UPSC Articles
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY/ POLITY
Topic: General Studies 3:
- Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life.
- Functions and responsibilities of various Constitutional Bodies (Election Commission)
Blockchain Technology and Voting
Context: The Election Commission in August 2020, held an online conference in collaboration with the Tamil Nadu e-Governance Agency (“TNeGA”) and IIT Madras, through which they explored the possibility of using blockchain technology for the purpose of enabling remote elections.
What is Blockchain Technology?
- A blockchain is a distributed ledger of information which is replicated across various nodes on a “peer-to-peer” network (P2P Network)
- The purpose of technology is of ensuring integrity and verifiability of data stored on the ledger.
- Blockchain ledgers have traditionally been used as supporting structures for cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum,however, their use in non-cryptocurrency applications too has seen a steady rise like enabling remote voting and elections.
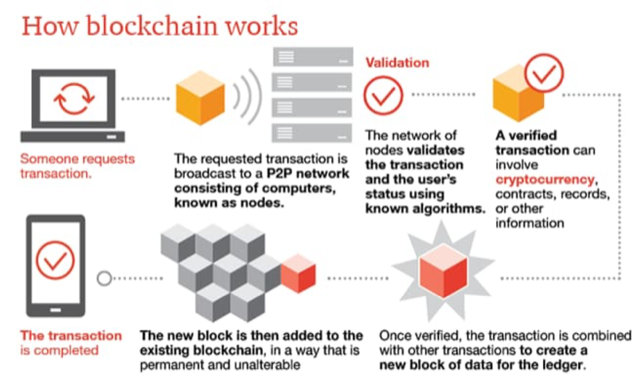
Picture: Shows the Schematic representation of working of Blockchain Technology
What are the benefits of remote voting?
- Solved the problem of ballot portability: Remote voting would appear to benefit internal migrants and seasonal workers, who account for roughly 51 million of the populace (Census 2011).
- Useful for People in Remote Places: The envisioned solution might also be useful for some remotely-stationed members of the Indian armed forces (although that exhaustive infrastructure of Elections has helped address this)
- Helps Increase Voter Participation: Remote voting solutions may facilitate the participation in elections by specific groups of citizens, including expats, military voters, voters resident in health and care institutions, and prisoners.
- Speed and Secure: The blockchain-based voting system not only provides real-time results, but also ensures that the counting is foolproof, and with blockchain, nobody can tamper the results.
What are the Challenges associated with Blockchain Remote Voting?
- Requirement of physical presence and biometric authentication: The electors would still have to physically reach a designated venue in order to cast their vote, whereby systems would use “white-listed IP devices on dedicated internet lines”, and the system would make use of the biometric attributes of electors
- Adds Vulnerability to failure: Digitisation and interconnectivity introduce additional points of failure external to the processes which exist in the present day
- Technology not yet fully secure: Blockchain solutions rely heavily on the proper implementation of cryptographic protocols. If any shortcomings exist in an implementation, it might be misused
- Prone to targeted Denial-of-Service attacks -where an attacker would be in a position to block traffic from the system, effectively preventing, or at the very least delaying the registration of votes
- Privacy Issues: With such intrusive technology being used in elections, which when interconnected can go against the Puttaswamy judgement [on the right to privacy]
Conclusion
- It is important to note that further digitisation, in itself, does not make processes more robust.
- Any solution to electoral problems must be software independent and fault tolerable, where failure or tampering of one mechanism — or several — would not affect the integrity or transparency of the overall process.














