IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 14th February 2020
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
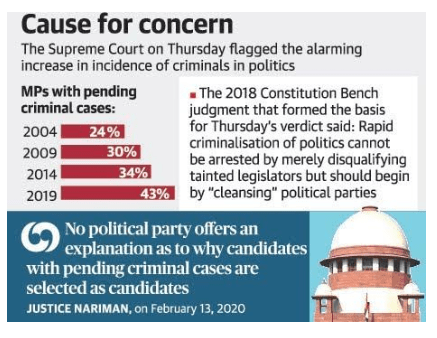
Publish criminal history of candidates, SC orders parties
In news:
- The Supreme Court ordered political parties to publish the entire criminal history of their candidates for the Assembly and Lok Sabha elections
- The information should be detailed and include the nature of the offences, charges framed against him, the court concerned and the case number.
- The information should be published in a local and a national newspaper as well as the parties’ social media handles.
- It should mandatorily be published either within 48 hours of the selection of candidates or less than two weeks before the first date for filing of nominations, whichever is earlier.
- SC also ordered political parties to submit compliance reports with the Election Commission of India within 72 hours or risk contempt of court action.
- This is applicable to parties both at the Central and State levels.
Why ?
- Unimpeded rise of criminals, often facing heinous charges like rape and murder, encroaching into the country’s political and electoral realms.
Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 14th February 2020
Src: The Hindu
https://epaper.thehindu.com/Home/ShareImage?Pictureid=GLI7467DL.1
Govt. notifies medical devices as drugs
In news:
- Health Ministry notified medical devices used on humans as drugs under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act
- Mandatory registration of such devices
- The notification will make companies accountable for quality
- Small manufacturers making low-risk equipment would find it tough to comply with the new rules.
From Prelims Point of View
The Drugs and Cosmetics Act
- The Drugs and Cosmetics Act the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare
- Amendments are related to the Conditions for License / Approval
- The proper name of the drug or fixed dose combination drug shall be printed or written in a conspicuous manner
- The name of the Drug shall be at least two font size larger than the brand name or the trade name
- The brand name or the trade name, if any, shall be written below or after the proper name on the label of the innermost container of the drug or every other covering in which the container is packed
- The first high-speed patrol boat being built for Vietnam under the $100-million Line of Credit (LoC) will be delivered
Background:
- In 2016, India had extended another $500 million defence LoC to Vietnam and discussions are under way to identify the equipment.
- India has also extended a defence LoC to Bangladesh and part of that is also for naval vessels.
IASBaba’s Value Addition:
- Line of Credit is a ‘soft loan’ provided on concessional interest rates to developing countries,
- LOCs helps to promote exports of Indian goods and services,
- The projects under LOCs are spread over different sectors (Agriculture, Infrastructure, Telecom, Railway, Transmission/Power, Renewable Energy etc.).
- The Indian Development Assistance Scheme (IDEAS) (2015) includes provisions to provide better terms of credit, which will be attractive to many developing countries, who are now seeking alternative means of finance.
Trade talks between India -U.S.
In news:
Trade Issues :
- Medical device price caps levied by India,
- a rationalisation of tariffs levied by both sides,
- Greater market access for U.S. agricultural and dairy products.
- Full restoration of GSP (Generalised System of Preferences)
Full restoration of GSP (Generalised System of Preferences is unlikely at present, given the USTR’s notice that aims to treat India and a number of other countries as “developed countries”,
New “health cess” (US) will impact pricing for medical devices, and the raising of tariffs on several items including electric vehicle (EV) components, dairy products, shelled walnuts, edible vegetable oils, infant foods, and soy products may also become an issue
From Prelims Point of View
Generalized System of Preferences (GSP)
- Umbrella that comprises the bulk of preferential schemes granted by industrialized nations to developing countries.
- Reduced Most Favored Nations (MFN) Tariffs or duty-free entry of eligible products exported by beneficiary countries to the markets of donor countries.
- GSP was adopted at UNCTAD in New Delhi in 1968
UNCTAD
- United Nation Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) is a permanent intergovernmental body established by the United Nations General Assembly in 1964.
- It supports developing countries to access the benefits of a globalized economy more fairly and effectively.
Slapping Sec. 144 during CAA protests ‘illegal’: HC
- The HC said the District Magistrate (DM) had failed to give “reasons” in order invoking Section 144
- It is in contravention to the parameters laid down by the Supreme Court in the cases of Anuradha Bhasin Vs Union of India and the Ramlila Maidan Incident Vs Union of India.
From Prelims Point of View
Section 144
- Section 144 of the Criminal Procedure Code (CrPC) of 1973 authorises the Executive Magistrate of any state or territory to issue an order to prohibit the assembly of four or more people in an area
- Every member of such ‘unlawful assembly’ can be booked for engaging in rioting.
- Imposed in urgent cases of nuisance or apprehended danger of some event that has the potential to cause trouble or damage to human life or property.
- Generally prohibits public gathering.
- Maximum punishment for such an act is three years.
- No order under Section 144 shall remain in force for more than two months but the state government can extent the validity for two months and maximum up to six months.
- It can be withdrawn at any point of time if situation becomes normal.
(MAINS FOCUS)
Governance
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- Statutory, regulatory and various quasi-judicial bodies.
Medical Devices (Amendment) Rules, 2020
Context
The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has notified changes in the Medical Devices Rules, 2017 to regulate medical devices on the same lines as drugs under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940
Need for such rules:
- Faulty hip implants by pharma major Johnson & Johnson – where the company agreed in court to pay Rs 25 lakh each to the 67 people who had had to undergo revision surgeries because the implants were defective.
- Government’s lack of regulatory teeth when it came to medical devices.
- Present Penal Provision: Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940- Manufacture or sale of substandard items is punishable with imprisonment of at least 10 years.
- At present, only 23 medical devices have been classified as drugs. In India, most implantable devices are unregulated, including pacemakers, defibrillators, continuous monitoring glucose monitors, etc.
- Inadequate FDI in the sector, as presently, investors shy away from an unpredictable, incomplete and incorrect regulatory environment for medical devices.
Changes in Rules:
- Requirement of online registration of such devices with the Central Licensing Authority through an identified online portal established by the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation for this purpose – generation of registration number
- This registration number should be mentioned on the label of medical device.
- Every medical device, either manufactured in India or imported, will have to have quality assurance before they can be sold anywhere in the country.
- The notification calls for a voluntary registration within a period of 18 months from April 2020
- These rules are applicable to devices intended for internal or external use in the diagnosis, treatment, mitigation or prevention of disease or disorder in human beings or animals
Objective of the rules:
- To regulate all medical devices so that they meet certain standards of quality.
- It will also make medical device companies accountable for quality and safety of their products.
What are the items covered under the Medical Device Rules?
- The devices used for diagnosis, monitoring, treatment, assistance for any injury or disability, investigation, replacement or modification or support of the anatomy or of a physiological process will now come within the scope of the definition of ‘Drugs’
- A large number of commonly used items like hypodermic syringes and needles, cardiac stents, perfusion sets, catheters, orthopaedic implants, bone cements, lenses, sutures, internal prosthetic replacements
- For some items such as sphygmomanometers (used to monitor blood pressure), glucometers (to check blood sugar), thermometers, CT scan and MRI equipment, dialysis and X-ray machines, implants etc, different deadlines for compliance have been set.
Is this a sudden move? – NO
- In April 2019, the Drugs Technical Advisory Board (DTAB) had recommended that all medical devices should be notified as “drugs” under the drug regulation law to ensure they maintain safety and quality standards.
- In October 2019, the Health ministry had circulated copies of the then proposed notification for public comments following recommendations of DTAB
Challenges
- Doubts remain about the ability of the Central Drugs and Standards Control Organisation (CDSCO) to effectively regulate both drugs and medical devices.
- Requiring State Cooperation (State DSCOs) in effectively ensuring the compliance of all firms manufacturing medical devices
- Lack of Patient Safety Medical Devices Law in India
- Need to reduce import dependence of medical equipment- India imports between 70 and 90 per cent of its medical devices.
- The changed rules will impact on the small and marginal players, largely Unorganised in the low-value high volume segment of the medical devices industry. Government should come with schemes to support such small firms (like subsidies on loans)
- Concerns are also raised that the rules are very rigid and any non-conformity can be treated as a criminal offence by any drug inspector under the Act at his discretion.
Did You Know?
- Drugs Technical Advisory Board is a statutory body constituted under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940.
- The function of DTAB is to advise the Central government and State government on technical matters related to drugs and cosmetics.
- As per industry estimates, the Indian medical devices market will grow to USD 50 billion by 2025
- 100% Foreign Direct Investment is permitted in Medical devices through the automatic route
- Medical Device Parks are planned across India, including Andhra Pradesh MedTech Zone Limited (AMTZ), a park in Sultanpur village (Telangana) and HLL Lifecare Mediparks in Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra and Gujarat.
Connecting the dots!
- National List of Essential Medicines
- National Pharmaceutical Authority
- Jan Aashudi Yojana
Society
Topic: General Studies 1:
- Social empowerment
- Salient features of Indian Society, Diversity of India.
Same-Sex Marriage: A marriage story for everyone
Context
A petition filed in the Kerala High Court by a male same-sex couple challenges the constitutionality of the Special Marriage Act on the ground that it discriminates against same-sex couples
The petition seeks logical extension of the rights already recognised by the Supreme Court in Navtej Johar Case
About Special Marriage Act
- It was enacted in 1954 which allows and facilitates the registration of inter-religious marriages.
- It thus acts as a legislative tool for social change, an attempt to remove a social barrier to the exercise of individual autonomy.
Navtej Singh Johar vs Union of India Case. 2018
- Supreme Court in this case decriminalised homosexuality by striking off parts of Section 377 of IPC which were held violative of Fundamental Rights of LGBTQ Community.
- SC upheld the pre-eminence of Constitutional morality in India by observing that equality before law (Article 14) cannot be denied by giving precedence to public or religious morality.
- SC while stating Yogyakarta Principles upheld the right of same-sex couples to express their sexual identity.
- SC also upheld the LGBTQ’s right to privacy and non-interference in the conduct of their personal affairs, and the right to be recognised as full members of society.
Why it is important to recognise marriages of same-sex couples?
- Legal Importance: Marriage carries a range of legal rights and protections, available during the marriage as well as on its dissolution by divorce (the right to seek maintenance) or death (the right to inherit property).
- Social Importance: Marriage continues to be the cornerstone of social legitimacy and family in India. Recognition of same-sex marriages will reduce their marginalisation and lead to wider acceptance in society
- Individual Importance: Marriage, commitment and family are not abstract legal concepts, but stages of human development, aspiration and give meaning to their personal lives.
- Political Importance: Same-sex marriage is recognised in nearly 30 countries across the world. Recognition of same in India will enrich the Democratic culture in India whereby every citizen is treated equally irrespective of their sexual orientation
Conclusion
- The petition in Kerala High Court provides a potential first step towards making marriage, as an institution, as a legal concept, more accessible and egalitarian, less arbitrary and exclusionary.
Value Addition
- Yogyakarta Principles recognize freedom of sexual orientation and gender identity as part of Human Rights.
- They were outlined in 2006 in Yogyakarta, Indonesia by a distinguished group of International Human Right experts.
- After the SC judgement in Navtej Singh Case, provisions of Section 377 remain applicable in cases of non-consensual carnal intercourse with adults, all acts of carnal intercourse with minors, and acts of bestiality
- Naz Foundation vs. Govt. of NCT of Delhi (2009) – Delhi High Court struck off section 377, legalising consensual homosexual activities between adults
- Suresh Kumar Koushal Case (2013) – Supreme Court overturned the Delhi High Court Judgement in Naz Foundation case
Connecting the dots!
- Marital rape and rights of women (Social empowerment)
- Reservation for Transgender
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q1. Consider the following statements :
Most international agencies which find Development Programme in India on intergovernmental bilateral agreements, mainly provide:
- Technical assistance
- Soft loans which are required to be paid back with interest
- Grants, not required to be paid back
- Food assistance to be paid back
Choose the options below
- 2 and 4 are correct
- 1, 2 and 3 are correct
- 1, 2 and 4 are correct
- 3 and 4 are correct
Q 2. Consider the following countries:
- Brazil
- Mexico
- South Africa
According to UNCTAD, which of the above is/are categorized as “Emerging Economies”?
-
- 1 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
ANSWERS FOR 13 FEB 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | C |
Must Read
About Women in Army:
About WEF and the issues associated with it :
About Pakistan’s action on Hafiz Saeed:











