IASbaba's Press Information Bureau, UPSC Articles
Press Information Bureau (PIB) IAS UPSC –2nd August to 8th August, 2020
GS-2
Bhoomi Pujan at ‘Shree Ram Janmabhoomi Mandir’
(Topic: Judiciary, Secularism)
Prime Minister Narendra Modi laid the first brick of the grand Ram Temple in Ayodhya at 12:44pm, as per the ‘muhurat’ for ‘bhoomi pujan’. He termed August 5 a ‘golden day’ and added that Ram Janmabhoomi stands ‘liberated’ today. CM Yogi Adityanath said that the temple construction is a moment to “showcase new India to the world, which does not discriminate on basis of caste and creed”.
- Hindus and Muslims claimed ownership over the site for decades. Hindu mobs had demolished a medieval mosque there in 1992, saying it was built on the ruins of a temple for Lord Ram, a revered deity.
- Last year, the top court gave the site to Hindus, ending a decades-long legal battle.
History and Significance of the Ram Temple
1528: Mughal emperor Babar’s commander Mir Baqi builds Babri Masjid in Ayodhya.
1858: Puja on premises – An FIR was filed on November 30 by Mohd Salim against a group of Nihang Sikhs who had conducted rituals inside the Babri Masjid. The dispute and riots led to the British building a seven-foot-high wall to separate the places of worships for Hindus and Muslims.
1885: Case for temple – Raghubar Das, who identified himself as mahant at the chabutra in the outer courtyard, filed a suit in the Faizabad civil court against the Secretary of State for India in Council seeking permission to build a makeshift temple there. The suit was dismissed. Subsequent civil appeals too were dismissed by the District Judge of Faizabad and the court of the Judicial Commissioner. A riot in 1934 led to demolition of a portion of the structure, which the British rebuilt.
1949: Emergence of idols – Abhiram Das, a Hindu priest, claimed he had a recurring dream of Ram making an appearance under the main dome of the Masjid. In the night of December 22 that year, idols were found at the place he had mentioned. While many Hindus believed that it was a miracle, then Faizabad DM K K Nayar on the morning of December 23 informed UP Chief Minister Govind Ballabh Pant about a group of Hindus entering the site and placing the idol. An FIR was filed, the gates to the structure were locked, and the city magistrate attached the property. A long legal battle ensued.
1989: VHP’s Shilanyas – Exactly three decades before, on the same day the Supreme Court approved the construction of the Ram Temple at the disputed site, on November 9, 1989, the VHP had put the first stone for the Ram Mandir in Ayodhya.
- The VHP was all set, but the Lucknow bench of Allahabad High Court ordered a status quo.
- Determined to defy the court order, VHP collected funds and bricks with Shree Ram written on them, organised kar sevaks and held prayers to go ahead with the Shilanyas.
- Later, as the fervour and communal tension escalated, the Centre and the state governments tried to get the VHP leaders to agree on conducting the Shilanyas outside the disputed site.
- But on November 9, a congregation of VHP leaders, including Sadhus, dug a 7x7x7 ft pit to lay the singhdwar (main entrance) of the sanctum sanctorium, clearly on the disputed land, defying the agreement they had made with the authorities.
1990: L K Advani’s Rath Yatra – The most important milestone in the BJP’s political journey. BJP leader L.K. Advani launches a Rath Yatra in support of the Ram Janmabhoomi movement from Somnath in Gujarat to Ayodhya.
1992: Babri Masjid demolition on December 6 – Frenzied karsevaks clambered up the domes of the 16th century Babri Masjid and pulled it down, again breaking the assurances given to the Centre and the state governments. The communal violence this sparked across the country left almost 2,000 people dead.
- President’s Rule was imposed in several states, dismissing the BJP governments in Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan and Himachal Pradesh.
- Liberhan Commission: The justice M S Liberhan Commission of inquiry was appointed within two weeks of the demolition and was asked to submit a report within three months. The Commission availed 48 extensions and finally submitted its 10,000-page report on January 30, 2009
1994: The Supreme Court, in the historic Ismail Faruqui judgment, says the Babri Masjid was not integral to Islam.
The legal battle is back in April 2002: The matter was back at the courts and yet another legal battle began. A three-judge Bench of the Allahabad High Court was hearing to determine the ownership of the disputed land. The HC ordered the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) to excavate the site and determine if it was a temple earlier.
- In 2003, ASI found evidence of the presence of a temple under the mosque. This re-energized the VHP, and its chief Ashok Singhal asked the then-BJP government to make a legislation to hand over the site to the Hindus so that the construction of the temple could begin.
- In September 2010, the High Court, which took the ASI’s findings along with other evidence before it into consideration, ruled that the disputed land should be divided into three parts — a third should go to Ram Lalla Virajman, represented by the Akhil Bharatiya Hindu Mahasabha; one-third to the Sunni Waqf Board; and the remaining to the Nirmohi Akhara.
- In December, the parties moved Supreme Court. Neither the VHP-BJP nor the Muslims was happy with the order. In May 2011, the apex court stayed the High Court order.
- Meanwhile, the VHP continued its campaign with vigour. But the BJP’s coming to power and its silence over the temple as well as the RSS leaderhsip’s advice not to escalate pressure over the Ram Temple forced them to lie low.
- Towards the end of 2018, the VHP again raised its pitch, with hundreds of thousands of Hindu seers and followers assembling in Ayodhya but BJP’s senior leaders convinced them that the government had to wait for the Supreme Court verdict.
On November 9, 2019: A five-judge Supreme Court bench led by then Chief Justice of India (CJI) Ranjan Gogoi ruled in favour of Ram Lalla, and said the entire disputed land spread over 2.7 acres will be handed over to a trust formed by the government, which will monitor the construction of the Ram Temple at the site.
February 5, 2020: The Union Cabinet approved the setting up of the Trust, with the Prime Minister making the announcement in the Lok Sabha.
- The Trust, named Shri Ram Janmabhoomi Tirtha Kshetra, is to take decisions independently on the construction of the Ram temple and related issues.
- It has been handed over the whole 67.703 acres acquired to maintain the sanctity of Ayodhya and for the construction of the temple, keeping in mind the needs of crores of devotees.
Update on Garib Kalyan Rojgar Abhiyaan
(Topic: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation)
The Garib Kalyan Rojgar Abhiyaan (GKRA), launched to boost employment and livelihood opportunities for migrant workers returning to villages and similarly affected citizens in rural areas, in the wake of COVID-19 outbreak, is now empowering villagers with livelihood opportunities in 116 districts of six states.
The Garib Kalyan Rojgar Abhiyaan is taking action on mission mode to provide employment to migrant workers who have returned to their native villages of these 6 states namely Bihar, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh.
- A total of about 17 crore mandays employment has been provided and Rs.13,240 crore has been spent so far in the of pursuit of objectives of the Abhiyaan.
- A large number of structures have been created under GKRA so far including 62,532 water conservation structures, 1.74 lakh rural houses, 14,872 cattle shed, 8,963 form ponds, 2,222 Community Sanitary Complex
- 5,909 works have been taken up through District Mineral Funds
- 564 Gram Panchayat have been provided internet connectivity
- 16,124 candidates have been provided skill training through Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs)
Jal Jeevan Mission: A reservoir of clean water & employment opportunities
(Topic: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation)
- In August, 2019, Government of India launched Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM).
- JJM aims at providing potable water at service level of 55 litre per capita per day (lpcd) to every rural household through Functional Household Tap Connection (FHTC) by 2024.
- The fund sharing pattern between the Centre and states is 90:10 for Himalayan and North-Eastern States, 50:50 for other states, and 100% for Union Territories.
Do you know?
Every village will prepare a Village Action Plan (VAP) which will have three components:
- Water source and its maintenance
- Water supply and
- Grey-water (domestic wastewater) management
Launches new version of India Water Resources Information System (India-WRIS): This portal contains information related to Water Resources through dashboards for rainfall, water levels & discharge of rivers, water bodies, ground water levels, reservoir storages, evapotranspiration and soil moisture, as well as modules on water resources projects, water bodies, hydro-met data availability and tools for GIS layer editing.
- Water information easily made available to users and general public, for decision makers, water managers, farmers & experts
- Direct access to hydro-met information from Central and State agencies
- Real-time data available with one click
- Variety of modules for different needs
- Latest technologies, continuous development and improvement
Draft Defence Production and Export Promotion Policy 2020
(Topic: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation)
Aim: To provide impetus to self-reliance in defence manufacturing, and to position India amongst the leading countries of the world in defence and aerospace sectors
The DPEPP 2020 is envisaged as overarching guiding document of MoD to provide a focused, structured and significant thrust to defence production capabilities of the country for self-reliance and exports.
Goals and objectives:
- To achieve a turnover of Rs 1,75,000 Crores (US$ 25Bn) including export of Rs 35,000 Crore (US$ 5 Billion) in Aerospace and Defence goods and services by 2025.
- To develop a dynamic, robust and competitive Defence industry, including Aerospace and Naval Shipbuilding industry to cater to the needs of Armed forces with quality products.
- To reduce dependence on imports and take forward “Make in India” initiatives through domestic design and development.
- To promote export of defence products and become part of the global defence value chains.
- To create an environment that encourages R&D, rewards innovation, creates Indian IP ownership and promotes a robust and self-reliant defence industry.
The Policy brings out multiple strategies under the following focus areas:
- Procurement Reforms
- Indigenization & Support to MSMEs/Startups
- Optimize Resource Allocation
- Investment Promotion, FDI & Ease of Doing Business
- Innovation and R&D
- DPSUs and OFB
- Quality Assurance & Testing Infrastructure
- Export Promotion
GS-3
Initiatives for Agricultural Mechanization
(Topic: Agriculture)
Agricultural Mechanization is one of the key drivers for sustainable development of agriculture sector which helps in increasing production by timely farm operations, reducing losses, reducing the cost of operations by ensuring better management of costly inputs. Mechanization also enhances the productivity of natural resources and reduces drudgery associated with various farm operations.
Sub-Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM): In order to lay special emphasis towards promotion of agricultural mechanization in the country and to bring more inclusiveness, Sub-Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM) had been initiated since 2014.
Crop Residue Burning: Paddy straw burning is currently practiced on a large scale in Punjab & Haryana to clear the fields for Rabi Crop sowing because the time window available between the harvesting of paddy crop and the sowing of next crops is very short (2-3 weeks). With an objective to wean away farmers of this region from Crop Residue Burning, the scheme of CRM (Crop Residue Management) was initiated since 2018 by Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare, wherein, farmers are provided machinery for in-situ management of crop residue through establishment of CHCs (Custom Hiring Centres). Individual farmers are also provided subsidy for procurement of machinery.
Multi lingual Mobile App “CHC- Farm Machinery” which connects the farmers with Custom Hiring Service Centers situated in their locality. This app is facilitating agricultural mechanization in the country by encouraging small & marginal farmers to take machines on rental basis for agriculture practices without them having to purchase the high priced such machines. The App has been further modified and now has been given the acronym of “FARMS-app” (Farm Machinery Solutions-app).
During COVID-19 padndemic
- Farming Operations by Farmers and Farm Workers in the field would continue during lock-down.
- Operations of Custom Hiring Centres (CHCs) related to Farm Machinery were relaxed.
- Shops of Agricultural machinery and its spare Parts (Including Supply Chain) and repairs to remain open.
- Seamless, intra and inter State movement of harvesting and sowing related machines like combine harvesters and other agriculture/horticulture implements was ensured.
- Under the Government subsidy programmes, agricultural manufactures were exempted from essential testing related activities like, random selection of test samples, subsequent batch testing after the expiry validity of test reports, updating of CMVR, COP &Type approval applicable to Tractors, Power Tillers, Combine Harvesters and other self-propelled agricultural machinery till 31.12.2020. Testing of tractors as per revised BIS Standard IS 12207-2019 and Implementation of new technical critical specifications of 51 agricultural machineries has also been deferred till 31.12.2020.
- Due to lock-down, closing out of borders and quarantine measures, disrupted the cross border movements of Agricultural machines like combine Harvesters & other agricultural machines across Districts & States. The timely intervention of the M&T Division of the Agriculture and Farmers Welfare Ministry and coordination with the State Nodal officers of Agricultural machineries, District Administration and Agricultural Machinery Manufacturers ensured the free movement of Agricultural machines across the borders.
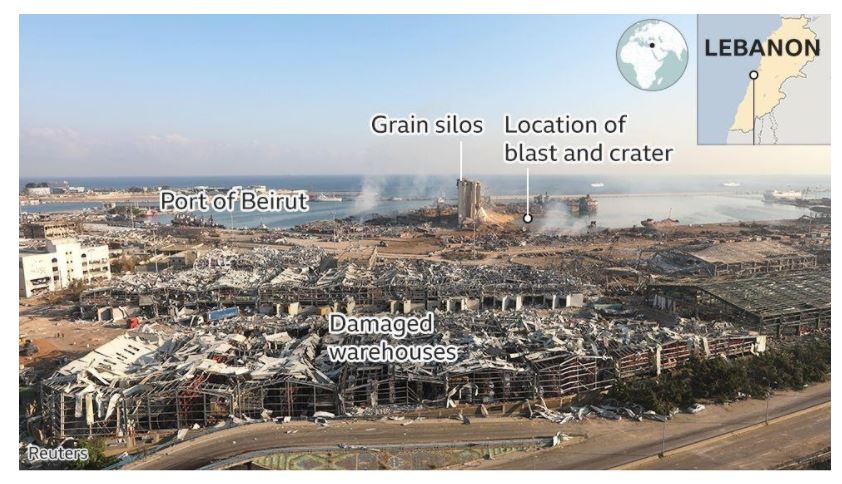
Explosion in Beirut city, Lebanon
(Topic: Lessons from Global Disaster)
The disaster was preceded by a large fire at the Port of Beirut, on the city’s northern Mediterranean coast.
- At least 100 people were killed and nearly 4,000 injured in a massive explosion at Lebanon’s capital Beirut.
- The explosion was of over 2700 tonnes of ammonium nitrate stored for six years in a warehouse in the port.
- As many as 300,000 people had been made temporarily homeless and that collective losses might reach $10-15bn (£8-11bn).
Do you know?
- Incident comes at one of the worst times for the country.
- The Western Asian country in the recent past has been crippled by serious economic crisis.
- It had led to large-scale closure of businesses and soaring prices of basic commodities resulting in social unrest.
- The country is also grappled by age-old Shia-Sunni rift.
What is ammonium nitrate and how dangerous is it?
Ammonium nitrate is a crystal-like white solid commonly used as a source of nitrogen for agricultural fertiliser. But it can also be combined with fuel oils to create an explosive used in the mining and construction industries. Militants have made bombs with it in the past.
Experts say that ammonium nitrate is relatively safe when stored properly. However, if you have a large amount of material lying around for a long time it begins to decay. The real problem is that over time it will absorb little bits of moisture and it eventually turns into an enormous rock. This makes it more dangerous because if a fire reaches it, the chemical reaction will be much more intense.
What caused the mushroom cloud?
- Videos from Beirut showed smoke billowing from a fire, and then a mushroom cloud following the blast.
- You have a supersonic shockwave that is travelling through the air, and you can see that in the white spherical cloud which travels out from the centre, expanding upwards.
- The shockwave is produced from compressed air. The air expands rapidly and cools suddenly and the water condenses, which causes the cloud.
Ammonium nitrate has been associated with deadly industrial accidents.
- In 1921, about 4,500 tonnes of ammonium nitrate caused an explosion at a plant in Oppau, Germany, killing more than 500 people
- The deadliest industrial accident in US history occurred in 1947 at Galveston Bay, Texas. At least 581 people were killed when more than 2,000 tonnes of the chemical detonated on-board a ship which had docked in the port
- More recently, an explosion involving ammonium nitrate and other chemicals killed 173 people in the port of Tianjin northern China in 2015.
Source: https://www.bbc.com/news/world-middle-east-53668493
INST scientists develop simple economical nonsurgical prevention of cataract
(Topic: Technology)
Cataract a major form of blindness that occurs when the structure of crystallin proteins that make up the lens in our eyes deteriorates, causing damaged or disorganised proteins to aggregate and form a milky blue or brown layer, which ultimately affects lens transparency. Thus, prevention of the formation of these aggregates as well as their destruction in the early stage of disease progression is a major treatment strategy for cataracts, and materials that can carry out this task could make cataract prevention affordable and accessible.
A team of scientists from the Institute of Nano Science & Technology (INST) has developed nanorods from the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) Aspirin, a popular medication used to reduce pain, fever, or inflammation and found it to be an effective non–invasive small molecule-based nanotherapeutics against cataract.
- Used the anti-aggregation ability of self-build aspirin nanorods as an effective non –invasive small molecule-based nanotherapeutics against cataract
- Aspirin nanorods prevent the aggregation of crystallin protein and various peptides derived from its fragmentation, which play a crucial role in cataract formation.
- They prevent the protein/peptide aggregation through biomolecular interactions, which convert beta-turn like the structure of the crystallin peptides, responsible for amyloid formation into coils and helices, those fail to aggregate.
- These were found to prevent cataract formation by inhibiting aggregation of crystallin, and crystallin derived peptide aggregates.
- As with aging and under various conditions, the lens protein crystallin aggregates to form opaque structures in the eye lens, which impairs vision and cause cataract.
Equipment-free, a simple paper-strip based naked-eye fluoride ion detection and quantification kit in drinking water to evade Fluorosis-based disorders
Fluorosis is a crippling disease resulting from deposition of fluorides in the hard and soft tissues of body due to excess intake of fluoride through drinking water/food products/industrial pollutants over a long period. It results in dental fluorosis, skeletal fluorosis, and non-skeletal fluorosis. Easy detection of fluorides in water can help preventing the public health hazards.
Technology has been developed – an equipment-free fluoride ion detection and quantification in drinking water with the naked-eye. It can be operated by non-experts for household use to evade Fluorosis-based disorders.
Prelims oriented News
Thenzawl Golf Resort: Implemented in Mizoram under the Swadesh Darshan Scheme
National Handloom Day: 7th August
Launch of BHARAT AIR FIBER: Introduced by BSNL as part of digital India initiates by the Government of India
- Aims to provide Wireless Connectivity in the range of 20 KMs from the BSNL Locations and thus customers at remote places also will be benefitted as BSNL comes with cheapest services with support of Telecom Infrastructure Partners (TIPs).
PM SVANidhi Scheme
- The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs recently launched a Special Micro-Credit Facility Scheme for providing affordable loans to street vendors.
- The scheme is PM SVANidhi – PM Street Vendor’s Atma Nirbhar Nidhi.
Key takeaways
- The vendors can avail a working capital loan of up to Rs. 10,000.
- It will be repayable in monthly instalments in the tenure of one year.
- On timely/early repayment of the loan, an interest subsidy at 7% per annum will be credited to the bank accounts of beneficiaries through Direct Benefit Transfer on six monthly basis.
- There will be no penalty on early repayment of loan.
- Over 50 lakh people, including vendors, hawkers, thelewalas, etc. are likely to benefit from this scheme.
- Street vendors from peri- urban/ rural areas have become beneficiaries of an urban livelihood programme for the first time.
- MFIs/ NBFCs/ SHG Banks have been allowed in a scheme for the urban poor due to their ground level presence for the first time.
IBBI amends the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (Liquidation Process) Regulations, 2016
About Insolvency & Bankruptcy
- Insolvency is the situation where the debtor is not in a position to pay back the creditor.
- For a corporate firm, the signs of this could be a slow-down in sales, missing of payment deadlines etc.
- Bankruptcy is the legal declaration of Insolvency.
Amendment
- The Regulations require the committee of creditors to fix the fee payable to the liquidator.
- Where the fee has not been fixed by the committee of creditors, the Regulations provide for a fee as a percentage of the amount realised and of the amount distributed by the liquidator.
- There have been instances where a liquidator realises the amount while another liquidator distributes the same to stakeholders.
- The amendment made to the Regulations today clarifies that where a liquidator realises any amount, but does not distribute the same, he shall be entitled to a fee corresponding to the amount realised by him.
- Likewise, where a liquidator distributes any amount, which is not realised by him, he shall be entitled to a fee corresponding to the amount distributed by him.
Making India Aatmanirbhar in Agarbatti Production: Khadi Agarbatti Aatmanirbhar Mission
- Aims at creating employment for unemployed and migrant workers in different parts of the country while increasing domestic Agarbatti production substantially
- The scheme designed by KVIC on PPP mode is unique in the sense that in a very less investment, it will create sustainable employment and help private Agarbatti manufacturers to scale up Agarbatti production without any capital investment by them.
- Under the scheme, KVIC will provide Automatic Agarbatti making machines and powder mixing machines to the artisans through the successful private Agarbatti manufacturers who will sign the agreement as business partners.
- KVIC has decided to procure only locally made machines by Indian manufacturers which also aims at encouraging local production.
- The current job work rate for Agarbatti making is Rs 15 per kg. At this rate, 4 artisans working on one Automatic Agarbatti machine will earn minimum Rs 1200 per day by making 80 kg of Agarbatti. Hence every artisan will earn at least Rs 300 per day. Similarly, on powder mixing machine, each artisan will get a fixed amount of Rs 250 per day.
- As per the scheme, the wages to the artisans will be provided by the business partners on weekly basis directly in their accounts through DBT only. Supply of raw material to the artisans, logistics, quality control and marketing of the final product will be the sole responsibility of the business partner.
Electronic Vaccine Intelligence Network (eVIN)
- The Electronic Vaccine Intelligence Network (eVIN) is an innovative technological solution aimed at strengthening immunization supply chain systems across the country.
- This is being implemented under National Health Mission (NHM) by Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- eVIN aims to provide real-time information on vaccine stocks and flows, and storage temperatures across all cold chain points in the country.
- This robust system has been used with the requisite customization during the COVID pandemic for ensuring continuation of the essential immunization services and protecting our children and pregnant mothers against vaccine preventable diseases.
- eVIN combines state-of-the-art technology, a strong IT infrastructure and trained human resource to enable real time monitoring of stock and storage temperature of the vaccines kept in multiple locations across the country.
- The Electronic Vaccine Intelligence Network has helped create a big data architecture that generates actionable analytics encouraging data-driven decision-making and consumption based planning that helps in maintaining optimum stocks of vaccines leading to cost savings. Vaccine availability at all times has increased to 99% in most health centers.
Theatre legend Ebrahim Alkazi
- Alkazi, credited for revolutionising theatre in India by combining native folk traditions and international acting techniques, became one of the most prominent theatre artistes in Mumbai during the 1940s and 1950s
- Served as the director of National School of Drama (NSD) from 1962 to 1977 — the longest tenure ever in the history of the institute.
- Alkazi evolved new training methodologies for student actors, directors and stage designers and spoke of new ethics and philosophy in theatre.
- As director of National School of Drama, he shaped the course for modern Indian theatre, establishing links between traditional vocabulary and modern idiom.
- In Bombay, Alkazi did powerful renditions of Greek tragedies, Shakespeare, Henrik Ibsen, Chekov and August Strindberg.
- He directed over 50 plays, including famous productions such as Girish Karnad’s Tughlaq, Mohan Rakesh’s Ashadh Ka Ek Din, Dharamvir Bharati’s Andha Yug and numerous Shakespearean and Greek plays. He mentored generations of actors, including Naseeruddin Shah and Om Puri.
- At 50, Alkazi quit the NSD and theatre and set up the gallery Art Heritage with his wife in New Delhi, and built his collection of art, photographs and books.
- He was conferred with honours such as the Kalidas Award, the Padma Shri, Padma Bhushan and Padma Vibhushan for his immense contributions to the Indian stage.












