IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 20th April 2020
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
NBFCs get ₹50,000-cr. liquidity booster
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economy
In News:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has announced a host of measures to provide liquidity support to non-banking financial companies (NBFCs).
- They shall receive ₹50,000 crore worth of liquidity booster.
Key takeaways:
- RBI has also decided to give them certain benefits for loans which are being extended to the commercial real estate sector.
- The RBI has also decided to provide special refinance facility of ₹50,000 crore to NABARD, SIDBI and NHB to enable them to meet sectoral credit needs.
Important value additions:
Reserve Bank of India
- It is India’s central bank, which controls the issue and supply of the Indian rupee.
- RBI is the regulator of entire Banking in India.
- RBI plays an important part in the Development Strategy of the Government of India.
- RBI was set up in 1935 under the Reserve Bank of India Act,1934.
Non-Banking Financial Company
- It is a financial institution that does not have a full banking license or is not supervised by a national or international banking regulatory agency.
- The most important difference between non-banking financial companies and banks is that NBFCs don’t take demand deposits.
National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD)
- It is an Apex Development Financial Institution in India.
- It deals with matters concerning Policy Planning and Operations in the field of credit for Agriculture and other Economic activities in Rural areas in India.
- It is active in developing Financial Inclusion policy.
- It was established on the recommendations of B.Sivaramman Committee, on 12 July 1982.
Small industrial Development Bank of India (SIDBI)
- It is a development financial institution in India.
- It serves as the principal financial institution in the Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) sector.
- It was established on April 2, 1990, through an Act of Parliament.
- It is headquartered in Lucknow.
- It operates under the Department of Financial Services, Government of India.
National Housing Bank (NHB)
- It is a Government of India owned entity.
- It was set up on 9 July 1988 under the National Housing Bank Act, 1987.
- It is an apex financial institution for housing.
Government approval mandatory for FDI from neighbouring countries
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations & GS-III – Investment
In News:
- In order to restrict Chinese investments, prior government approval has been made mandatory for foreign direct investments (FDI) from countries which share a land border with India.
Key takeaways:
- Revised FDI policy has stated that entities from countries which share a land border with India will now be permitted to invest only under approval route.
- Previously, only investments from Pakistan and Bangladesh faced such restrictions.
- The revised FDI policy is aimed at preventing opportunistic takeovers/acquisitions of Indian companies due to the current COVID-19 pandemic.
- The rules shall apply to fresh as well as existing FDI.
- Transfer of ownership of any existing or future FDI where the direct or indirect beneficiary is from these countries will also require government approval.
- This restriction will also apply if the beneficial owner of the investment is an entity situated in or a citizen of such countries.
Important value additions:
India’s FDI policy
- A foreign direct investment (FDI) is an investment in the form of a controlling ownership in a business in one country by an entity based in another country.
- India’s FDI policy allows foreign investment in certain sectors under the automatic route.
- 100% FDI is permitted under the automatic route in manufacturing, oil and gas, greenfield airports, construction, railway infrastructure etc.
- In other sectors, FDI is allowed under the automatic route upto a certain threshold, say 26% or 49%.
- Such conditions apply to defence, broadcast and print media, aviation and other sectors.
- There is also a list of prohibited sectors, such as lottery, cigarettes, atomic energy where FDI is not permitted.
India’s neighbouring countries
- India shares a land border with:
- China
- Pakistan
- Bangladesh
- Nepal
- Myanmar
- Bhutan
- Afghanistan
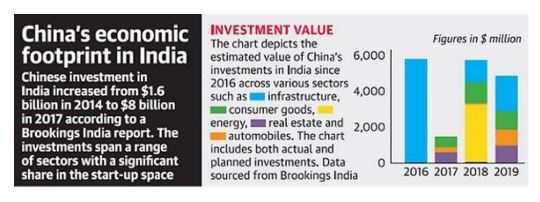
Government approval mandatory for FDI from neighbouring countries
Image Source – Click here
Miscellaneous
Kisan Rath mobile application launched
- Ministry of Agriculture recently launched Kisan Rath Mobile App to facilitate transportation of foodgrains and perishables during lockdown.
- This is developed by the National Informatics Centre.
- This app shall facilitate farmers and traders in searching transport vehicles for movement of agricultural and horticultural produce.
- It will also help farmers and traders for transporting produce from farm gate to mandi and mandi to mandi all over the country.
- The App will also facilitate traders in transportation of perishable commodities by Refrigerated vehicles.
- It is ready for pan-India use with the app being available in eight Indian languages.
- National Informatics Centre (NIC) is an attached office under Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), Government of India.
(MAINS FOCUS)
GOVERNANCE/ ECONOMY/ ETHICS
Topic: General Studies 3:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- Behavioural Economics
COVID-19: Need for a Social Vaccine
What is a social vaccine?
- A social vaccine is a metaphor for a series of social and behavioural measures that governments can use to raise public consciousness about unhealthy situations through social mobilisation
- A social vaccine addresses barriers and facilitators of behaviour change, whether attitudinal, social, cultural, or economic.
- Social Vaccine supplements information, education, and communication (IEC) with targeted social and behaviour change communication (SBCC) strategies.
Advantages of Social Vaccine achieved through Social Mobilization
- Empowers populations to resist unhealthy practices
- Increase resilience
- Foster advocacy for change
- Drive political will to take action in the interests of society
- Hold governments accountable
Lessons from HIV (Human immunodeficiency virus) Pandemic
- HIV that causes AIDS is believed to have made the zoonotic jump from monkeys through chimpanzees to humans in Africa as early as the 1920s
- However, the HIV/AIDS epidemic was detected in 1981 & was a pandemic by 1985.
- Extent of Pandemic: From 1981 to 2018, around 74.9 million people worldwide were HIV-infected, and around 32.0 million died from AIDS-related illnesses.
- Social vaccine helped “flatten the curve” till effective treatments were discovered that dramatically reduced mortality, viral loads and infection transmission.
How Social Vaccine was used in HIV/AIDS pandemic?
- There were widespread information campaigns stating that infection occurred predominantly through sexual transmission and intravenous drug use.
- IEC and SBCC activities targeted (and partnered) individuals, community networks, leaders, social & health systems to change attitudes and behaviours.
- The core preventive messages involved
- Being faithful to one sexual partner
- 100% condom use during sexual intercourse outside stable relationships
- Resisting peer-pressure for risky behaviours like intravenous drug use
- Religious and community leaders were key change agents
- For example, the Catholic Church in Uganda did not initially support promoting condoms since its use prevents life.
- However, later they acknowledged that their religion did not preclude the use of condoms to prevent deaths – which was an important turning point
How Social Vaccine can be adapted for current pandemic?
- Effective IEC and SBCC strategies should contain the persuasive messages of
- Maintaining physical distancing in social situations
- Wearing cloth masks in public by 100% of people (and 100% of the time)
- Regular disinfection of oneself and one’s surroundings.
- Leading by Example: People are more likely to practise these behaviours if all leaders promote them publicly and consistently
- Proper information, support, and materials should be made available and accessible.
- Re-purposing and funding relevant industries and small and medium businesses to produce materials such as PPE, hand sanitisers and medical equipment
Challenges Ahead
- The components of the social vaccine should be in place before relaxing or lifting the lockdown.
- A social vaccine also requires people to hold leaders accountable to
-
- Invest in rapidly scaling-up testing
- Meet the basic and economic needs of vulnerable sections
- Providing psychological support where needed
- Not communalising or politicising the pandemic
- Not compromising the privacy and dignity of infected individuals and their families in the interest of public health
Connecting the dots:
- Persuasive VS Coercive methods – which is better suited for India? And why?
- Nudge Economics – Example: Give It Up Campaign, Swachh Bharat Mission
INTERNATIONAL/ POLITY
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests
- Comparison of the Indian constitutional scheme with that of other countries.
China’s one party system vs Democracy
Context: Critics blame China for unleashing COVID-19 across the world through the lack of transparency inherent in its one-party authoritarian system.
In order to counter this negative perception, China has unleashed a sustained propaganda campaign that is based on two aspects
- Superiority of Authoritarian System vis-à-vis Democracy
- Chinese system was able to arrest the pandemic within the country through drastic measures on a massive scale (Ex: Lockdown of Wuhan)
- China’s strategy was successful than ineffective measures taken in Democratic countries especially in USA
- Benevolence of China
- China wants to garner goodwill by providing much-needed medical equipment and medical teams to assist affected countries
- The recipients have often been “persuaded” to express praise for China.
What is the Chinese view on the Pandemic?
- The COVID-19 virus did erupt in Wuhan, but it may not have originated in China
- The delay in acknowledging the seriousness of the crisis was due to missteps by the local leadership in Wuhan city and Hubei province
- Once the gravity of the situation was recognised, Chinese leaders promptly informed the WHO and shared the DNA sequence of the virus.
- The unprecedented measures adopted by Chinese authorities imposed great suffering on the Chinese people but bought valuable time for the rest of the world to get prepared to deal with the pandemic.
- China’s economy is beginning to recover and this will contribute to the recovery of the global economy.
- All these reinforces the merits of China’s political System (One-Party rule)
Is China’s one-party system better compared to democracies?
Not necessarily, this is because
- COVID-19 may not have become a pandemic if China were a democracy with a free flow of information through an independent media and accountable political leadership
- There are democracies which have done well to contain the Epidemic Ex: Taiwan, South Korea, Japan, India
- Criticism of China’s assistance being defective and low-quality
- Criticism from African Countries against harsh China’s actions as there were reports from Guangzhou(China) on racial discrimination against stranded African students
- The result of being a democracy is that we have a better chance of
- Knowing the true dimensions of the crisis i.e. Transparency of government functioning
- Being able to obtain constant feedback on people’s reactions
- Access the best advice from multiple sources.
Conclusion
Beijing’s response to Covid underlines that the world needs more democracy, not less
Connecting the dots:
- China’s Economic Model
- COVID-19’s impact on Global Political and Economic Structure
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Consider the following statements regarding Kisan Rath App:
- Kisan Rath App has been launched by Ministry of Agriculture.
- It will facilitate farmers in searching the transport vehicles for their produce.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 Consider the following statements with regards to financial institutions:
- National housing Bank is an apex financial institution for housing.
- The most important difference between non-banking financial companies and banks is that NBFCs don’t give loans.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 India shares a land border with which of the following countries?
- Bangladesh
- Myanmar
- Bhutan
- Afghanistan
Select the correct code:
- 1 and 2 only
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q.4 Consider the following statements regarding Foreign Direct Investment:
- 100% FDI is permitted under the automatic route in oil and gas.
- FDI is completely prohibited in atomic energy sector.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 18th April 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | A |
| 2 | D |
| 3 | B |
| 4 | C |
Must Read
About convalescent plasma to fight COVID-19:
About impact of lockdown on Economy:
About Communalization and COVID-19 crisis:













