UPSC Articles
Arctic Amplification phenomenon
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Environment; Climate change
In news
- A team of scientists have identified iodic acid (HIO3) which is driver of new aerosol particle formation in the Arctic.
- This is responsible for Arctic Amplification or Arctic Warming.
- Also, presence of Iodic acid in the region had not been observed previously.
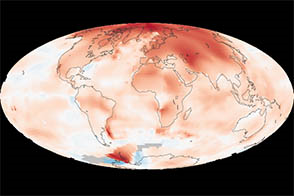
- Over the past 30 years, the Arctic has warmed at roughly twice the rate as the entire globe. This phenomenon is known as Arctic amplification.
- Global warming and climate change are impacting the Arctic more than the rest of the world.
- Changes have become much more pronounced since the 1980s.
Key takeaways
- These aerosol particles influence the formation of clouds.
- These clouds reflect solar radiation which is known as Aerosol Radiative Forcing.
- Also, clouds can retain heat on the Earth’s surface. Thus, they have an influence on the warming of the Arctic.
Reasons for Arctic Amplification
- Change in Albedo: It is a measure of how much light that hits a surface is reflected without being absorbed.
- Changing Ocean currents: Ocean currents normally bring in warmer water from the Pacific, and colder water exits out of the Arctic into the Atlantic. However, such currents may be changing because more melting ice is injecting the Arctic Ocean with freshwater.
- Changing Weather: Ocean currents also drive the polar jet stream, which moves hot and cold air masses around the Northern Hemisphere. This happens due to temperature differences between the Arctic and the tropics. But as the Arctic warms, the jet stream now undulates wildly north and south due to which the Arctic gets warm air.
Do you know?
- There is no Antarctic amplification.
- Antarctic warming is not as alarming as Arctic Warming.
- This is so because Antarctica is surrounded by the vast Southern Ocean, which is soaking up much of the atmosphere’s excess heat.