IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 3rd June 2020
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) takes suo motu cognisance of migrants’ plight
Part of: GS-Prelims and GS-II – Statutory Bodies
In News:
- Recently, The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) issued notices to the Union Home Ministry, the Railway Board and the Bihar and Gujarat governments.
- The notices were in connection with the reported deaths of some migrant workers on Shramik Special trains and the lack of food and water for the passengers on these trains.
- NHRC took suo motu (on its own) cognisance of media reports about the trains starting late and taking many days to reach destinations.
Important value additions
National Human Rights Commission (NHRC)
- It is a statutory body.
- NHRC was established on 12th October, 1993 under the Protection of Human Rights Act (PHRA), 1993.
- The Act also provides for the creation of the State Human Rights Commission as well.
- The NHRC is an embodiment of India’s concern for the promotion and protection of human rights.
- The commission is a multi-member body consisting of a chairman and five members.
- The chairperson is a retired chief justice of India or a judge of the Supreme Court.
- They are appointed by the President on the recommendations of a six-member committee consisting of:
- Prime Minister (head)
- Speaker of the Lok Sabha
- Deputy Chairman of the Rajya Sabha
- Leaders of the Opposition in both the Houses of Parliament
- Union Home Minister.
- They hold office for a term of three years or until they attain the age of 70 years, whichever is earlier.
- The President can remove them from the office under specific circumstances.
Asian Development Bank (ADB) and India sign $177 million loan for Maharashtra roads
Part of: GS-Prelims and GS-II – Global Groupings & GS-III – Infrastructure (Roads)
In News:
- The Asian Development Bank (ADB) and the Indian Government recently signed a $177 million loan to upgrade state highways and major district roads in the state of Maharashtra.
Key takeaways
- The project will improve connectivity between rural areas and urban centers in the state.
- It will enable rural communities to better access markets, employment opportunities and services.
- Mobility will improve.
- It will expand development and livelihood opportunities to second-tier cities and towns which will lead to reduction in income disparities.
- It will also strengthen road safety measures by developing a road safety audit framework that will protect vulnerable groups such as the elderly, women, and children.
- Another feature is to update road maintenance system by encouraging 5-year performance-based maintenance obligations to contractors.
Important value additions
Asian Development Bank (ADB)
- It is a regional development bank.
- It was established on 19 December 1966.
- Headquarters: Mandaluyong, Philippines.
- It was established to promote social and economic development in Asia.
- Motto: ADB is committed to achieving a prosperous, inclusive, resilient and sustainable Asia & the Pacific, while sustaining its efforts to eradicate extreme poverty.
- It offers hard loans (currency) on commercial terms primarily to middle income countries in Asia and
- It provides soft loans (loan with a below-market rate of interest) to poorer countries in the region.
- Both types of loans are sourced from the bank’s ordinary capital resources (OCR).
- Five largest borrowing countries are China, India, Pakistan, Indonesia and Bangladesh.
Bodoland University develops fungal powder to boost immunity
Part of: GS-Prelims and GS-III – Biotechnology
In News:
- Bodoland University has said that it has developed a fungal powder to help people boost their immunity to disease.
- The powder is from a parasitic but rare “super mushroom” called Cordyceps militaris.
- A potent pinch of C. militaris was powdered through lyophilisation or freeze-drying at – 80°C.
Important value additions
Cordyceps
- The earth has more than 400 species of Cordyceps.
- It is a fungus parasitic on insects as well as other fungi.
- It is often referred to as a super mushroom.
- It is known for its anti-ageing, anti-viral, energy and immunity-boosting effect.
- Cordyceps militaris is spread throughout the northern hemisphere.

Image source: Click here
Miscellaneous
A3i coronavirus type
- Scientists at multiple CSIR laboratories have identified a coronavirus type – A3i – that may be the second most prevalent in India and may comprise 3.5% of the genomes globally.
- The most dominant coronavirus type in India is the A2a.
- There are 11 SARS-CoV-2 types identified globally with at least 6 of them identified in India.
Cyclone Nisarga
- It is headed towards the coastline of north Maharashtra and south Gujarat on the western coast of India.
- In strength and intensity, it would be much weaker than Cyclone Amphan that struck recently and passed through West Bengal on its way to Bangladesh.
- Cyclones formed in the Bay of Bengal side more frequent and stronger than those on the Arabian Sea side.
- The relatively cold waters of the Arabian Sea are main cause of less cyclones in the sea.
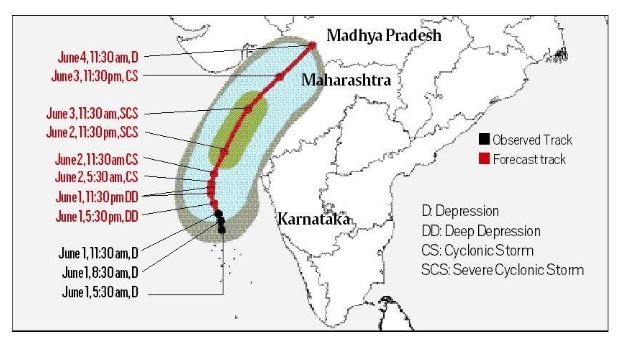
Image source: Click here
(MAINS FOCUS)
GOVERNANCE/ SECURITY
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- Important aspects of governance (Law & order)
The challenge of law enforcement post-COVID-19
Context: The COVID-19 has impacted the Policing and has given new challenges in short term
Law Enforcement during Pandemic times
- Essential: In a society struck by a deadly virus, strict maintenance of public order is most essential. Police ensured strict observance of guidelines, including physical distancing norms which reduced the disease spread.
- Criticality: Law enforcement was considered next only to healthcare in its critical function of preventing disease spread.
- Public cooperation during the pandemic helped the police to overcome the challenges of manpower and mobility.
- Use of Social Media: Police skilfully used social media to disseminate all relevant information to a majority of the population, both in urban and rural areas.
- Overall drop in crime: Zero Traffic on major highways lead to sharp reduction in traffic accidents & fatalities. Delhi Police reported a 70% fall in heinous crimes (murders and rapes) between April 1 and 15 compared to the same period last year.
- Uptick in domestic violence: The Tamil Nadu Police, for instance, reportedly received 2,963 calls on domestic violence in April 2020 alone
What are the possible reasons for increase in domestic violence?
There are two major factors for this rise.
- Most men were at home, either without work on in fear of losing their jobs. Data show that domestic violence increases when there is greater unemployment.
- The second reason is the non-availability of liquor during the lockdown period, which caused frustration among those men who are habituated to drinking.
- There was a similar increase in sexual and gender-based violence in West Africa during the 2013-16 Ebola outbreak
What will be the challenges for Police in Post-COVID time?
- New dangers of Organised Crime: Due to restrictions across borders, crime gangs innovate to adapt to changing nature of illicit market. They may infiltrate health services and make profits through the sale of tightly regulated drugs
- Rise in Cyber Crime: Various fake portals have been launched to get people to donate money for the cause of combating COVID-19
- Low quality Products: Police will also have the responsibility to curb large-scale manufacture of ineffective masks and hand sanitizers.
- Issue of Prisoners: One of the major challenge will be keeping prisons free of the virus given the scenario of overcrowded prisons in India.
Way Ahead
- Government has to draft a comprehensive Standard Operating Procedure by keeping COVID-19 in perspective since the virus is here to stay for atleast a year.
- Supreme Court has directed the States to constitute high-powered committees to consider releasing convicts who have been jailed up to seven years on parole, in order to decongest prisons.
- Public Cooperation experienced during the pandemic has to become the building block for future police-public relations
Connecting the dots:
- Police reforms – Prakash Singh Case
- 2nd ARC
FEDERALISM / GOVERNANCE/ ECONOMY
Topic: General Studies 2,3:
- Issues and challenges pertaining to the federal structure, devolution of powers
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources
Federalism: State’s Borrowing conditions altered
Context: SpaceX’s The Centre increased the borrowing limit of states to 5% of gross state domestic product (GSDP) in 2020-21 from 3%. However, incremental borrowing beyond 3.5% of GSDP will be linked to reforms undertaken by the states.
Did You Know?
- States borrowing relaxation was the fifth and final tranche of the Centre’s Rs 20 lakh crore economic stimulus package.
- The Centre has already hiked its planned borrowing for 2020-21 by 54% to Rs 12 lakh crore from Rs 7.8 lakh crore estimated earlier for Covid-19-related emergencies
- Total net borrowing by states for 2020-21 stood at Rs 6.41 lakh crore, based on 3% of GSDP
What are the conditions insisted by Centre to avail the increased borrowing limit?
- Of the additional borrowing, the first 0.5% will be unconditional,
- The next 1% will be in four equal tranches, each linked to clearly specified, measurable and feasible reform action.
- The remaining 0.5% will be given if milestones are achieved in at least three out of four reform areas which are
- Universalisation of ‘One Nation, One Ration card’(ONOR) Scheme
- Improvements in Ease of doing business
- Power distribution reforms: States to bring down the aggregate technical and commercial (AT&C) losses and narrow the gap between average cost and average revenues.
- Urban Local Bodies – Empowering them with more resources
How does the enhanced borrowing limit help States?
- Availability of Additional Capital: This move that will make an additional Rs 4.28 lakh crore available to States
- Addresses Revenue Shortfall: Enhancement of borrowing limit will help to absorb the expected plunge in States’ revenue receipts.
- Avoid Cut in Capital Expenditure: Due to fixed expenditure on salaries & pensions and on politically sensitive issues like subsidies, a reduction in revenue will eventually lead to cut in infrastructure creation that is not good in long term
- Helps plug the shortfall in Centre’s Devolution: The budgeted Rs 7.8 lakh crore of devolution for FY21 could end up closer to Rs 5 lakh crore, since the Centre’s Rs 24.2 lakh crore target will not be met
- Conditions being insisted upon are more in the nature of reforms
-
- Power Sector: Despite UDAY scheme, States did not reform. As a result, currently state electricity boards (SEBs/discoms) owe power-generating firms about Rs 90,000 crore.
- Local Governance: Conditions like those on property tax will only help urban local bodies function better since their finances will improve as a result.
- Migrants: ONOR Scheme and installing PoS machines at Fair Price Shops will ultimately benefit the local population as well as migrants
- Investment: Condition on ease of doing business norms and the business environment will help attract investment.
Criticism of the measure
- States have alleged that it is unfair for the Centre to set conditions on them in these difficult times.
- The central government penchant to levy ‘cesses’ instead of straightforward taxes in many areas means less has to be shared with the states under the finance commission formula. This has also partly led to inadequate resources with States.
- Hence, going forward Centre should reduce its focus on cesses
Connecting the dots:
- Devolution of powers (legislative, executive, financial)
- Sarkaria Commission and Punchhi Commission
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Consider the following statements regarding National Human Rights Commission:
- It is a statutory body formed under the Protection of Human Rights Act, 1993.
- The chairperson of the commission should be a retired Chief Justice of India or a judge of the supreme court
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 Where is the headquarter of Asian Development Bank located?
- Philippines
- China
- Singapore
- Malaysia
Q.3 Recently, Bodoland University has developed a fungal powder to boost immunity using super mushroom of the genus Cordyceps. Consider the following regarding Cordyceps:
- It is a fungus which parasitizes bacteria.
- It is known for its ant-aging and anti-viral effects also
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.4 Cyclone Nisarga is headed towards the coastline of which of the following state of India?
- Maharashtra
- Gujarat
- Both a and b
- Andhra Pradesh
ANSWERS FOR 2nd June 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | B |
| 2 | A |
| 3 | C |
| 4 | C |
Must Read
About George Floyd incident and Civil protest happening in USA:
About Central Vista Project:
About Monsoons and IMD’s Weather forecast:












