The Big Picture- RSTV, UPSC Articles
SERO-SURVEY
Archives
TOPIC: General Studies 2
- Response to COVID-19 Crisis
In News: The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare have decided to conduct a population-based ‘sero survey’ in select districts of the country with an aim to monitor the trend in the prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 virus which causes the Covid-19 disease. The move was announced after the death toll due to COVID-19 rose to 2,293 and the total number of cases climbed to 70,756 in the country
The survey will be coordinated by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR’s) National Institute of Epidemiology (NIE) and National Institute of Research in Tuberculosis (NIRT), Chennai.
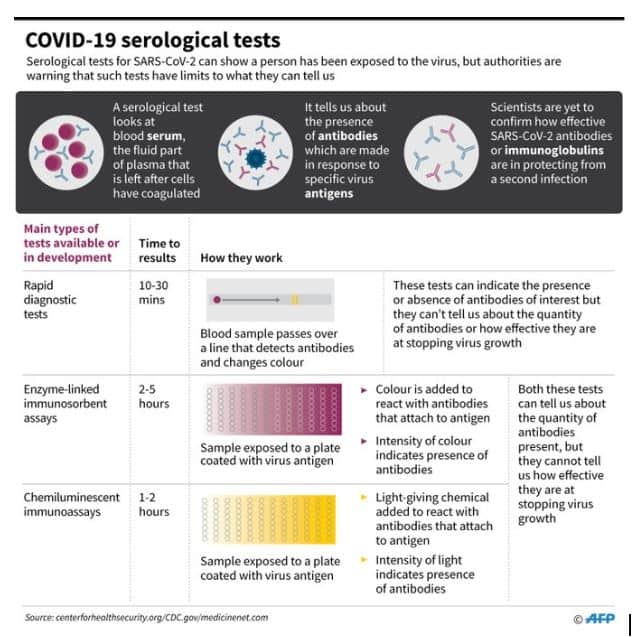
What is sero-survey?
A serosurvey involves testing of blood serum of a group of individuals to determine the presence of antibodies against that infection. The facility-oriented surveillance is an expansion of the testing of flu and serious respiratory cases in hospitals being carried out by the government.
Why sero-testing?
There is a need to establish systematic surveillance for SARS-CoV-2 infection in all districts of the country. This surveillance will be in addition to the routine testing as per current testing guidelines
- To help determine the burden of infection at the community level
- To monitor the trends in its transmission and help generate evidence on role of asymptomatic and mild infections in transmission.
- Check for community transmission in any part of the country
The outcomes will help in designing and implementing suitable Coronavirus containment measures.
There is no evidence yet of community transmission in the country. There are large outbreaks in some clusters but the sharp exponential rise in cases as in community transmission has not happened.
How does the survey work?
A sero-survey involves testing of blood serum of a group of individuals to determine the presence of antibodies against that infection. People from Red, Orange and Green zones in a district will be tested for COVID-19 at random to check if they have developed antibodies against the infection even though they are asymptomatic or show mild symptoms.
The survey will involve collection of venous blood samples from 400 randomly selected individuals (one per household) from 10 clusters in each selected district, divided into low risk and high risk groups.
- The survey will be conducted at 10 health facilities (six public and four private), testing outpatient attendees and pregnant women (constituting the low-risk group), and frontline healthcare workers (constituting high-risk population).
- At least 100 samples of healthcare workers from selected districts will be tested per week (400 per month). Besides, 50 samples each of the outpatient attendees and pregnant women will be collected per week (200 per month). Throat and nasal swabs will be collected for RT-PCR tests and samples should be tested in a one-time pool of 25.
- In addition to throat/nasal swabs, blood samples should be collected for detecting Immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies for ELISA testing. In subsequent rounds, IgG ELISA-based testing of serum samples will replace RT-PCR based testing for surveillance purpose.
- Data on demographic characteristics will be collected on a specifically designed standard data collection form. The data will be analysed locally for action using standard indicator formats. Indicators for person, place, time and trend analysis will be made.
Post the survey –
- Data on demographic characteristics will be collected on a specifically designed standard data collection form.
- The data will be analyzed locally for action using standard indicator formats.
- Indicators for person, place, time and trend analysis will be made.
Connecting the Dots:
- Demographic and Health Survey (DHS) framework to ascertain the prevalence of COVID-19