IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis

IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 8th February 2020
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Pro-militant tweets cited in PSA(Public Safety Act ) file
Part of: GS Prelims –Polity and GS-II- Constitution
In news:
- Former Chief Minister and PDP president Mehbooba Mufti has been booked under Public Safety Act (PSA)
From Prelims Point of View:
- The Public Safety Act (PSA) of Jammu & Kashmir is an administrative detention law
- Act extends to the whole of Jammu & Kashmir.
- Allows detention of any individual for up to two years without a trial or charge.
- Without a warrant, specific charges, and often for an unspecified period of time.
- The detaining authority is not required to reveal any facts “which it considers being against the public interest to disclose”.
- Detention order under the PSA is issued either by the Divisional Commissioner or District Magistrate.
“in the case of a person acting in any manner prejudicial to the security of the state”,
“any person is acting in any manner prejudicial to the maintenance of public order”.
- (2012 Amendment ) the detention of a person below the age of 18 was strictly prohibited under this Act.
- Produced before the magistrate within 24 hours.
- The Advisory Board is a non-judicial body established to review detention orders and determine whether there is sufficient cause for detention.
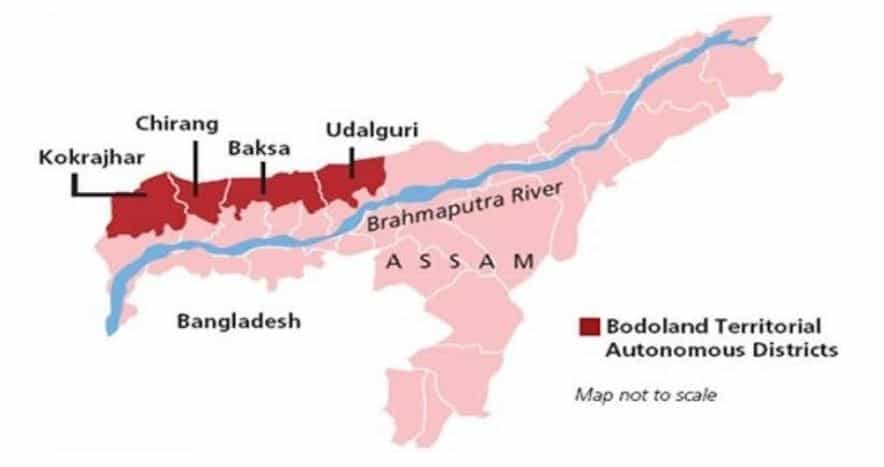
Bodoland Territorial Area District (BTAD)
Part of: GS Prelims –Polity and GS-II- Federalism
In news:
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi advised the youth in central India’s Maoist belt and in Jammu and Kashmir to emulate the Bodos and shun the path of violence.
IASBaba’s Value Additions:
- Recently, the central government, the Assam government and the Bodo groups, signed an agreement to redraw and rename the Bodoland Territorial Area District (BTAD) as the Bodoland Territorial Region (BTR), in Assam.
From Prelims Point of View:
Bodoland Territorial Area District :
- BTAD is spread over four districts of Kokrajhar, Chirang, Baksa and Udalguri.
- The BTAD and other areas mentioned under the Sixth Schedule of the Constitution have been exempted from the Citizenship (Amendment) Act (CAA), 2019.
Bodo:
- The Bodo are a Tibeto-Burmese-speaking ethnic group in Assam.
- Politically active and dominant in the Kokrajhar, Baksa, Udalguri and Chirang districts of the Bodoland autonomous region in the state of Assam.
- The Bodo people speak the Bodo language, a Tibeto-Burman language recognized as one of twenty-two scheduled languages in the Indian Constitution.
- The Bodo people are recognized as a plains tribe in the Sixth Schedule of the Indian Constitution.
- The Bodo people are concentrated within the Assamese districts of Udalguri, Chirang, Baksa, Bajali, Sonitpur, Goalpara, Dhemaji, Lakhimpur, and Kokrajhar.
Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 8thth February 2020
Habitat loss felled leopards
Part of: GS Prelims –Environment and GS-III- Conservation
In news:
- India’s leopard population is only a tenth of what it was over a century ago
- Due to human pressures, conflicts with humans, poaching, habitat loss and availability of prey
- Scientists say that an initiative similar to ‘Project Tiger’ is required
- Decline of 75% to 90% between 120 and 200 years ago,
- Centre for Wildlife Studies & Wildlife Institute of India Reports
From Prelims Point of View:
Project Tiger:
- Project Tiger was launched in Jim Corbett National Park of Uttarakhand in 1973.
- Tiger reserves are governed by the Project Tiger (1973).
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme of the Ministry of Environment and Forests.
- Administered by the National Tiger Conservation Authority.
- Aim: Protect tigers from extinction by ensuring a viable population in their natural habitats.
- Government has set up a Tiger Protection Force under PT to combat poachers.
- PT funds relocation of villagers to minimize human-tiger conflicts.
Bank of India, State Bank cut interest rates:
Part of: GS Prelims –Economy and GS-III- Banking
In news:
- Recently, The State Bank of India (SBI) and the Bank of India (BoI) have reduced their lending rates by cutting the marginal cost of fund-based lending rate (MCLR)
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) announced measures to ease interest rates
From Prelims Point of View:
Marginal cost of fund-based lending rate:
- The minimum interest rate that a bank can lend at.
- MCLR is a tenor-linked internal benchmark, which means the rate is determined internally by the bank depending on the period left for the repayment of a loan.
- It is closely linked to the actual deposit rates and is calculated based on four components: the marginal cost of funds, negative carry on account of cash reserve ratio, operating costs and tenor premium.
- Reserve Bank of India introduced the MCLR methodology for fixing interest rates from 1 April 2016.
- It replaced the base rate structure, which had been in place since July 2010.banks are free to offer all categories of loans on fixed or floating interest rates.
- The actual lending rates for loans of different categories and tenors are determined by adding the components of spread to MCLR.
- Therefore, the bank cannot lend at a rate lower than MCLR of a particular maturity, for all loans linked to that benchmark.
(MAINS FOCUS)
Indian Foreign (Trade) Policy
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
Topic: General Studies 3
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
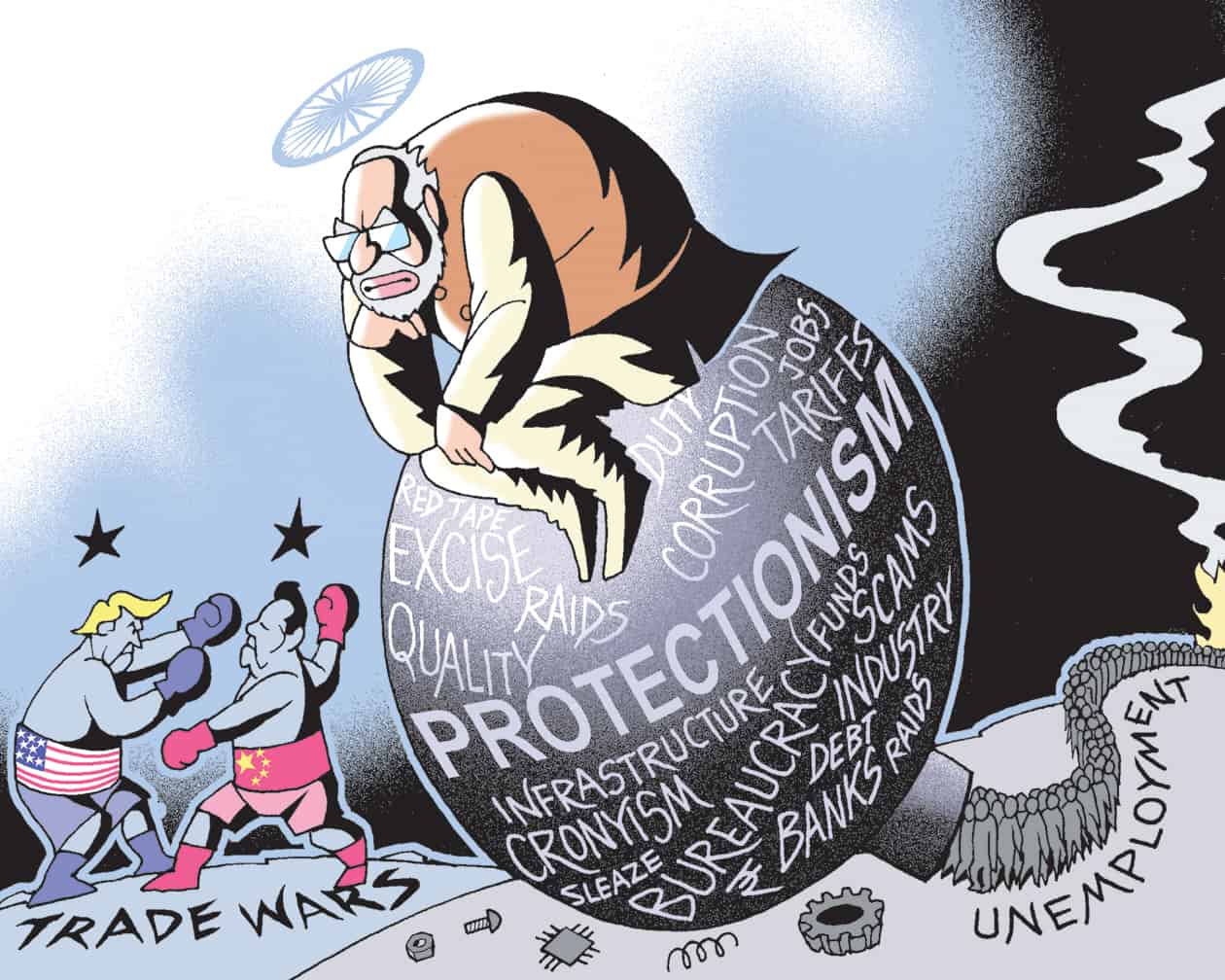
Protectionism: In an economically interconnected and technologically inseparable world
Context
India’s international trade posture has appeared to turn protectionist with recent actions by the Indian government
What events has led to the perception for rising Protectionism in India?
- During the presentation of Union Budget 2020-21, Finance Minister made several references to the problems with free trade and preferential trade agreements (FTAs and PTAs) that pose undue risk to domestic industry
- Government raised tariffs on the import of more than 50 items.
- Changes in Customs Act provisions to penalise imports suspected to originate from third countries, which try to misuse FTA & PTAs
- India declined to attend a meeting of trade negotiators in Bali (February 3-4) that was discussing the next step in the ASEAN led RCEP trade agreement.
- Government’s decision to scrap all bilateral investment treaties with 57 countries and bringing in a new Bilateral Investment treaty (BIT) model in 2015.
Reasons given by India for taking above measures:
- Rise in trade deficits with FTA partner thus the need to revisit the treaties
- The primary motive of rising trade barriers is to protect Indian markets from dumping — primarily by Chinese goods
- Countries (EX: RCEP) unwilling to consider the agreement in Services, that involves migration of professionals, which is India’s strong area
India’s unfinished agenda with regard to Trade treaties
- Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA) being negotiated with Australia since 2011. However, talks hit a dead end in September 2015. With Australia’s focus on RCEP, no progress has been made since then.
- India-UK trade agreement will not able to see the light of the day until UK finalises its Brexit deal with EU
- India- EU Bilateral Trade and Investment Agreement (BTIA) has not made any progress since 2013. India coming up with new BIT model in 2015 by scrapping earlier BITS had made the negotiations harder than before thus delaying the inking of agreement
- India-US FTA- At present there have only been some “non-paper” talks on the issue, and possible take years to fructify given the rising protectionism in US and India alike
- Bilateral trade agreements – India wished to renegotiate its FTA with ASEAN, South Korea and Japan given that these agreements have increased India’s trade deficit with these countries. However, all these Nations will be ready to negotiate only after finalising their RCEP deal which would take couple of years more.
India moving in a direction opposite to that of world
India is currently focusing on inking bilateral trade agreements rather than go for multi-lateral trade treaties (not signing RCEP). However, world is now divided into multilateral regional FTAs which include:
- North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) for North America,
- Southern Common Market (MERCOSUR for its Spanish initials) for South America
- The European Union
- Eurasian Economic Union (Russia and neighbours)
- African Continental Free Trade Agreement (AfCFTA)
- Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) FTA
- RCEP
India is not a member of any of these regional trade agreements. India has also virtually abandoned SAARC. Additionally, world does not favour trade in services the way it does in goods, as most countries have turned migration-averse.
Conclusion
India’s cannot rise in Asia without closer trade links with the East or the backing of South Asia.
Historically, the decline of colonial powers and more ancient empires can be traced to times when they turned inward and disengaged from foreign trade
India thus needs to adopt a more open approach towards global trade.
Did you know?
- Only three countries: Kyrgyzstan, Belarus and most recently Brazil have agreed to sign a new investment treaty based on that model.
- India has trade surpluses with smaller economies, particularly in the neighbourhood, where Indian exports form more than 80% of total trade with Nepal, Bangladesh, Bhutan and Sri Lanka, respectively.
Connecting the dots!
- WTO settlement body decline – India’s avenue to resolve any bilateral disputes reduces
- Impact on rupee value and investment flow due to protectionist measures
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q 1. Which of the following provisions of the Constitution of India have a bearing on Education?
- Directive Principles of State Policy
- Rural and Urban Local Bodies
- Fifth Schedule
- Sixth Schedule
- Seventh Schedule
Select the correct answer using the codes given below :
- 1 and 2 only
- 3, 4 and 5 only
- 1, 2 and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Q 2. The provisions in Fifth Schedule and Sixth Schedule in the Constitution of India are made in order to
- protect the interests of Scheduled Tribes
- determine the boundaries between States
- determine the powers, authority and responsibilities of Panchayats
- protect the interests of all the border States
Q3. What is/are the purpose/purposes of the ‘Marginal Cost of Funds based Lending Rate (MCLR)’ ?
- These guidelines help improve the transparency in the methodology followed by banks for determining the interest rates on advances.
- These guidelines help ensure availability of bank credit at interest rates which are fair to the borrowers as well as the banks
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 07 FEB 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | D |
| 3 | D |
Must Read
About maternity benefits:
About sentencing process:
About Trump’s impeachment victory:











