect of a telecom monopoly or duopoly.
Background:
- In 1990s
-
- India had merely 7 million telephones with a waiting time of seven to eight years to get a connection. The reason was that the cost of installing a landline telephone was too high and the required average revenue per user (ARPU) just to break even was ₹1,250 per month, which was too high for most Indians at that time.
- Indian telecom grew at a slow pace.
- In 1995,
-
- Wireless telephony was introduced which brought down the capital cost, made telephones affordable in India, brought in private investments.
- The first telecom auctions for private players through “Licence Fee Model”
- The financial bids were unbelievably high which went on to be economically unsustainable.
- Several legal ploys were used to stop the payment against bids, cases multiplied
- In 1999, “Revenue Share Model” was introduced
-
- The installation cost of wireless telephony was less than one-fourth of a landline telephone.
- Low ARPU was no longer a big concern.
- By 2003,
- India had around 300 million telephone lines and the urban market was saturating.
- Airtel, Vodafone and Idea, with their GSM mobile-licence, were the leaders and were happy with the urban market though it was saturating.
- GSM trio resisted reduction in tariffs which was the necessity if the market had to penetrate the rural areas
- 2003-2007
-
- Market grew at a slow pace
- After 2007,
-
- government found ways to give new GSM licences using primarily revenue-share.
- Newcomers, primarily Reliance Communications (RCOM) and Tata Teleservices, dropped tariffs and introduced per-second billing. Others had to follow.
- The market grew quickly to 900 million lines.
- The operators were making decent money, even with lower tariffs.
- India was still using only 2G telephony. Data and Internet was at very low speed;
- 3G telephony was just being introduced and operators were haggling for more 3G spectrum in 900 MHz and 1800 MHz bands.
- The government was periodically conducting auctions since 2010, fetching large spectrum bids.
- After 2013,
-
- Government made available some spectrum in the 2300-2500 MHz band which was not considered suitable for 3G telephony then
- 4G growth
-
- It was in its infancy and there was some concern about technology standards and technology readiness.
- A new company, Reliance Jio, betted on it and won the whole spectrum pan-India through a partner company at a relatively lower price as there was little interest from established operators.
- After 2016,
-
- Jio had to wait four years to get the technology ready and launched the 4G service late in 2016 and caught the imagination of users.
- It made voice calls almost free and offered good quality video on smart handsets at very low tariffs.
- Others did follow suit but paid higher amounts for spectrum in later auctions.
- Jio has been gaining market share since then.
- The older operators have been on the defensive, facing serious erosion in market share and profitability.
- RCOM and Tata Teleservices have been wiped out
- Vodafone and Idea merged to just about survive.
- Airtel, the strongest operator two years back, continues to lose market share and profitability.
- 2019,
-
- SC ruling on revenue-sharing agreement
- Future steps needed from the govt
- Government needs to act, just like it did in 1999.
- The government should not look at the telecom sector primarily as a revenue-earner.
- They could offer the operators payment of principal in instalments and waive off interest and penalties which will limit the government’s taxes and earnings from telecom
- This will help bring back multiple players in telecom services.
- Help India is to reap the benefit of being fully digital
- The money could be better spent by operators to improve today’s average service-quality.
- This would help telecom reach the remotest parts of the country and the service needs to continue to be affordable.
Connecting the dots:
- What are the challenges being faced by the Telecom sector? Discuss.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1) Consider the following statements about Gangetic dolphin
- The International Union for Conservation of Nature has listed the Gangetic dolphin as an endangered species in India.
- The main threat to the Gangetic dolphin is the creation of dams and irrigation projects.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements about Anaemia Mukt Bharat
- It is Strategy under POSHAN Abhiyaan with the aim to reduce anaemia prevalence by three percentage points every year till 2030
- Itis a 6x6x6 strategy that is targeting six age groups, with six interventions and six institutional mechanisms.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3) Consider the following statements about Power of Siberia
- It is the first cross-border gas pipeline between Russia and China
- It is not only central to China’s energy security but also for bolstering special ties between Beijing and Moscow
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.4) Consider the following statements about National Human Rights Commission (NHRC)
- It is a statutory organization established under the Protection of Human Rights Act (PHRA), 1993
- It can investigate the violation of human rights or the failures of the state to prevent a human rights violation only through a petition of a person and cannot take suo moto cases.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.5) Consider the following statements about Chief of Defence Staff (CDS)
- It was created in 2000 post 1999-Kargil conflict.
- The postwill act as the single-point military adviser to the government on military and strategic issues and oversee procurement, training and logistics.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 02 DEC 2019 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | D |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | A |
| 4 | A |
| 5 | A |
MUST READ
Winning the peace: on Gotabaya Rajapaksa’s India visit
Terror in London: on London Bridge knife attack
A GST Revamp to Make it More Effective
Fast and Loose Do Not Gel With Bullet Trains
Supreme Court’s recent judgments reaffirm its role as a vigilant monitor











