IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
New investment policy: Revised FDI Norms
Part of: GS Mains III – Indian Economy and issues related to it; Security issues
Context:
- In April, the current government made it mandatory for countries which share a land border with India get prior government approval for foreign direct investments (FDI).
- Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) notified the new FDI policy which said – “…an entity of a country, which shares land border with India or where the beneficial owner of an investment into India is situated in or is a citizen of any such country, can invest only under the Government route.”
- The move is aimed at “curbing opportunistic takeovers/acquisitions of Indian companies due to the current COVID19 pandemic.
- Investors from countries that are not covered by revised FDI new policy only have to inform the Reserve Bank of India after the completion of a transaction rather than seek prior clearance from the administrative ministry.
Do you know?
- Earlier, FDI was allowed in non-critical sectors through the automatic route without the MHA’s nod.
- Prior government approval or security clearance from MHA was required for investments in critical sectors such as defence, media, telecommunication, satellites, private security agencies, civil aviation and mining and any investments from Pakistan and Bangladesh.
200 proposals from China wait for security clearance by MHA
- About 200 investment proposals from China are awaiting security clearance from the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA).
- However, none of the proposals have been cleared so far.
Key facts:
- China has been India’s largest trading partner for many years in a row with cumulative investment in India exceeding $8 billion.
- India shares land borders with Pakistan, Afghanistan, China, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh and Myanmar.
Amendment to General Financial Rules, 2017
- Last week, the Centre amended the General Financial Rules, 2017
- The amendments aim to enable imposition of restrictions on bidders from countries which share a land border with India in relation to public procurement for reasons of national security and other factors directly or indirectly related to the country’s defence.
Institutional structure for disaster management
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains III – Disaster Management
In news:
- National Disaster Response Force (NDRF) is fighting against the COVID-19; Floods in Assam and Bihar.
About NDRF
- NDRF was established in 2006 under The Disaster Management Act, 2005
- It comes under Ministry of Home Affairs
- It is the only dedicated disaster response force in the world
- It works under National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) which lays down policies, plans and guidelines for disaster management.
- Capabilities for undertaking disaster response, prevention, mitigation and capacity building
- At present there are 12 battalions in NDRF (three each from the BSF and CRPF and two each from CISF, ITBP and SSB) which are deployed strategically across country to provide immediate response.
- All battalions have been equipped and trained to respond natural and man-made disasters including chemical, biological, radiological and nuclear (CBRN) emergencies.
Do you know?
- The Disaster Management Act, 2005 deals with the management of disasters. This act envisaged a three tier Disaster Management structure in India at National, States and District levels.
- Under the act, the NDMA, SDMA, NEC, NDRF, NIDM and disaster related funds were established.
National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA)
- It is a National Authority responsible for laying down the policies, plans and guidelines for disaster management and for ensuring timely and effective response to disaster.
- It consists of nine members with prime minister as its ex-officio chairperson.
National Executive Committee (NEC)
NEC is responsible for assisting NDMA in execution of various functions for disaster management like –
- Implementing the plans and policies of NDMA;
- Ensuring compliance with the directives of Central Government;
- To act as a coordinating and monitoring body for disaster management;
- Prepare the National Plan to be approved by the NDMA;
- Prepare guidelines for different ministries with respect to disaster management.
State Disaster Management Authority (SDMA)
- A state Disaster Management Authority is established by every state government.
- The Chief Minister of the state is the chairperson of SDMA. There are maximum 9 members other than the chairperson.
State Executive Committee (SEC)
- The state government also creates a State Executive Committee to assist the State Authority in the performance of its functions and to coordinate action in accordance with the guidelines laid down by the State Authority and ensure the compliance of directions issued by the State Authority.
- Its powers and functions are almost a replica of the NEC at state level.
District Disaster Management Authority
- The DDMA are set up by state government via a notification in the state budget. It consists of Chairperson and seven members. The collector or District Magistrate or Deputy Commissioner would be the chairman.
- The DDMA works as a district planning, coordinating and implementing body for disaster management.
- It will coordinate with the upper two tiers of the structure and will plan the implementation of the prevention, mitigation and preparedness at local level.
National Disaster Response Force
- For the purpose of specialist response to a threatening disaster situation or disaster. The general superintendence, direction and control of the Force shall be vested and exercised by NDMA.
National Disaster Response Fund
- For meeting any threatening disaster situation or disaster. The central government will be able to use the money from this fund to meet expenses for emergency response, relief and rehabilitation.
National Institute of Disaster Management
- It is responsible for planning and promoting training and research in the area of disaster management.
- It is a premier national organization working for human resource development at national level in the area of disaster management.
National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF)
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains II – Education reforms
About:
- NIRF is an annual report card on the performance of the Higher Education Institutions (HEIs).
- It was launched in 2015, outlines a methodology to rank institutions across the country.
The NIRF ranks institutions based on five parameters:
- Teaching Learning and Resources (TLR), Research and
- Professional Practice (RP),
- Graduation Outcome (GO),
- Outreach and Inclusivity (OI) and
- Perception.
Do you know?
- For institutions to improve their ranking, they should ensure cent per cent enrolment of students, adequate experienced and qualified faculty (with a faculty:student ratio of 1 : 15), enrolment of students from other states and countries, increased number of women students and faculty, scholarships, more quality research publications and funded research projects, higher pass percentage in the exams, facilities for physically-challenged and good reputation among employees and academic peers.
Poseidon and Tsirkon (Zircon) hypersonic cruise missile
Part of: GS Prelims II and III – International Affairs; Defence
In news:
- Russian Navy will soon get hypersonic nuclear weapons.
- The weapons include – Poseidon underwater nuclear drone, designed to be carried by submarines, and the Tsirkon (Zircon) hypersonic cruise missile, which can be deployed on surface ships.
Istanbul Convention to combat violence against women
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains II – International Affairs; Gender equality
About
- The Council of Europe Convention on preventing and combating violence against women and domestic violence, better known as the Istanbul Convention, is a human rights treaty of the Council of Europe against violence against women and domestic violence.
- The convention aims at prevention of violence, victim protection and “to end with the impunity of perpetrators”.
In news:
- Poland to withdraw from Istanbul Convention. It alleged that the convention was “harmful” because it required schools to teach children about gender.
- The ruling Law and Justice (PiS) party and its coalition partners are closely aligned to the Catholic Church, and the government has promised to promote traditional family values.
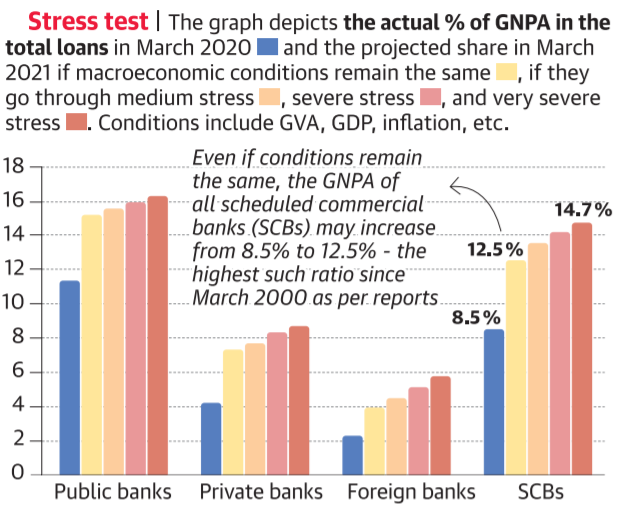
Financial Stability Report: GNPA to rise
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains III – RBI reforms; Economy
About:
As per RBI’s latest Financial Stability Report –
- COVID-19 lockdown, which impacted industries, will have a bearing on banks which have made loans to them.
- The report predicts a two-decade-high Gross Non-Performing Assets (GNPA) ratio in banks by next year March as industries which never defaulted were also impacted.
Miscellaneous
21st anniversary of Kargil Vijay Diwas
In news:
- PM paid homage to those who lost their lives during the Kargil War.
- PM urged the citizens not to do anything that might affect the honour of the armed forces serving on the borders.
“Mahatma Gandhi’s talisman urged people to keep the most oppressed at the centre of all actions in case of doubt. In similar lines, the citizens should keep martyred soldiers in mind while saying anything.” – PM said.
Conservation of River Nag
In news:
- Bombay High Court recently noted that the Nag river, from which Nagpur city derives its name used to be a vibrant and clear rivulet. It warned that Industrialisation has reduced Nag river to a cursed lady.
- The Bench said unless a comprehensive plan dealing with all aspects of the clean-up, beautification and maintenance of the river is drawn up, “no major success in restoring the river to its original state is going to be achieved”.
- The river serves as drainage for Nagpur and as a result its ecosystem is heavily polluted by urban waste from the city.
Do you know?
- Nag River Rejuvenation was cleared by National River Conservation Directorate in November 2019.
- Share of Centre in the project is 60%, 25% of state and remaining 15% of Nagpur Municipal Corporation (NMC).
- Japan International Cooperation Agency is expected to approve long term loan for shares of Centre and State. France-based AFD (French Development Agency) is preparing the Detailed Project Report and likely to approve long term loan for the project.
- Expected cost for Rejuvenation and Beautification is approx. 1600 crores.
Imported vaccines may be fast-tracked
Part of: GS Mains II – Measures taken by Government; Health issue
Context:
- Indian companies looking to import or test potential COVID19 vaccines that have been developed internationally, could get leeway in the number of India-specific tests and trials they would need to conduct.
- Normally, a vaccine that has been licensed in another country, would still need to repeat all human safety tests in India.
Itolizumab
About:
- Itolizumab is a labcloned antibody drug approved for psoriasis.
- It is developed by Bengalurubased Biocon Biologics.
- It has been approved for emergency use in the treatment of moderate and severe disease by the DCGI, in patients who manifest acute respiratory disease.
- However, COVID19 task force is not in favour of the emergency use of psoriasis drug.
(MAINS FOCUS)
JUDICIARY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic: General Studies 2
- Structure, organization and functioning of the Judiciary
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Contempt of Court: Prashant Bhushan Controversy
Context: The Supreme Court has initiated suo motu proceedings for criminal contempt against Advocate Prashant Bhushan for two of his tweets on Chief Justice of India S.A. Bobde as well as former CJIs
Who is Prashant Bhushan?
Prashat Bhushan is a lawyer-activist whose work has contributed to various legislations. He has also been outspoken critic of some of the drawbacks of Judiciary.
What were those tweets?
- In one of his tweets, Bhushan had written about the “role of the Supreme Court” in the “destruction” of democracy during the last 6 years, and had also mentioned the “role of the last 4 CJIs” in it.
- In another tweet, Bhushan had commented on Chief Justice of India S.A. Bobde astride a Harley Davidson bike. He had questioned the CJI for riding a bike without a helmet and a face mask, while “he keeps the SC in lockdown mode”.
What does contempt of court mean?
- Contempt of court is an act of disrespect or disobedience towards a judge or court’s officers or interference with its orderly process.
- The Contempt of Courts Act of 1971 categorises contempt of courts as
- Civil contempt: It is willful disobedience to any judgment, decree, direction, order, writ or other processes of a court or wilful breach of an undertaking given to the court.
- Criminal contempt: Anything that “scandalises or tends to scandalise” the judiciary or “lowers the court’s authority”
- Safeguards: However, innocent publication and distribution of some matter, fair and reasonable criticism of judicial acts and comment on the administrative side of the judiciary do not amount to contempt of court.
- Punishments: The supreme court and high courts have the power to punish for contempt of court, either with simple imprisonment for a term up to six months or with fine up to 2,000 or with both.
- Amendment in 2006: Truth and good faith were recognised as valid defences against charges of contempt of court
What is the significance of Contempt Powers of Judiciary?
- Safeguards the status & dignity of courts: Judicial Contempt power is needed to punish wilful disobedience to court orders as well as interference in the administration of justice and overt threats to judges.
- Protects Judges: Contempt powers help judges to do their duties of deciding cases without fear, favour, affection or ill will
- Ensures Public Trust: It insulates the institution from unfair attacks and prevent a sudden fall in the judiciary’s reputation in the public eye.
Is there any Constitutional Backing for Contempt power for Judiciary?
- Article 129: Grants Supreme Court the power to punish for contempt of itself.
- Article 142(2): Enables the Supreme Court to investigate and punish any person for its contempt.
- Article 215: Grants every High Court the power to punish for contempt of itself.
Criticism of the Contempt Powers of Court
- Not aligned with spirit of Article 19(1)(a): Contempt powers of Court tries to curb people’s freedom to speak against the court’s functioning.
- Liable to Misuse: The law is very subjective which might be used by the judiciary arbitrarily to suppress their criticism by the public.
- Colonial Hangover: Contempt powers of judiciary started during Colonial rule has been continued in India, whereas England abolished the offence of “scandalising the court” in 2013.
- Wrong Signal: These cases show that the country’s highest court is not tolerant of its outspoken critics and that it is highly sensitive to criticism (not the spirit of Democracy)
- Not aligned with Sedition jurisprudence: While the courts have made some effort to narrow the remit of sedition, they have not insisted on a similarly demonstrable link with obstruction of justice of the contemptuous act or speech
- Distorted Priorities of Apex Court: There are dozens of constitutional cases that need to be desperately addressed, such as CAA, the electoral bonds matter, or the issue of habeas corpus petitions from J&K, but SC has chosen to file case based on two tweets of a lawyer Prashant Bhushan
What is the way ahead?
- Besides needing to revisit the need for a law on criminal contempt, even the test for contempt needs to be evaluated.
- If such a test ought to exist at all, it should be whether the contemptuous remarks in question actually obstruct the Court from functioning.
- Contempt Power should not be allowed to be used as a means to prevent any and all criticism of an institution.
Connecting the dots:
- Sedition Law
- Also think about Shreya Singhal Case (related to Freedom in Social Media)
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1) FDI is prohibited in which of the following?
- Nidhi Company
- Atomic Energy
- Chit Funds
Select the correct code:
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 1 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Consider the following regarding National Disaster Response Force (NDRF)
- National Disaster Response Force consist of 12 battalions
- Assam Rifles and CISF are the two most specialized battalions of NDRF
- NDRF is under the control of Ministry of Home Affairs
Which of the given statement/s is/are correct?
- 1 and 3
- 3 only
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.3) Sendai Framework is related to?
- Chemical Warfare
- Biological Warfare
- Nuclear Energy
- Disaster Management
Q.4) Global Financial Stability Report is released by –
- World Bank
- IMF
- World Economic Forum
- UNCTAD
Q.5) The National River Conservation Directorate (NRCD) is under
- Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change
- Ministry of Drinking Water and Sanitation
- Ministry of Water Resources
- Ministry of Urban Development
Q.6) Ministry of Human Resource Development has introduced National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF). Which of the following statements regarding NIRF are correct?
- It has been introduced to rank all type of Institutions of Higher education in India.
- According to the area of operations, separate rankings are given to different type of institutions.
- For ranking purpose, parameters have been grouped in five clusters with equal weightage for each parameter.
Select the code from following:
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 1 and 3
- All of the above
ANSWERS FOR 25th July 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | A |
| 3 | A |
Must Read
About fall of Hong Kong
About need for changes in policy mindset
About House Vs Court











