IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 21st February 2020
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
H1N1: MNC tells staff to work from home
Part of: GS Prelims –Sci & Tech and GS-II- Health
In news:
- Multinational company in Bengaluru has given a “work from home” guidance to its employees after two of them tested positive for influenza ‘A’ H1N1
From Prelims Point of View:
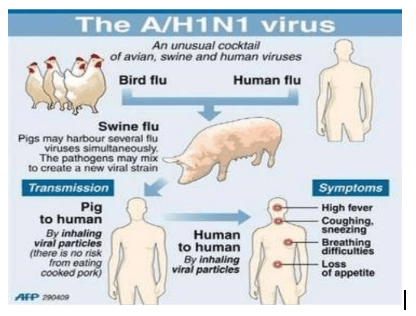
Swine Flu
- Human respiratory infection caused by an influenza strain that started in pigs.
- First recognised in the 1919
- Swine flu is caused by the H1N1 virus strain, which started in pigs.
Symptoms
- Fever, cough, sore throat, chills, weakness and body aches.
Spreads
- Airborne respiratory droplets (coughs or sneezes).
- Skin-to-skin contact (handshakes or hugs)
- Saliva (kissing or shared drinks).
- Touching a contaminated surface (blanket or doorknob)
Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 21st February 2020
‘Bulk of Jharkhand’s deleted ration cards weren’t fake’
Part of: GS Prelims –Polity and GS-II- Vulnerable section
In news:
The randomised control study found
- 90% of ration cards deemed fake and deleted by the Jharkhand government between 2016 and 2018 actually belonged to existing, valid households.
- Almost 56% of these deleted ration cards were not linked with Aadhaar.
- 18 starvation deaths have been reported in Jharkhand due to lack of access to subsidised food, mostly because beneficiaries’ ration cards were not linked to Aadhaar.
Government data
- 5.9% (1.44 lakh) ration cards were deleted out of a total 24.5 lakh cards
- Study found 88%, were found to belong to valid beneficiary families

Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 21st February 2020
From Prelims Point of View:
Randomized controlled trial
- A randomized controlled trial is a type of scientific (often medical) experiment that aims to reduce certain sources of bias when testing the effectiveness of new treatments;
- This is accomplished by randomly allocating subjects to two or more groups, treating them differently, and then comparing them with respect to a measured response.
- One group—the experimental group—has the intervention being assessed, while the other—usually called the control group—has an alternative condition, such as a placebo or no intervention.
- The groups are followed under conditions of the trial design to see how effective the experimental intervention was.
- Treatment efficacy is assessed in comparison to the control. There may be more than one treatment group or more than one control group.
- Back in the late 1990s, this was not a well-known concept, let alone a widely practised research method. Moreover, research in economics was still largely theoretical although the shift in a more empirical direction had already started.
A.R. Rahman’s NGO gets FCRA licence
Part of: GS Prelims –Economy and GS-II- Money laundering
In news:
- The Union government has granted Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA) licence this year to more than 20 non-governmental organisations (NGOs), including the A.R. Rahman Foundation
- Any NGO or association that intends to receive foreign funds has to compulsorily register under the FCRA, monitored by the Union Home Ministry.
- In 2014, the FCRA licences of more than 16,000 NGOs were cancelled
- Under the FCRA Act, registered NGOs can receive foreign contribution for five purposes — social, educational, religious, economic and cultural.

Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 21st February 2020
From Prelims Point of View:
NGOs
- The term ‘NGO’ is used to describe a body that is neither part of a government nor a conventional for-profit business organisations
- Groups of ordinary citizens that are involved in a wide range of activities that may have charitable, social, political, religious or other interests.
- Helpful in implementing government schemes at the grassroots.
- In India, NGOs can be registered under Indian Societies Registration Act, 1860, Religious Endowments Act,1863, Indian Trusts Act, etc.
- India has the largest number of active NGOs in the world,(In 2009, 33 lakh)
- NGOs receive funds from abroad, if they are registered with the Home Ministry under the Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act (FCRA).
Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act (FCRA), 2010
- Implemented by the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- The Acts ensures that the recipients of foreign contributions adhere to the stated purpose for which such contribution has been obtained.
- Under the Act, organisations require to register themselves every five years.
Kashmir journalist wins AFP’s Kate Webb Prize
Part of: GS Prelims –Art & culture
In news:
-
Freelance reporter Ahmer Khan was named the winner of the 2019 Kate Webb Prize
-
For his coverage on the ground in India-controlled Kashmir during Delhi’s lockdown of the region
From Prelims Point of View:
Kate Webb
- New Zealand-born Australian war correspondent
- Earned a reputation for fearless reporting throughout the Vietnam War
- She continued to report from global hotspots including Iraq during the Gulf War.
Vehicle registrations sputter, slide 7% on poor sentiment
Part of: GS Prelims –Polity and GS-II- Policy
In news:
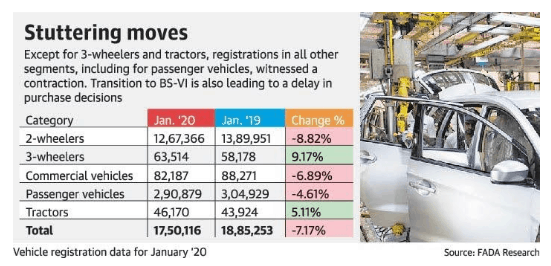
Federation of Automobile Dealers Associations (FADA) reports:
- Automobile sector continued the slow lane in January 2020 total vehicles registrations declining 7.17% year-on-year
Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 21st February 2020
From Prelims Point of view:
Federation of Automobile Dealers Associations (FADA)
- Apex national body representing automobile dealers of India
- Founded in 1964 by four regional Auto Trade associations
- Objectives: To protect and promote the Indian retail automobile market.
- Registered body under the Companies Act 1956.
Vodafone Idea pays ₹1,000 cr. in AGR dues
Part of: GS Prelims –Economy and GS-III- Taxation
In news
- Vodafone Idea paid ₹1,000 crore more to the Department of Telecommunications (DoT)
From Prelims Point of View:
Adjusted Gross Revenue (AGR)
- It is the usage and licensing fee that telecom operators are charged by the Department of Telecommunications (DoT).
- It is divided into spectrum usage charges and licensing fees
Spectrum Usage Charge
- It is the charge that is required to be paid by the licensees providing mobile access services, as a percentage of their Adjusted Gross Revenue (AGR).
- The spectrum slabs/rates for the same are notified by the Government from time to time.
(MAINS FOCUS)
Economy & International Affairs
Topic: General Studies 2,3:
- Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
US-India Trade Deal: Threat to Dairy Sector
Context
During Trumps’s visit to India, these are prospects of Indo-US deal being finalised in specific sectors including dairy sector (with potential of $100 million).
Market access for US dairy products in India may have adverse impact on domestic dairy sector.
Significance of the dairy sector in India’s overall economic scheme
- Rural Livelihoods: 80 million rural households are dependent on Dairy sector for their livelihood
- Largest agricultural commodity- Milk and milk products output is 20.6 per cent of the combined output of paddy, wheat and pulses
- Provides alternative employment: crop production generates employment for the rural workforce for an average of 90-120 days in a year, while dairy sector can provide employment during the remaining period.
- Contribution to National Economy:
-
- While the share of agriculture and allied (A&A) sector in the gross value added (GVA) has consistently declined from 18.2% in 2014 to 17.2% in 2017, the share of livestock to GVA has increased from 4.4 % to 4.9 % during the same period
- Within the A&A sector, among the key livestock products, milk and milk products have the highest share, at around 67.2 per cent in 2017.
Dairy Trade: India and USA
- US is a net exporter in dairy trading, with its share in global exports standing at 4.9 per cent as opposed to an import share of around 2.8 per cent in 2018
- Share of India is minuscule at 0.3 per cent and 0.06 per cent in global dairy exports and imports, respectively, in 2018.
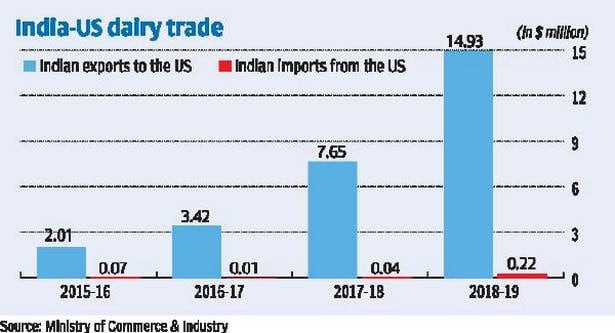
- India’s dairy exports to US have increased by almost seven times from $2.1 million in 2015-16 to $14.9 million in 2018-19. However, India’s imports from US has seen moderate increase from $0.07 million in 2015-16 to $0.22 million in 2018-19
- Thus, India has a trade surplus vis-à-vis USA in dairy sector of nearly $14.41 million in 2018-19
Reasons behind India’s trade surplus with the US in dairy
- India has a comparative advantage in the export of ‘melted butter’ and ‘processed cheese’ to the US because the cost of production of both these products is cheaper in India
- Melted butter’ (ghee) has the largest share in exports to the US at 56%, followed by ‘processed cheese’ (21%), butter (10%), ‘other cheese’ (3.9%), and ‘other fats’ and ‘oils derived from milk’ (3.5%) in 2018-19.
- Lower duties on dairy products in the US help provide a boost to diary exports from India. An average final bound duty on dairy products in the US is around 19 per cent, as against close to 64 per cent in India.
- Cultural and religious sentiments: Indian authorities’ mandatory certification (non-negotiable considering religious sentiments) from the concerned US agency states that “the source animal should not have been fed animal-derived blood meal”. This weeds out significant imports from the US

Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 21st February 2020
Comparison of Indian dairy farmer vs US dairy farmer
- In 2017, India contributed 21% of the world’s milk production, thus making it the largest milk producer in the world.
- This has been made possible by the almost 73 million marginal and landless farmers who directly work in the dairy sector and hold, on average, two milch animals per farmer.
- Indian farmers enjoy favourable terms of trade in the dairy arena, with their share in the consumer price standing at around 60 per cent (highest in the world)
- However, in the US, there are around 0.04 million dairy farmers holding an average of 241 milch animals per farmer. These big farmers only get around 43 per cent of what the consumer pays.
- According to The World Dairy Situation,2019 report, milk yield per cow in the US is the highest in the world, standing at 10,500 kg per cow as against 1,715 kg per cow in India
- Importantly, a dairy farmer in the US is able to sell milk at a price 16.6 per cent above the average world market price, as compared with the similar number standing at 15.6 per cent in India
Implications on India due to Trade deal in dairy sector
- It is evident from the numbers that despite lower milk yield and dominance of small and marginal farmers in dairy activity, India is comfortably placed to produce milk at a cheaper rate
- Thus, opening market access for the sector is likely to place these dairy farmers (largely small & marginal) in a disadvantaged position in relation to the large-scale dairy farmers in US.
- For the Indian dairy industry, the trade deal will not only adversely affect the industry as a whole but also the socio-economic conditions of millions of small, landless and marginal farmers — especially women, who are active in this industry.
- It is likely to temper the sentiments in the rural economy, which is already dealing with a gamut of problems at present
- The deal could play spoil sport in fulfilling the goal of doubling farmers income by 2022
Conclusion
Thus, it will be prudent on the part of Indian authorities to take adequate precautionary measures in proceeding ahead with the trade pact with the US on dairy products
Connecting the dots!
- RCEP and India – Dairy Sector (New Zealand)
- Trade deal in other sectors like manufacturing, financial services etc – implication on India’s domestic economy
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q 1. H1N1 virus is sometimes mentioned in the news with reference to which one of the following diseases?
- AIDS
- Bird flu
- Dengue
- Swine flu
Q 2. Robert Webster is known for his work associated with which one of the following?
- Cardiology
- Influenza virus
- HIV/AIDS
- Alzheimer
Q 3. Which of the following statements with respect to the FCRA (Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act ) 2010 are true ?
- Any person who receives foreign contribution as per provisions of this Act, shall transfer to other person though that person is not authorized to receive foreign contribution as per rules made by the Central Government
- Any organisation of a political nature have been placed in the category prohibited to accept foreign contribution.
- All organizations engaged in social sector implementation of government programmes have been exempted from the provisions of the act.
-
- 2 only
- 2 & 3 only
- 1 & 3 only
- all of the above
ANSWERS FOR 20 FEB 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | A |
| 2 | A |
| 3 | B |
Must Read
About Assistive Reproductive Technology Bill :
About Politics in Turkey :
About Politics in Iran:
About freebies and Welfare measures:











