IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 4th June 2020
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
15 MPs nominated to the Delimitation Commission by the Lok Sabha Speaker
Part of: GS-Prelims and GS-II – Statutory Bodies; Indian Constitution
In News:
- Lok Sabha Speaker recently nominated 15 MPs from Jammu and Kashmir, Assam, Manipur, Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh to assist the Delimitation Commission in redrawing the Lok Sabha and the Assembly constituencies of the northeastern States and the Union Territory of J&K.
Important value additions
The Delimitation Commission
- It is appointed by the President of India.
- It works in collaboration with the Election Commission of India
- It means the act or process of fixing limits or boundaries of territorial constituencies in a country to represent changes in population.
- The Delimitation Commission Act was enacted in 1952.
- It is usually composed of the retired Supreme Court judge, Chief Election Commissioner and Respective State Election Commissioners.
- Objectives:
- To provide equal representation to equal segments of a population.
- Fair division of geographical areas so that one political party doesn’t have an advantage over others in an election.
- Functions:
- It determines the number and boundaries of constituencies to make the population of all constituencies nearly equal.
- It also identifies the seats reserved for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes.
- Its orders have the force of law and cannot be called in question before any court.
- The 84th Amendment Act of 2001 extended the ban on readjustment for another 25 years (2026). Earlier it was till year 2000 only.
- The 87th Amendment Act of 2003 provided for the delimitation of constituencies on the basis of the 2001 census and not 1991 census.
GDP growth slows to an 11-year low of 4.2%
Part of: GS-Prelims and GS-III – Economy
In News:
- According to data released by the National Statistical Office, economic growth slowed to an 11-year low of 4.2% in 2019-20.
- In the final quarter of the year (January-March, 2020) the growth rate of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) fell to 3.1%.
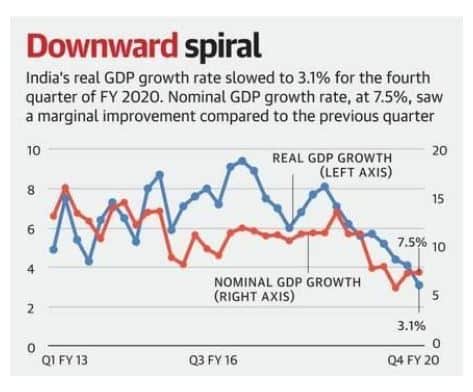
Image source: The Hindu
Important value additions
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
- It is a measure of economic activity in a country.
- It is the total value of a country’s annual output of goods and services.
- GDP = Private consumption + Gross investment + Government investment + Government spending + (exports-imports)
Nominal GDP
- It is GDP evaluated at current market prices taking into account current inflation or deflation.
Real GDP
- It is calculated in a way such that goods and services are evaluated at some constant set of prices.
The National Statistical Office (NSO)
- It is the central statistical agency of the Government mandated under the Statistical Services Act, 1980.
- It comes under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation.
- It provides statistical information services so that the Government can formulate better policies.
- The services include collecting, compiling and disseminating official statistical information.
G-7 Summit gets postponed
Part of: GS-Prelims and GS-II – Global Groupings
In News:
- Recently, G-7 Summit was postponed by the US President citing the Covid-19 pandemic.
- He also expressed his desire to expand the Group to G10 or G11, where he wanted to include India, Russia, Australia and South Korea also.
Important value additions
The G-7 or ‘Group of Seven’
- It is an intergovernmental organisation that was formed in 1975 by the top economies of the time as an informal forum to discuss pressing world issues.
- G-7 includes countries of Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
- It is an annual summit that is presided over by leaders of member countries on a rotational basis.
- Wide range of global issues is discussed at the summit.
- Russia was expelled as a member in 2014 following the latter’s annexation of the Crimea region of Ukraine.
- It does not have a permanent headquarter.
- The decisions taken by leaders during annual summits are non-binding
India-Bhutan MoU on cooperation in the areas of Environment approved
Part of: GS-Prelims and GS-II – International Relations
In News:
- The Union Cabinet recently approved the signing of the MoU between India and Bhutan on Cooperation in the areas of Environment.
Key takeaways
- The MoU will cover the following areas of environment:
- Air
- WasteChemical Management
- Climate Change
- Any other areas jointly decided upon.
- This MoU shall enter into force on the date of signature and shall continue to remain in force for a period of ten years.
- It will facilitate exchange of best practices and technical knowhow through both public and private sectors.
- It shall contribute to sustainable development.
- It provides the possibility for joint projects in areas of mutual interest.
- However, no significant employment generation is envisaged.
Important value additions
Bhutan
- Bhutan is a landlocked country in South Asia.
- It is located in the Eastern Himalayas.
- It is bordered by the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north, the Chumbi Valley of Tibet, China and Sikkim and West Bengal in the west, and Assam, West Bengal and Arunachal Pradesh in the south and east.
- Bhutan is geopolitically in South Asia.
- It is the region’s second-least-populous nation after the Maldives.
- Thimphu is its capital.
- In 2008, Bhutan transitioned from an absolute monarchy to a constitutional monarchy.
- In South Asia, Bhutan ranks first in economic freedom, ease of doing business and peace and is the least corrupt country in the region as of 2016.
- It continues to be a least developed country, but expects to graduate from this status by 2023.
- Bhutan pioneered the concept of Gross National Happiness.
Image source: Click here
Miscellaneous
Antifa
- It was recently designated as a terrorist organisation by the US President.
- Its origin dates back to as far back as Nazi Germany.
- The movement has had its presence in several European countries.
- It came into focus in the United States following the election of President in 2016.
- It does not have a formal organisational structure.
- It draws its members from other movements such as Black Lives Matter and the Occupy movement.
- Antifa members typically dress in black and often wear a mask at their demonstrations, and follow far-left ideologies such as anti-capitalism.
- They take up causes such as LGBTQ and indigenous rights.
- It is known for violence.
Bimal Julka Committee
- An Expert Committees on Rationalisation of Film Media Units and Review of Autonomous Bodies was recently formed under the chairmanship of Bimal Julka.
- It has suggested an umbrella configuration with 4 broad categories under which institutes should work.
- They are – Production, Festival, Heritage and Knowledge.
- It has recommended that these categories should be headed by professionals.
- It has also recommended creation of Film Promotion Fund for independent filmmakers for making commercial films.
Depsang
- Reports of a heavy Chinese presence at Depsang have increased tensions between Indian and Chinese troops recently.
- It is an area at a crucial dip (called the Bulge) on the Line of Actual Control (LAC).
- India controls the western portion of Depsang plains as part of Ladakh, whereas the eastern portion is part of the Aksai Chin region, which is controlled by China and claimed by India.
- In April 2013, the Chinese PLA troops had set up a temporary camp in the Depsang Bulge, but later withdrew as a result of a diplomatic agreement with India.
Image source: Click here
(MAINS FOCUS)
INTERNATIONAL/ ECONOMY
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests
- Regional groupings involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
On India and G-7
Context: U.S. President Donald Trump announced that he would like to expand G-7 to a G-11, by adding India, Russia, South Korea and Australia.
US President followed up his announcement with invitations to these four country’s leaders, to attend the 2020’s G-7 summit in the U.S.
About G-7
- G7 is a forum of the world’s seven largest developed economies whose government leaders meet annually to discuss international economic and monetary issues.
- It is an informal gathering.
- G-7 has its roots in an informal meeting of the finance ministers of France, West Germany, the U.S, Great Britain, and Japan (the Group of Five) in the wake of the 1973 oil crisis.
- With addition of Canada & Italy, first G7 was held in 1976
- In 1998, Russia was added to form G8. However, in 2014, Russia was suspended from the group after the annexation of Crimea and tensions in Ukraine.
- Since then, meetings have continued within the G7 process
- It does not have a permanent headquarter.
- The decisions taken by leaders during annual summits are non-binding.
Did You Know?
- In 2019, the 45th G-7 summit held at France was unable to issue a joint communiqué due to differences on various issues— a first in its history.
- The G20 was formed in 1999, so as to bring more countries on board to address global economic concerns. India is a member and is slated to host G20 summit in 2022.
What has been the reaction of countries on G-11 plan?
- India has welcomed the decision and commended Trump for his “creative and far-sighted” decision to expand the format of the grouping to keep up with the new realities of the “post-COVID world”.
- Australia and South Korea have also welcomed the invitation,
- Russia, that lost its membership of the grouping in 2014 over its annexation of Crimea, has stated it would attend “if treated as an equal”
Consequences of G-11 plan for India
- The proposed G-11 grouping would recognise India’s place amongst the world’s richest nations. Membership will acknowledge India’s global voice
- It will provide a platform for India to address its concerns like terrorism and ensure that world work towards it
- It helps increase the soft power of India
- Exclusion of China from G-11 means possible strengthening of India’s alliance against China
- This is step in democratization of international institutions which are facing the criticism of being biased in favour of developed countries
Critical Analysis of G-11 Plan
- Improves Effectiveness: Expansion is needed to improve the groupings effectiveness as a multilateral forum to arrive at consensus on issues like climate change, security contributions, Iran, etc
- Against G-8+ 5: China, India, Brazil, Mexico and South Africa, were invited regularly to G-8 summits as an outreach by the developed world to the five emerging economies. The G-11 plan leaves out all these members except India
- Potential fora for Cold War: The summit appears aimed at fuelling a new Cold War between the U.S. and China.
- Adds fire to US-China tensions: US and China are fighting each other over trade, IPR, 5G Technology, Hong Kong, South China Sea, Climate issues and recently over origins of Coronavirus. This action by US will further widen their rift
- Long Way: As host, Mr. Trump can invite any country as a G-7 special invitee, but changing its composition will require the approval of the other members.
- Opposition from within G-7: There are some concerns by European countries over Russia joining the group, which could derail the entire G-11 plan
- Short term Challenges: It is unclear when the summit will actually be held, given the November polls in the U.S. This might derail the plan in initial stages itself
Conclusion
India deserves its place on the global stage, but on G-11 which excludes China, it must be clear about its aims given that the plan further polarise the world into two camps
Connecting the dots:
- International Solar Alliance
- East Asia Summit
GOVERNANCE/ ECONOMY
Topic: General Studies 2,3:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources
Atmanirbhar Bharat: Success depends on how Governance proceeds
Context: The pursuit of Atmanirbharta sows the seeds for a new course of long-term development for India
Significance of Atmanirbharat
- It is based on Swadeshi philosophy and Mahatma Gandhi’s concept of a self-reliant India.
- It could serve as the pivot on which India can emerge as a hub for manufacturing and investments.
What should be the direction of government’s policies to achieve it?
- Focus on Raw materials: Incentivising the establishment of production facilities in the country is critical, not just for assembly, but for raw materials, too
- Country Specific Foreign Policy: The government should consider moving away from broad-stroke international policies and shift to a country-to-country model
- Bilateralism over multilateralism: The focus should remain on bilateral trade agreements, which ensure a balance of payments as well as technology-sharing.
- Partnership based on Complementarities: The government should forge partnership/alliance models with other countries and companies, especially in areas where indigenous capabilities do not exist.
- Promote Innovation: India should also need to incentivise innovation, research and development to keep India at the cutting edge of the industry
Way Ahead
- R& D development: Global innovation centres needs to be set up in India. Also, NASA-ISRO like partnership should be enhanced across institutions and fields.
- Governance Simplification: Heavy investment on technology in government procedures and bureaucracy is needed to improve ‘ease of doing business’ climate.
- Infrastructure Financing: Building world-class infrastructure is extremely critical, and this requires huge investments. A strong framework for collaboration (e.g. contracting) and financing such investments needs to be established.
- Collaborative Federalism: While competitive federalism is required in the long term, ensuring a common playing field, with a more cohesive and consistent policy framework achieved through collaboration, is vital.
- Change in Mindset: A cultural shift is required in the public sector and bureaucracy to avoid the constant distrust—whether it is towards private organisations or the public at large
- Act Faster: If bold measures are not taken, in land, labour & law areas, over the next five to ten years, China might dominate as superpower and India’s ability to achieve economic independence will get drastically impacted.
Conclusion
- There has been a resurgence in protectionist policies in recent years. The success of the self-reliance vision will depend on how well India is able to negotiate terms with countries, especially the US and European nations
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 With regard to the Delimitation Commission, consider the following statements:
- The members of the commission are appointed by the Election Commissioner of India.
- Delimitation of constituencies is based on 2001 census.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding nominal GDP and real GDP:
- Nominal GDP is evaluated at some constant set of prices.
- Real GDP is evaluated at current market prices.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 National Statistical Office comes under which of the following Ministry?
- Ministry of Commerce
- Ministry of Finance
- Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation
- Ministry of Home Affairs
Q.4 Which of the following countries are not part of the G7 Summit?
- Canada
- France
- Germany
- Italy
Select the correct code:
- 1 and 2 only
- 1,3 and 4 only
- 1 and 4 only
- None of the above
Q.5 Which of the following is/are landlocked country/countries in South Asia?
- Afghanistan
- Bhutan
- Nepal
- Bangladesh
Select the correct code:
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
ANSWERS FOR 3rd June 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | A |
| 3 | B |
| 4 | C |
Must Read
About India’s coronavirus trends:
About India-China tension:
About Parliament missing in action:













